Bifren capsules 250 mg blister No. 60
Instructions for Bifren capsules 250 mg blister No. 60
Composition
active ingredient: phenibut;
1 capsule contains phenibut 250 mg;
excipients: microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, colloidal anhydrous silica, magnesium stearate, talc; capsule composition: gelatin, titanium dioxide (E 171).
Dosage form
Capsules.
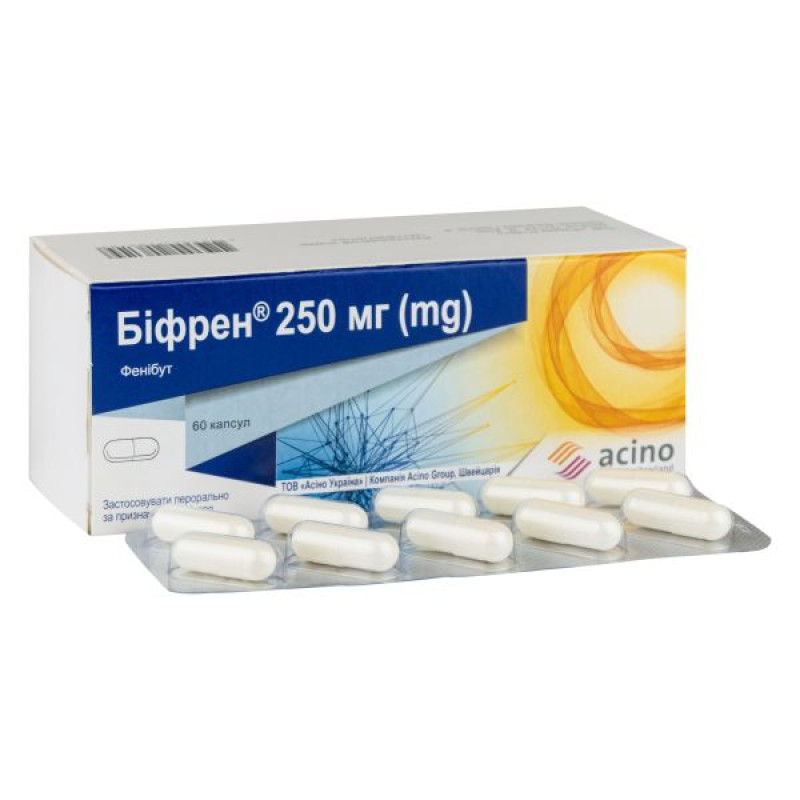
Main physicochemical properties: hard gelatin capsules, with a white opaque cap and a white opaque body.
The contents of the capsules are white or almost white powder.
The presence of compressed columns or lumps that fall apart when pressed is allowed.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Other psychostimulants and nootropics
ATX code N06B X22
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics.
Nootropics are also called psychometabolic stimulants, as they have a beneficial effect on metabolic processes in the brain. Phenibut is a derivative of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and beta-phenylethylamine. Phenibut has both nootropic activity and anxiolytic (tranquilizing) activity, characteristic of GABA derivatives. Phenibut does not affect cholinergic and adrenoreceptors. It reduces anxiety, anxiety, fear and improves sleep, so the drug can be used to treat neuroses, as well as before surgery. Phenibut prolongs and enhances the effect of hypnotics, narcotics, neuroleptics and antiparkinsonian drugs. It does not have an anticonvulsant effect. Phenibut prolongs the latent period of nystagmus, reduces its duration and manifestations. Phenibut significantly reduces the manifestations of asthenia and vaso-vegetative symptoms, including headache, feeling of heaviness in the head, sleep disturbances, irritability, emotional lability and increases mental performance. Phenibut improves psychological parameters - attention, memory, speed and accuracy of sensory-motor reactions.
