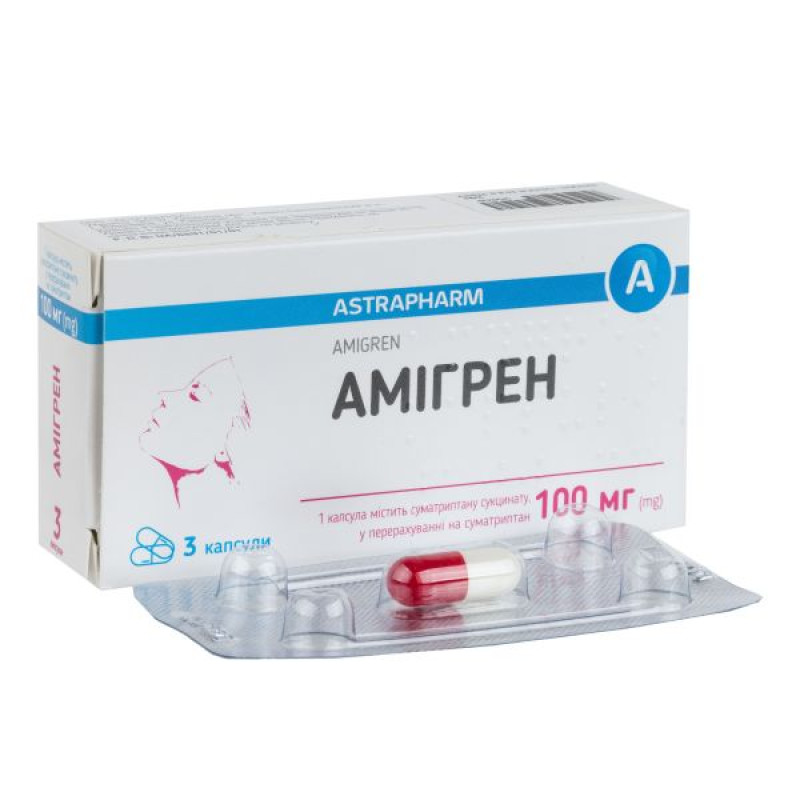
Amigren capsules 100 mg No. 3
Instructions for Amigren capsules 100 mg No. 3
Composition
active ingredient: sumatriptan;
1 capsule contains sumatriptan succinate equivalent to sumatriptan 100 mg;
excipients: lactose monohydrate; microcrystalline cellulose; croscarmellose sodium; magnesium stearate;
capsule shell composition: gelatin, titanium dioxide (E 171), Ponceau 4R (E 124).
Dosage form
Capsules.
Main physicochemical properties: hard gelatin capsules No. 1, cylindrical in shape with hemispherical ends; body – white, cap – red.
The contents of the capsules are white or almost white, odorless powder.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Selective agonist of serotonin 5HT1 receptors. Drugs used in the treatment of migraine. ATC code N02C C01.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Sumatriptan is a selective agonist of 5HT1 receptors that does not affect other 5HT receptors. These receptors are mainly located in the craniocerebral blood vessels. Studies have shown that sumatriptan has a selective vasoconstrictor effect on vessels in the carotid artery system, but does not affect cerebral blood flow. The carotid artery system supplies blood to extra- and intracranial tissues, such as the meninges. Migraine develops as a result of the expansion of these vessels. In addition, experimental data have shown that sumatriptan inhibits the activity of the trigeminal nerve. These are two possible mechanisms by which sumatriptan exerts its antimigraine activity.
The clinical effect is observed 30 minutes after oral administration of 100 mg of the drug.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, sumatriptan is rapidly absorbed, reaching 70% of the maximum concentration after 45 minutes. After taking 100 mg, the average maximum plasma concentration is 45 ng/ml. Bioavailability after oral administration is 14%, partly due to first-pass metabolism, partly as a result of incomplete absorption. Plasma protein binding is low (14-21%), the average volume of distribution is 17 l. The average total plasma clearance is approximately 1160 ml/min, and the average renal clearance is approximately 260 ml/min. Non-renal clearance is approximately 80% of the total clearance, which suggests that sumatriptan is excreted mainly in the form of metabolites. The main metabolite, the indoleacetic analogue of sumatriptan, is excreted in the urine, where it is found in the form of the free acid and a glucuronide conjugate. It does not exhibit 5HT1 or 5HT2 activity. Other metabolites have not been identified. The pharmacokinetics of oral sumatriptan are not significantly altered during a migraine attack.
