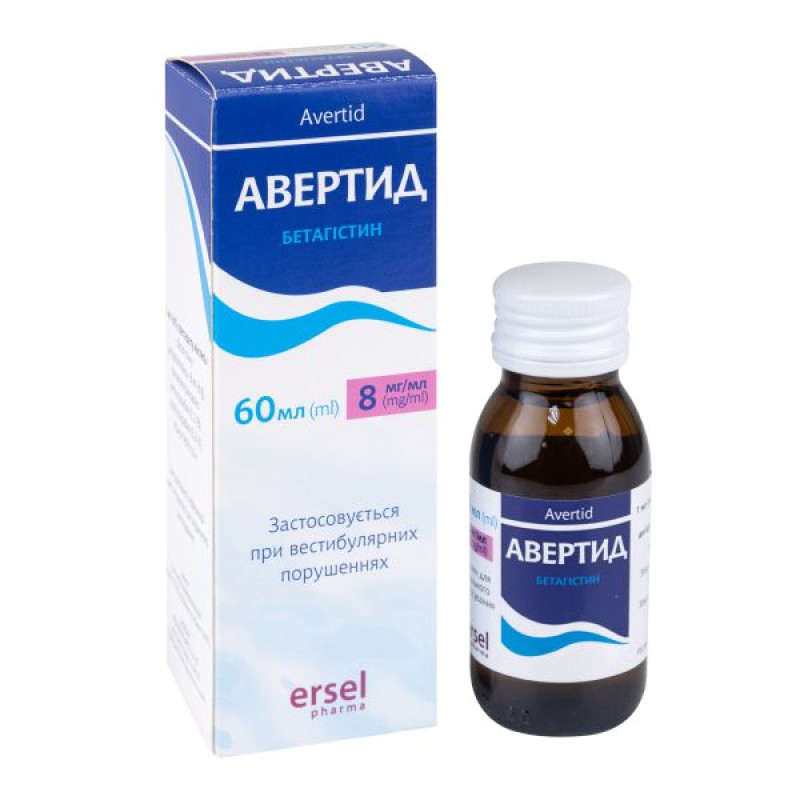
Avertide oral solution 8 mg/ml container 60 ml

Instructions Avertid oral solution 8 mg/ml container 60 ml
Composition
active ingredient: betahistine;
1 ml of the drug contains betahistine dihydrochloride 8 mg;
excipients: sodium saccharin, methylparaben (E 218), propylparaben (E 216), ethanol 96%, fruit flavoring, purified water.
Does not contain sugar or dyes.
Dosage form
Solution for oral use.
Main physicochemical properties: clear, colorless liquid with a specific odor, a yellowish tint is allowed.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Drugs used in vestibular disorders. ATX code N07C A01.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
The mechanism of action of betahistine is to affect the histamine H1- and H3-receptors of the labyrinth and vestibular nuclei of the central nervous system (CNS). By exhibiting a pronounced H1-agonistic effect on the receptors of the vessels of the inner ear, the drug promotes local vasodilation and significantly improves blood circulation in the stria vascularis. The H3-antagonistic effect of the drug on the receptors of the neurons of the vestibular nuclei improves microcirculation, capillary permeability, increases histamine release and increases fluid exchange at the level of the microcirculatory bed of the vascular strip, which leads to normalization of endolymph pressure in the labyrinth and cochlea. In addition, betahistine improves neuronal transmission processes by increasing the concentration of serotonin in the synapses. The drug is also an inhibitor of the enzyme diamine oxidase, which inactivates histamine. Betahistine binding to voltage-gated calcium channels of nerve cells, which are directly involved in the processes of ischemic damage, has also been noted. The drug does not affect the H2-histamine receptors of the stomach and does not lead to an increase in the secretion and concentration of hydrochloric acid, both basal and stimulated. Betahistine does not have a sedative effect, and it also does not affect systemic blood pressure. Unlike other drugs in this group (cinnarizine, flunarizine), betahistine does not cause extrapyramidal disorders and can be used in elderly patients with parkinsonism syndrome.
Pharmacokinetics
When taken orally, betahistine is completely absorbed from the digestive tract, slightly binds to blood plasma proteins. The drug does not accumulate in body tissues and does not have a cumulative effect, it is completely excreted in the urine in the form of an inactive metabolite - 2-pyridyl acetic acid within 24 hours. The half-life of the drug is 3-4 hours.
Indication
Meniere's disease and syndrome, which are characterized by three main symptoms:
dizziness, sometimes accompanied by nausea and vomiting; hearing loss (hearing loss); tinnitus.
Symptomatic treatment of vestibular vertigo.
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug; pheochromocytoma; treatment with disulfiram derivatives (Avertide contains 5% by volume of ethyl alcohol).
Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions
In vivo studies have not been conducted to investigate the interaction of betahistine with other drugs. Based on in vitro data, inhibition of cytochrome P450 enzyme activity in vivo is not expected.
