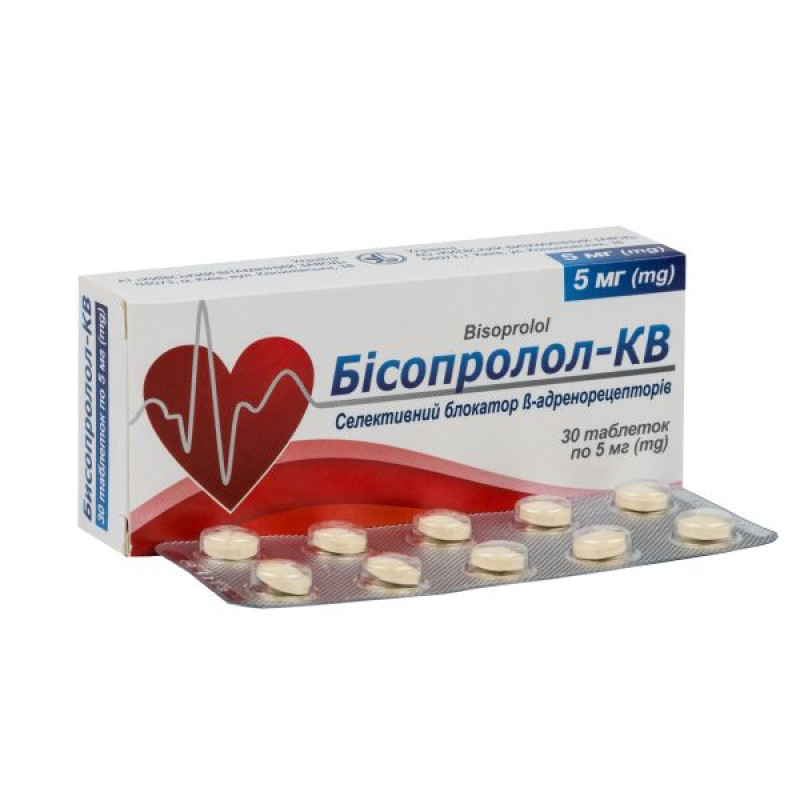
Bisoprolol-KV tablets 5 mg blister No. 30
Instructions for use Bisoprolol-KV tablets 5 mg blister No. 30
Composition
active ingredient: bisoprolol;
5 mg: 1 tablet contains bisoprolol fumarate 5 mg;
excipients: lactose monohydrate; microcrystalline cellulose; crospovidone; magnesium stearate; iron oxide yellow dye (E 172);
10 mg: 1 tablet contains bisoprolol fumarate 10 mg;
Excipients: lactose monohydrate; microcrystalline cellulose; crospovidone; magnesium stearate; iron oxide yellow (E 172) and iron oxide red (E 172) dyes.
Dosage form
Pills.
Main physicochemical properties:
5 mg: round tablets with a biconvex surface, with a score, brownish-yellow color; inclusions are allowed on the surface of the tablets;
10 mg: round tablets with a biconvex surface, with a score, brownish-pink color; inclusions are allowed on the surface of the tablets.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Selective β-adrenergic blockers. Bisoprolol. ATC code C07A B07.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics.
Bisoprolol is a highly selective β1-adrenergic blocker. When used in therapeutic doses, it does not have intrinsic sympathomimetic activity and clinically pronounced membrane-stabilizing properties. It has antianginal and hypotensive effects. It reduces myocardial oxygen demand by reducing heart rate and cardiac output, as well as reducing blood pressure, and increases myocardial oxygen supply by reducing end-diastolic pressure and prolonging diastole. The drug has a very low affinity for β2-receptors of bronchial and vascular smooth muscle, as well as for β2-receptors of the endocrine system.
The maximum effect of bisoprolol occurs 3-4 hours after administration. The half-life from blood plasma is 10-12 hours, which results in 24-hour efficacy after a single dose. The maximum antihypertensive effect is achieved after 2 weeks of administration.
Pharmacokinetics.