Indication
For rapid relief of migraine attacks, with or without aura.
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to any component of the drug. History of myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease, Prinzmetal's angina, peripheral vascular disease or symptoms characteristic of coronary artery disease. History of stroke or transient ischemic attack. Moderate or severe arterial hypertension and mild uncontrolled arterial hypertension. Severe hepatic impairment.
Concomitant use of ergotamine or its derivatives (including methysergide) (see section "Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions").
Concomitant use of any triptan/5-hydroxytryptamine receptor (5-HT1) agonist (see section "Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions").
Concurrent administration of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) and Amigren. Amigren should not be used within 2 weeks of discontinuation of MAOIs.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions
There are no data on interactions with propranolol, flunarizine, pizotifen, or alcohol.
Data on concomitant use with medicinal products containing ergotamine or other triptan/5-HT1 receptor agonists are limited. Theoretically, prolonged vasospastic reactions are possible, therefore such concomitant use is contraindicated (see section 4.3).
The time interval that should be observed between taking sumatriptan and medicines containing ergotamine or other triptan/5-HT1 receptor agonists is unknown. It depends on the doses and types of medicines used. Since these effects may be potentiated by taking Amigren, a 24-hour interval should be observed between taking medicines containing ergotamine and other triptan/5-HT1 receptor agonists and taking Amigren. Accordingly, medicines containing ergotamine and other triptan/5-HT1 receptor agonists should not be used within 6 hours of taking Amigren.
There have been isolated reports of patients developing serotonin syndrome (including altered mental status, visceral instability, neuromuscular disorders) after taking selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and sumatriptan. There have been reports of serotonin syndrome with the simultaneous use of triptans and serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) (see section "Special instructions").
Application features
Amigren capsules are used only with a clearly established diagnosis of migraine.
Amigren is not used to treat hemiplegic, basilar, and ophthalmoplegic migraine.
As with other drugs, for the relief of migraine attacks in patients with no previous diagnosis of migraine and in patients with a diagnosis but atypical symptoms, other serious neurological pathology should be excluded before starting sumatriptan. It should be noted that patients with migraine have an increased risk of cerebrovascular disorders (stroke, transient ischemic attack).
The use of sumatriptan in some patients causes transient symptoms such as pain, tightness in the chest, which may be intense and extend to the larynx (see section "Adverse reactions"). If such symptoms indicate ischemic heart disease, appropriate cardiac examination should be performed.
Sumatriptan should not be prescribed to patients with suspected heart disease without prior examination to detect cardiovascular pathology. This group includes postmenopausal women, men over 40 years of age and patients with risk factors for coronary heart disease. However, such examination may not always detect the presence of heart disease, therefore, in rare cases, severe cardiac complications occur in patients with undiagnosed heart disease. Amigren should be prescribed with caution to patients under supervision for arterial hypertension, since a small number of patients may experience a transient increase in blood pressure and peripheral vascular resistance.
Isolated cases of serotonin syndrome (including altered mental status, visceral instability, neuromuscular disorders) have been described in patients taking selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and sumatriptan. There are reports of serotonin syndrome developing with the simultaneous use of triptans and serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). If the simultaneous use of Amigren and SSRI/SNRI is clinically justified, it is advisable to conduct a preliminary examination of the patients (see section "Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions").
Concomitant use of sumatriptan with any triptan/5HT1 agonist is not recommended.
Amigren should be prescribed with caution to patients with significant impairment of drug absorption, metabolism or excretion, for example, in renal and hepatic insufficiency.
Amigren should be prescribed with caution to patients with a history of seizures or with risk factors for a lowered seizure threshold.
Patients with hypersensitivity to sulfonamides may experience allergic reactions after the use of Amigren. Reactions may range from skin hypersensitivity to anaphylaxis. Cross-sensitivity is limited, but caution should be exercised when prescribing the drug to such patients.
The recommended doses of Amigren should not be exceeded.
Intensive treatment of acute migraine attacks is associated with exacerbation of headache (intensive treatment headache) in susceptible patients. Discontinuation of treatment may be necessary.