In vitro data indicate inhibition of betahistine metabolism by drugs that inhibit monoamine oxidase (MAO) activity, including subtype B-selective MAO inhibitors (e.g. selegiline). Caution is recommended when betahistine is administered concomitantly with MAO inhibitors (including B-selective MAO inhibitors).
When using Avertide together with histamine H1-receptor blockers, the effectiveness of betahistine decreases, therefore antihistamines must be discontinued before using the drug.
The finished product contains 5% by volume of ethyl alcohol, which must be taken into account when treating with disulfiram derivatives or other drugs that block acetaldehyde breakdown enzymes (e.g. metronidazole, nitrofuran derivatives).
Application features
During treatment with the drug, it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of patients with bronchial asthma and/or a history of gastric and duodenal ulcers. In case of exacerbation of bronchial asthma, the drug should be discontinued.
Use Avertide with caution in cases of peptic ulcer of the stomach or duodenum in the active phase.
Accidental inhalation of betahistine solution can theoretically cause bronchospasm and a decrease in blood pressure.
This medicinal product contains 5% by volume of alcohol (ethanol). Taking into account the highest individual dose (3 ml of oral solution contains 120 mg of ethanol), this is equivalent to 3 ml of beer or 1.3 ml of wine in a single dose. This is harmful for people suffering from alcoholism. The alcohol content of the medicinal product should be taken into account when prescribing the medicinal product to women during pregnancy or breastfeeding, children and patients in high-risk groups, for example with liver disease or epilepsy.
Ability to influence reaction speed when driving vehicles or other mechanisms
Betahistine is indicated for the treatment of Ménière's syndrome, characterized by a triad of main symptoms: dizziness, hearing loss, tinnitus, and for the symptomatic treatment of vestibular vertigo. Both conditions may adversely affect the ability to drive or use machines. According to clinical studies investigating the effect of this drug on the ability to drive or use machines, betahistine had no or negligible influence on this ability.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding
Pregnancy: There are no adequate data from the use of betahistine in pregnant women.
In humans, the potential risk to the fetus and newborn is unknown. Avertide should not be used during pregnancy unless clearly necessary.
Breastfeeding. It is not known whether betahistine is excreted in human milk. Betahistine is excreted in rat milk. Effects observed after delivery in animal studies were only observed at very high doses. Breastfeeding should be discontinued for the entire period of use of Avertide.
Fertility: Studies in rats have shown no effect on fertility.
Method of administration and doses
Adults should take Avertid orally 2-3 times a day, preferably during or after meals. Accurate dosing of the drug should be carried out using the syringe included in the package. It is allowed to use the undiluted solution, washing it down with a small amount of liquid, as well as dilute the drug in a small amount of liquid. A reduction in symptoms is sometimes observed only after 2-3 weeks of treatment. The best results are achieved when taking the drug for several months.
Usually, the drug should be used at 8 mg (1 ml) 3 times a day. In case of severe symptoms of the disease or ineffectiveness of treatment, the dose can be increased to 16 mg (2 ml) 3 times a day or the drug can be used at 24 mg (3 ml) 2 times a day. The maximum daily dose of the drug is 48 mg.
Liver and kidney dysfunction.
No specific clinical trials on efficacy and safety have been conducted in this patient group, but based on post-marketing experience, no dose adjustment is required.
Elderly patients. Although clinical trial data in this patient population are currently limited, extensive post-marketing experience suggests that no dose adjustment is necessary for this patient population.
Children
Do not apply.
Overdose
Several cases of overdose have been reported. Some patients have experienced mild to moderate symptoms (nausea, drowsiness, abdominal pain) after taking doses of up to 640 mg. More serious complications (convulsions, cardiac or pulmonary complications) have been observed in cases of intentional overdose of betahistine, especially in combination with overdose of other drugs.
Treatment: symptomatic and supportive therapy.
Adverse reactions
During placebo-controlled clinical trials, the following adverse reactions were observed in patients treated with betahistine with the following frequencies: very common (≥ 1/10); common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10); uncommon (≥ 1/1,000 to < 1/100); rare (≥ 1/10,000 to < 1/1,000); very rare (< 1/10,000).
On the part of the immune system: hypersensitivity reactions, including immediate type (anaphylaxis).
From the nervous system: often - headache.
Gastrointestinal: often - nausea and dyspepsia. In some cases, there were complaints of minor stomach disorders (vomiting, pain in the digestive tract, abdominal pain due to bloating and flatulence). These side effects usually disappear when the drug is taken with food or after reducing the dose.
Skin: in isolated cases, hypersensitivity reactions of the skin and subcutaneous fat, including angioedema, rash, itching and urticaria, have been observed.
The drug contains methylparaben (E 218) and propylparaben (E 216), which may cause allergic reactions (possibly delayed).
Expiration date
3 years.
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Keep out of reach of children.
Packaging
60 ml in containers. Container with dosing syringe in a cardboard box.
Vacation category
According to the recipe.
Producer
RECIPHARM PARETS, S.L.Yu.
Location of the manufacturer and its business address
Ramon y Cajal Street, 2, 08150 Parets del Valles (Barcelona), Spain.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.