Absorption. After oral administration, the drug is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Bioavailability is about 90% after oral administration and is independent of food intake. The pharmacokinetics of bisoprolol and plasma concentrations are linear in the dose range from 5 mg to 20 mg. The maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) is reached after 2-3 hours.
Distribution: The volume of distribution is 3.5 l/kg. Plasma protein binding is about 30%.
Metabolism and excretion. Bisoprolol is excreted from the body in two ways: 50% is biotransformed in the liver with the formation of inactive metabolites and excreted by the kidneys, 50% is excreted by the kidneys unchanged. In vitro studies using human liver microsomes have shown that bisoprolol is metabolized with the participation of CYP3A4 (95%), CYP2D6 plays only a minor role. The total clearance of bisoprolol is 15 l/h. The half-life is 10-12 hours.
Indication
– Arterial hypertension;
– ischemic heart disease (angina);
– chronic heart failure with left ventricular systolic dysfunction, in combination with ACE inhibitors, diuretics, and if necessary, with cardiac glycosides.
Contraindication
– Acute heart failure or heart failure in a state of decompensation requiring inotropic therapy;
– cardiogenic shock;
– atrioventricular block II and III degree (except in patients with an artificial pacemaker);
– sick sinus syndrome;
– pronounced sinoatrial block;
– symptomatic bradycardia;
– symptomatic arterial hypotension;
– severe bronchial asthma or severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease;
– late stages of peripheral circulatory disorders or Raynaud's disease;
– untreated pheochromocytoma;
– metabolic acidosis;
– hypersensitivity to bisoprolol or other components of the drug.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions
Combinations that are not recommended for use.
Treatment of chronic heart failure.
- Class I antiarrhythmics (e.g. quinidine, disopyramide, lidocaine, phenytoin, flecainide, propafenone): possible potentiation of the effect on atrioventricular conduction and increased negative inotropic effect.
All indications.
- Calcium antagonists (verapamil group, to a lesser extent diltiazem): negative effect on myocardial contractile function and atrioventricular conduction.
Intravenous administration of verapamil to patients taking ß-blockers may result in severe hypotension and atrioventricular block.
- Centrally acting antihypertensives (clonidine, methyldopa, moxonidine, rilmenidine): possible worsening of heart failure due to decreased central sympathetic tone (decreased heart rate and cardiac output, vasodilation). Abrupt withdrawal of the drug, especially if preceded by withdrawal of ß-adrenoceptor blockers, may increase the risk of rebound hypertension.
Combinations that should be used with caution.
- Class I antiarrhythmics (e.g. quinidine, disopyramide, lidocaine, phenytoin, flecainide, propafenone): possible potentiation of the effect on atrioventricular conduction and increased negative inotropic effect.
All indications.
– Dihydropyridine calcium antagonists (e.g. nifedipine, felodipine, amlodipine): possible increased risk of arterial hypotension. The possibility of increased negative effects on myocardial inotropic function in patients with heart failure cannot be excluded.
– Class III antiarrhythmic drugs (e.g. amiodarone): possible potentiation of the effect on atrioventricular conduction.
– Topical ß-blockers (e.g. contained in eye drops for the treatment of glaucoma): possible enhancement of the systemic effects of bisoprolol.
– Parasympathomimetics: possible increase in atrioventricular conduction time and increased risk of bradycardia.
– Insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents: potentiation of the hypoglycemic effect. Blockade of ß-adrenoceptors may mask the symptoms of hypoglycemia.
– Anesthetic agents: increased risk of myocardial depression and hypotension (see section “Special warnings and precautions for use”).
– Cardiac glycosides: decrease in heart rate, increase in atrioventricular conduction time.
– Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): possible weakening of the hypotensive effect of bisoprolol.
– ß-sympathomimetics (e.g. orciprenaline, isoprenaline, dobutamine): use in combination with Bisoprolol-KV may lead to a decrease in the therapeutic effect of both drugs. Higher doses of adrenaline may be required for the treatment of allergic reactions.