In patients with asthenia and in emotionally labile patients, from the first days of therapy with the drug, well-being improves, interest and initiative increase, motivation for active activity without sedative effect or excitement. In terms of anti-asthenic activity (fatigue, fatigue, hypodynamia, mental and physical asthenia), phenibut is more active than piracetam.
Pharmacokinetics.
Absorption and distribution
The drug is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract after oral administration and penetrates well into all body tissues, passes well through the blood-brain barrier (about 0.1% of the administered dose of the drug penetrates into the brain tissue, and in young and elderly people to a much greater extent). The greatest binding of phenibut occurs in the liver (80%), it is non-specific. In healthy volunteers, the maximum concentration (Cmax) of the active substance in the blood plasma after a single oral dose of 250 mg during food intake is achieved after about 3 hours. Cmax after a single oral dose of 250 mg is approximately 2593 ng/ml, and Cmax in the equilibrium state on the 4th day after multiple oral doses of 250 mg three times a day is approximately 4057 ng/ml.
Biotransformation and excretion
80-95% of phenibut is metabolized in the liver, the metabolites are pharmacologically inactive.
Distribution in the liver and kidneys is close to uniform, and in the brain and blood - less uniform. About 5% of the dose is excreted in the urine unchanged. Cumulation is not observed with repeated administration.
The elimination half-life in healthy volunteers is approximately 7 hours after a single oral dose of 250 mg administered after a meal and approximately 8 hours on day 4 after repeated oral doses of 250 mg administered three times a day.
Indication
- Asthenic and anxiety-neurotic conditions: restlessness, fear, anxiety; insomnia, night restlessness in the elderly; prevention of stressful conditions before operations.
- Meniere's disease and dizziness associated with dysfunction of the vestibular analyzer of various origins.
- Prevention of motion sickness (a specific condition characterized by nausea, vomiting, prostration, and vestibular dysfunction caused by being in a moving object, such as a ship or airplane).
- Stuttering, tics in children aged 8 to 14 years.
- As an adjunct in the treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome.
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions
Bifren® can be combined with psychotropic drugs, reducing the doses of Bifren® and the drugs used with it.
Bifren® enhances and prolongs the effect of hypnotics, narcotics, neuroleptics, and anti-Parkinsonian drugs.
Application features
Caution should be exercised in patients with gastric or intestinal ulcers. To protect the mucous membrane from the irritating effects of phenibut, these patients are prescribed lower doses. With prolonged use, the cellular composition of the blood and liver function tests should be monitored.
Post-marketing experience with phenibut at therapeutic doses has not shown any withdrawal syndrome. However, literature data indicate that abrupt discontinuation of phenibut at doses higher than therapeutic may result in withdrawal syndrome, which may be severe and require hospitalization. Insomnia, psychomotor agitation, psychosis, auditory and visual hallucinations, anxiety, depression, dizziness, convulsions, nausea, vomiting, palpitations, and tachycardia have been reported in some cases.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Animal studies have not revealed any mutagenic, teratogenic or embryotoxic effects of phenibut. The use of Bifren® during pregnancy or breastfeeding is contraindicated, as there is insufficient data on the use of the drug during this period.
There is no information on the effect of phenibut on fertility.
The ability to influence the reaction speed when driving or working with other mechanisms.
Patients who experience drowsiness or other central nervous system disturbances during treatment with the drug should refrain from driving or operating other machinery.
Method of administration and doses
Method of application
Take orally after meals, drinking plenty of water.
Adults
For asthenic and anxiety-neurotic conditions in adults
Assign 250-500 mg 3 times a day. The maximum single dose is 750 mg, for elderly patients - 500 mg. The course of treatment is 2-3 weeks. If necessary, the course of treatment can be increased to 4-6 weeks.
For Meniere's disease and dizziness associated with dysfunction of the vestibular analyzer of various origins
In case of impaired function of the vestibular analyzer of infectious origin and in case of exacerbation of Meniere's disease:
- 750 mg 3 times a day for 5-7 days,
- If the severity of vestibular disorders decreases, continue treatment at a dose of 250-500 mg 3 times a day for 5-7 days, and then 250 mg once a day for 5 days.