Adverse reactions may occur more frequently during concomitant use of triptans and medicinal products containing St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum).
Prolonged use of any painkiller may worsen headaches. If this symptom occurs or is at risk, consult a doctor and discontinue treatment. Patients who experience frequent or daily headaches due to regular use of headache medications may be diagnosed with headache due to painkiller overuse.
The drug contains lactose, therefore patients with rare hereditary forms of galactose intolerance, lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome should not use the drug.
Ability to influence reaction speed when driving vehicles or other mechanisms
Drowsiness can be a consequence of both migraine and its treatment with Amigren, so you should avoid driving or operating other machinery while taking the drug or having a migraine attack.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding
Amigren is not recommended for use in pregnant women. If necessary, the expected benefit to the mother should be weighed against the potential risk to the fetus.
Use with caution during breastfeeding. Breastfeeding is not recommended for 24 hours after taking the drug.
Method of administration and doses
Amigren capsules should not be used to prevent attacks.
Amigren is recommended to be used as early as possible after the onset of a migraine attack, although it is equally effective at each stage of the attack.
The recommended dose of Amigren for adults is 50 mg (1 tablet). In some cases, the dose can be increased to 100 mg (2 capsules).
Amigren can be used for new migraine attacks, but if the first dose of the drug is ineffective, the drug should not be used again during the same attack.
If the patient has responded to the first dose but symptoms recur, a second dose may be administered within the next 24 hours, with the total daily dose not exceeding 300 mg.
The capsules should be swallowed whole with water.
Elderly patients (aged 65 years and over)
There is insufficient experience with sumatriptan in patients over 65 years of age. Although the pharmacokinetics of the drug do not differ from those in younger individuals, until additional clinical data are available, the use of Amigren in elderly patients is not recommended.
Children
To date, the efficacy and safety of sumatriptan for the treatment of children have not been established, therefore Amigren is not recommended for use in this category of patients.
Overdose
Doses exceeding 400 mg (oral) did not cause any side effects other than those listed below.
Treatment: supportive therapy and patient observation for at least 10 hours.
The effect of hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis on the level of Amigren in blood plasma has not been established.
Adverse reactions
On the part of the immune system: hypersensitivity reactions - from skin hypersensitivity to cases of anaphylaxis.
Nervous system: dizziness; drowsiness; sensory disturbances, including paresthesia and hypoesthesia; convulsions. Although some of these cases were observed in patients with a history of convulsions or conditions that may lead to them, there are cases of convulsions in patients without any predisposition to them; tremor, dystonia, nystagmus, scotoma.
From the psyche: excitement.
From the cardiovascular system: transient increase in blood pressure immediately after taking the drug, blood flow, bradycardia, tachycardia, palpitations, arrhythmia, transient ischemic changes on the ECG, coronary artery spasm, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, arterial hypotension, Raynaud's disease.
Respiratory system: shortness of breath.
On the part of the digestive tract: nausea and vomiting, which occur in some patients, but their relationship with the use of sumatriptan is not fully understood; ischemic colitis, diarrhea; dysphagia.
Musculoskeletal system: feeling of heaviness, myalgia. These symptoms are usually transient, may be intense and affect any part of the body, including the chest and throat; stiffness of the neck muscles, arthralgia.
On the part of the organs of vision: flickering, diplopia, decreased visual acuity, loss of vision (usually transient). However, visual disturbances may be a consequence of the migraine attack itself.
Skin: hyperhidrosis.
General disorders: pain, feeling of warmth or cold, tightness or tightness (these symptoms are usually transient, may be intense and affect any part of the body, including the chest and throat); feeling weak, tired (these symptoms are mainly mild or moderate and transient)
Increased pain after injury, increased pain during inflammation.
Laboratory parameters: minor changes in liver function tests were observed.
Expiration date
2 years.
Storage conditions
Store in the original packaging at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Keep out of reach of children.
Packaging
1 capsule in a blister; 3 blisters in a box.
Vacation category
According to the recipe.
Producer
ASTRAPHARM LLC, Ukraine
Location of the manufacturer and its business address
08132, Kyiv region, Kyiv-Svyatoshynskyi district, Vyshneve town, Kyivska st., 6.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.