– Sympathomimetics that activate α- and β-adrenergic receptors (e.g. adrenaline, noradrenaline): α-adrenergic receptor-mediated vasoconstriction may occur, leading to increased blood pressure and increased intermittent claudication. This interaction is more likely with non-selective β-blockers.
When used concomitantly with antihypertensive agents and agents with hypotensive effects (e.g. tricyclic antidepressants, barbiturates, phenothiazines), the risk of arterial hypotension may increase.
Possible combinations.
– Mefloquine: possible increased risk of bradycardia.
– MAO inhibitors (except MAO inhibitors type B): increased hypotensive effect of ß-blockers, but there is a risk of developing hypertensive crisis.
Application features
Treatment of stable chronic heart failure with bisoprolol should begin with a titration phase.
In patients with coronary heart disease, treatment should not be stopped abruptly without urgent need, as this may lead to transient deterioration of the condition. Initiation and discontinuation of bisoprolol treatment requires regular monitoring.
Currently, there is insufficient therapeutic experience in the treatment of heart failure in patients with the following diseases and pathological conditions: type 1 diabetes mellitus (insulin-dependent), severe renal impairment, severe hepatic impairment, restrictive cardiomyopathy, congenital heart disease, hemodynamically significant acquired valvular heart disease, myocardial infarction within the last 3 months.
The drug should be used with caution in patients with the following conditions:
– bronchospasm (in bronchial asthma, obstructive airway diseases);
– diabetes mellitus with significant fluctuations in blood glucose levels, while symptoms of hypoglycemia (tachycardia, palpitations, sweating) may be hidden;
– strict diet;
– desensitization therapy. Like other ß-blockers, bisoprolol may increase sensitivity to allergens and increase the severity of anaphylactic reactions. In such cases, treatment with adrenaline does not always give a positive therapeutic effect;
– atrioventricular block I degree;
– Prinzmetal's angina;
– obliterating diseases of peripheral arteries (at the beginning of therapy, complaints may increase);
– general anesthesia.
In patients undergoing general anesthesia, the use of ß-blockers reduces the incidence of arrhythmias and myocardial ischemia during induction of anesthesia, intubation, and the postoperative period. It is recommended to continue the use of ß-blockers during the perioperative period. It is imperative to warn the anesthesiologist about the use of ß-adrenoceptor blockers, as the doctor must take into account the potential interaction with other drugs, which can lead to bradyarrhythmia, reflex tachycardia, and a decrease in the ability of the reflex mechanism to compensate for blood loss. In the case of discontinuation of bisoprolol before surgery, the dose should be gradually reduced and the drug should be discontinued 48 hours before general anesthesia.
Although cardioselective ß-blockers (ß1) have less effect on lung function than non-selective ß-blockers, their use, like all ß-blockers, should be avoided in obstructive airway diseases unless there are compelling reasons for therapy. If necessary, Bisoprolol-KV should be used with caution. In patients with obstructive airway diseases, treatment with bisoprolol should be started at the lowest possible dose and patients should be monitored for the appearance of new symptoms (such as dyspnea, exercise intolerance, cough).
In bronchial asthma or other chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases that may cause symptoms, concomitant therapy with bronchodilators is indicated. In some cases, patients with bronchial asthma may require higher doses of ß2-sympathomimetics due to increased airway resistance while taking the drug.
Patients with psoriasis (including those with a history of psoriasis) are prescribed ß-blockers (e.g. bisoprolol) after careful benefit/risk assessment.
Patients with pheochromocytoma are prescribed the drug only after the appointment of α-adrenoblocker therapy. Symptoms of thyrotoxicosis may be masked while taking the drug. When using the drug Bisoprolol-KV, a positive result may be noted during doping control.
The drug contains lactose, so it should not be prescribed to patients with rare hereditary forms of galactose intolerance, lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding
Pregnancy: Bisoprolol has pharmacological properties that may cause harmful effects on the course of pregnancy and/or the development of the fetus/newborn.
In general, β-blockers reduce placental blood flow, which can cause intrauterine growth retardation, intrauterine death, spontaneous abortion, or premature birth. Adverse effects in the fetus and newborn (e.g., hypoglycemia, bradycardia) may occur. If treatment with β-blockers is necessary, it is preferable that it be a β1-selective adrenoblocker.