For relatively mild diseases, use Bifren® 250 mg 2 times a day for 5-7 days, and then 250 mg once a day for 7-10 days.
To eliminate dizziness in vestibular dysfunctions of vascular and traumatic origin: prescribe the drug Bifren® 250 mg 3 times a day for 12 days.
For the prevention of motion sickness (kinetosis): administer at a dose of 250-500 mg once 1 hour before the expected onset of motion sickness, or at the first symptoms.
In the presence of severe manifestations (e.g. vomiting), the use of the drug is ineffective.
For the relief of alcohol withdrawal syndrome: the drug Bifren® is prescribed in the first days of treatment at 250-500 mg 3 times a day and 750 mg at night, with a gradual decrease in the daily dose.
Patients with hepatic insufficiency
In patients with hepatic insufficiency, high doses of the drug may cause hepatotoxicity. Lower doses are prescribed to this group of patients.
Patients with renal insufficiency
There are no data on the side effects of phenibut in patients with impaired renal function when taking therapeutic doses.
No development of drug dependence or withdrawal syndrome has been observed during the use of this drug. There are publications in the literature about isolated cases of tolerance caused by phenibut therapy.
Children.
Children aged 8 to 14 years - 250 mg 3 times a day; the duration of treatment is from 2 to 6 weeks. The drug is not used in children under 8 years of age.
Overdose
In therapeutic doses, the drug is low-toxic.
Symptoms: drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, dizziness.
With prolonged use of high doses, the development of arterial hypotension, acute renal failure, eosinophilia and fatty liver disease is possible.
Postmarketing data indicate serious cases of phenibut overdose, manifested by symptoms such as depression (including decreased level of consciousness, decreased muscle tone, stupor, respiratory depression), thermoregulation disorders, hypertension or hypotension, and tachycardia. Psychomotor agitation, hallucinations, seizures, and delirium have also been reported. Overdoses have been associated with the use of phenibut-containing medicinal products in doses exceeding the therapeutic range.
Treatment: symptomatic therapy.
There is no specific antidote.
Side effects
Phenibut, like all medicines, can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Classification of adverse reactions by frequency of development: very common (≥ 1/10); common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10); uncommon (≥ 1/1000 to < 1/100); rare (≥ 1/10,000 to < 1/1000); very rare (< 1/10,000); frequency unknown (cannot be estimated from the available data).
Immune system disorders: frequency unknown - hypersensitivity reactions, including rash, itching, urticaria, skin redness, angioedema, facial swelling, tongue swelling.
Nervous system: frequency unknown - drowsiness (at the beginning of treatment), headache and dizziness (in doses above 2 g per day, with a decrease in the dose, the severity of the side effect decreases).
Liver and biliary tract: frequency unknown - hepatotoxicity (with prolonged use of high doses).
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: rarely - allergic reactions (rash, itching).
There is some evidence that if used incorrectly, children may experience emotional lability and sleep disturbances.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions after the registration of a medicinal product is important. They allow for continuous safety monitoring, as well as an assessment of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product.
Expiration date
2 years.
Do not use after the expiry date stated on the packaging.
Storage conditions
Store out of the reach of children, in the original packaging at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Packaging
10 capsules in a blister; 1, 2 or 6 blisters in a cardboard pack.
Vacation category
According to the recipe.
Producer
"Pharma Start" LLC.
Location of the manufacturer and address of its place of business.
Ukraine, 03124, Kyiv, Vaclav Havel Boulevard, 8.
In case of adverse reactions or questions regarding the safety and effectiveness of the medicinal product, please contact the Pharmacovigilance Department of ASINO UKRAINE LLC at the address: Vaclav Havel Boulevard, 8, Kyiv, 03124, tel/fax: +38 044 281 2333.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.