During pregnancy, the drug should be used only if the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. It is necessary to monitor uteroplacental blood flow and fetal growth. In case of harmful effects on the course of pregnancy or the fetus, alternative treatment should be considered.
After delivery, the newborn should be closely monitored. Symptoms of hypoglycemia and bradycardia can be expected during the first 3 days.
Breastfeeding. There is no data on the excretion of bisoprolol into breast milk, therefore, the use of the drug during breastfeeding is not recommended.
Ability to influence reaction speed when driving vehicles or other mechanisms
In individual cases, the drug may affect the ability to drive or operate complex mechanisms. Particular attention should be paid at the beginning of treatment, when changing the dose of the drug or when interacting with alcohol.
Method of administration and doses
The tablets should be taken without chewing, in the morning, on an empty stomach or during breakfast, with a small amount of liquid.
Arterial hypertension; coronary heart disease (angina pectoris)
The recommended dose is 5 mg (1 tablet of Bisoprolol-KV 5 mg) per day. In case of moderate hypertension (diastolic blood pressure up to 105 mm Hg), a dosage of 2.5 mg (½ tablet of 5 mg) is acceptable.
If necessary, the daily dose can be increased to 10 mg (1 tablet of Bisoprolol-KV 10 mg) per day. The maximum recommended dose is 20 mg per day.
Dose changes and adjustments are determined by the doctor individually, depending on the patient's condition.
Bisoprolol-KV must be used with caution in patients with arterial hypertension or ischemic heart disease accompanied by heart failure.
Chronic heart failure with left ventricular systolic dysfunction, in combination with ACE inhibitors, diuretics, and if necessary, cardiac glycosides
Standard therapy for chronic heart failure: ACE inhibitors (or angiotensin receptor blockers in case of intolerance to ACE inhibitors), β-adrenergic blockers, diuretics and, if necessary, cardiac glycosides.
Bisoprolol-KV is prescribed for the treatment of patients with chronic heart failure without signs of exacerbation.
Treatment of chronic heart failure with Bisoprolol-KV should be initiated according to the titration scheme below and may be adjusted depending on individual body responses.
– 1.25 mg** of bisoprolol fumarate once daily for 1 week, increasing to
– 2.5 mg* bisoprolol fumarate (½ 5 mg tablet) once daily for the next 1 week, increasing to
– 3.75 mg** bisoprolol fumarate once daily for the next 1 week, increasing to
– 5 mg of bisoprolol fumarate once daily for the next 4 weeks, increasing to
– 7.5 mg of bisoprolol fumarate (1 ½ tablets of 5 mg) once a day for the next 4 weeks, increasing to
* At the beginning of therapy for chronic heart failure, it is recommended to use the drug at a dosage of 2.5 mg;
** Use in appropriate dosage.
The maximum recommended dose of bisoprolol fumarate is 10 mg once daily.
Regular monitoring is necessary at the beginning of treatment for persistent chronic heart failure. During the titration phase, vital signs (blood pressure, heart rate) and symptoms of progression of heart failure should be monitored.
Treatment modification
If worsening of heart failure, hypotension or bradycardia occurs during or after the titration phase, dose adjustment is recommended, which may require a temporary reduction in the dose of bisoprolol or possibly discontinuation of treatment. Treatment can be continued once the patient's condition has stabilized.
The course of treatment with Bisoprolol-KV is long.
Do not stop treatment suddenly or change the recommended dose without consulting your doctor, as this may worsen the patient's condition. If necessary, treatment with the drug should be discontinued slowly, gradually reducing the dose.
Patients with hepatic and renal insufficiency
Arterial hypertension; ischemic heart disease. For patients with mild to moderate hepatic or renal impairment, dose adjustment is usually not required. For patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 20 ml/min) and patients with severe hepatic impairment, the daily dose should not exceed 10 mg bisoprolol.
Chronic heart failure. There are no data on the pharmacokinetics of bisoprolol in patients with chronic heart failure concomitant with impaired liver and/or kidney function, therefore, increasing the dose should be done with caution.
Elderly patients do not require dose adjustment.
Children
There is no clinical data on the efficacy and safety of the drug for the treatment of children, therefore the drug should not be used in this category of patients.
Overdose
Symptoms. In case of overdose (for example, using a daily dose of 15 mg instead of 7.5 mg), cases of third-degree atrioventricular block, bradycardia and dizziness have been recorded. The most common signs of overdose with ß-blockers are bradycardia, hypotension, acute heart failure, hypoglycemia and bronchospasm. Currently, several cases of overdose in patients with arterial hypertension and/or ischemic heart disease (maximum dose - 2000 mg of bisoprolol) are known. Bradycardia and/or hypotension were noted. All patients recovered. There is a wide variability in individual sensitivity to a single high dose of bisoprolol, patients with heart failure may be more sensitive to the drug. Therefore, treatment should be started with a gradual increase in dosage (see section "Method of administration and dosage").
Treatment. In case of overdose, discontinue treatment with the drug and provide supportive and symptomatic therapy. There is limited evidence that bisoprolol is difficult to dialyze. In case of suspected overdose, the following general measures should be considered, based on the expected pharmacological action and recommendations for other ß-blockers.
For bradycardia: intravenous atropine. If there is no response, isoprenaline or another drug with a positive chronotropic effect is administered with caution. In exceptional cases, transvenous administration of an artificial pacemaker may be necessary.
For hypotension: intravenous fluids and vasoconstrictors. Intravenous glucagon may be useful.
In case of second and third degree atrioventricular block: careful observation and infusion of isoprenaline or transvenous pacemaker.
In case of exacerbation of chronic heart failure: intravenous administration of diuretics, inotropic drugs, vasodilators.
For bronchospasm: bronchodilators (e.g. isoprenaline), ß2-adrenomimetics and/or aminophylline.
For hypoglycemia: intravenous glucose administration.
Side effects
Cardiac: bradycardia (in patients with chronic heart failure, arterial hypertension or ischemic heart disease), signs of worsening heart failure (in patients with chronic heart failure, arterial hypertension or ischemic heart disease), atrioventricular conduction disorders.
Nervous system: dizziness*, headache*, syncope.
On the part of the organs of vision: decreased tear secretion (should be taken into account when wearing contact lenses), conjunctivitis.
On the part of the auditory organs: hearing impairment.
Respiratory system: bronchospasm in patients with a history of bronchial asthma or obstructive airway diseases, allergic rhinitis.
On the part of the digestive tract: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation.
Skin and connective tissue disorders: hypersensitivity reactions including pruritus, redness, rash, alopecia. Treatment with ß-blockers may result in worsening of psoriasis in the form of psoriatic rash.
Musculoskeletal system: muscle weakness, cramps.
On the part of the vascular system: feeling of coldness or numbness in the extremities, arterial hypotension (in patients with chronic heart failure, with arterial hypertension or ischemic heart disease), orthostatic hypotension (in patients with chronic heart failure).
From the reproductive system: impaired potency.
Mental disorders: depression, sleep disorders, nightmares, hallucinations.
Laboratory indicators: increased triglyceride levels in the blood, increased activity of liver enzymes in blood plasma (AST, ALT).
General disorders: asthenia (in patients with chronic heart failure, hypertension or ischemic heart disease), fatigue*.
* Applies only to patients with arterial hypertension or coronary heart disease. These symptoms usually occur at the beginning of therapy, are mild and disappear within the first 1-2 weeks.
In case of side effects or adverse reactions, you should immediately inform your doctor.
Expiration date
3 years.
Storage conditions
Store in the original packaging at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Keep out of reach of children.
Packaging
10 tablets in a blister; 3 blisters in a pack.
Vacation category
According to the recipe.
Producer
PJSC "Kyiv Vitamin Plant".
Address
04073, Ukraine, Kyiv, Kopylivska St., 38.
Website: www.vitamin.com.ua.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.