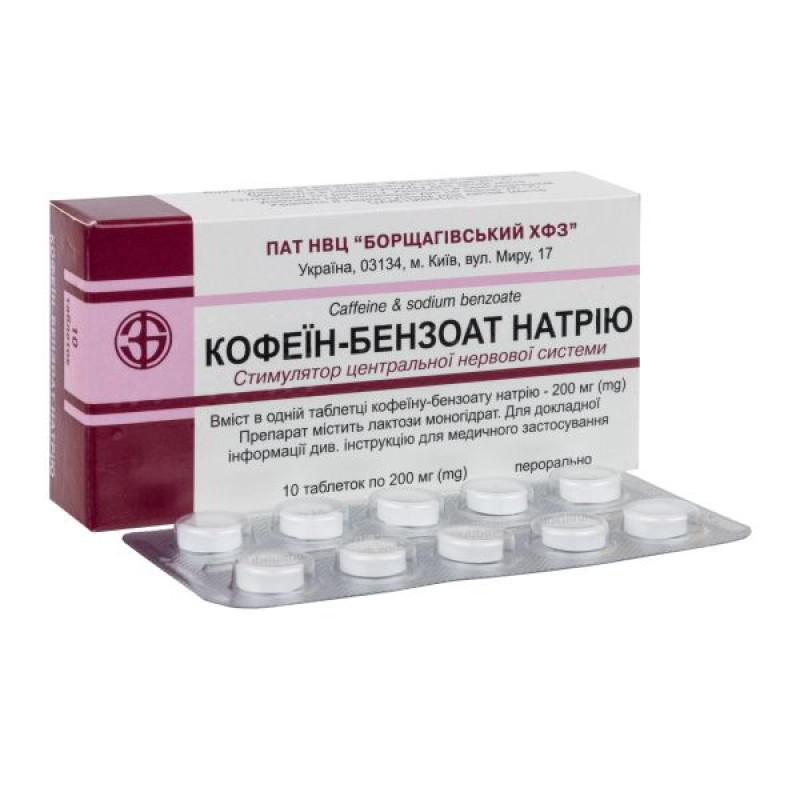
Caffeine-sodium benzoate tablets 200 mg blister No. 10
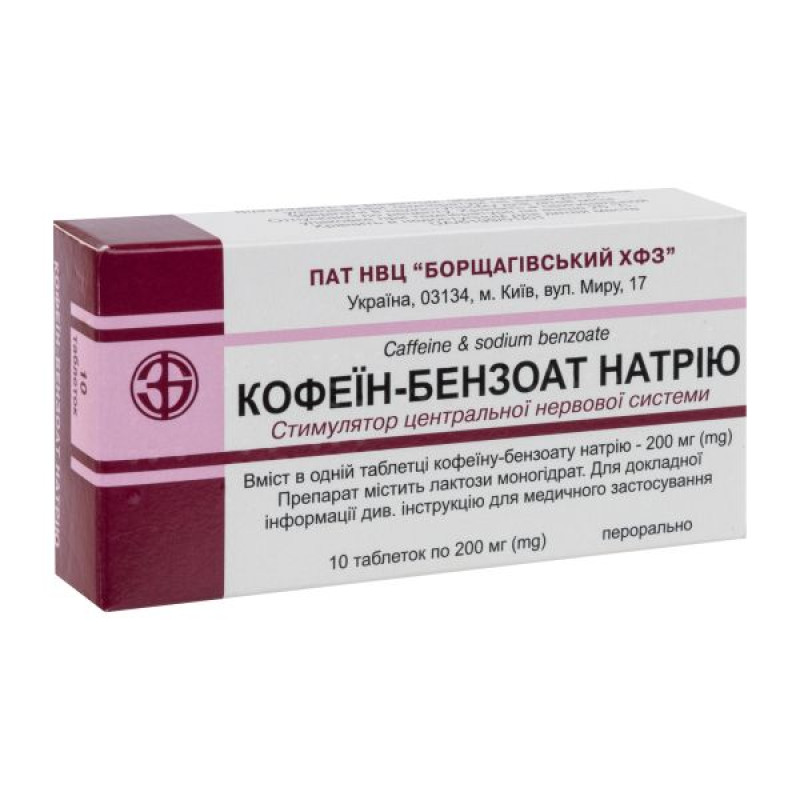
Instructions Caffeine-sodium benzoate tablets 200 mg blister No. 10
Composition
active ingredient: caffeine sodium benzoate;
1 tablet contains caffeine sodium benzoate (calculated on 100% dry matter) – 200 mg;
excipients: lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, corn starch, povidone, calcium stearate.
Dosage form
Pills.
Main physicochemical properties: round tablets, white in color, with a flat surface with beveled edges and a score.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Psychostimulants, drugs for use in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and nootropics. Xanthine derivatives.
ATX code N06B C01.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Caffeine sodium benzoate is used primarily as a central nervous system stimulant.
The mechanism of action of the drug is based on the inhibition of the enzyme phosphodiesterase by caffeine, which leads to the accumulation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate inside the cells. The latter enhances glycogenolysis, stimulates metabolism in organs and tissues, including the central nervous system and muscles. An important link in the mechanism of the stimulating effect of the drug is the binding of caffeine to purine receptors in the brain.
Caffeine enhances and regulates the processes of excitation in the cerebral cortex, enhances positive reflexes, and increases motor activity. These effects are dose-dependent, contributing to increased mental and physical performance, reduced fatigue and drowsiness. In excessively high doses, caffeine can lead to exhaustion of nerve cells.
The drug weakens the effect of hypnotics and narcotics, increases the reflex excitability of the spinal cord, stimulates the respiratory and vasomotor centers. Under the influence of the drug, cardiac activity increases, the heart rate increases.
Under the influence of caffeine-sodium benzoate, diuresis is slightly increased (mainly due to a decrease in electrolyte reabsorption in the renal tubules).
Pharmacokinetics
The drug is well absorbed from the digestive tract. It is evenly distributed in the body. It easily penetrates the blood-brain barrier. It penetrates the placenta and is excreted in breast milk. In the process of biotransformation, it undergoes demethylation and oxidation. The half-life is 3-7 hours. It is excreted from the body with urine and feces in the form of metabolites, a small part (about 8%) is unchanged.
Indication
Infectious and other diseases accompanied by depression of the central nervous and cardiovascular systems;
arterial hypotension;
asthenic syndrome;
spasms of cerebral vessels;
drowsiness;
increasing mental and physical performance.
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to caffeine, other xanthine derivatives (theophylline, theobromine) or to any of the components of the drug;
increased excitability;
insomnia;
pronounced increase in blood pressure, arterial hypertension;
organic diseases of the cardiovascular system (including acute myocardial infarction, paroxysmal tachycardia, atherosclerosis);
glaucoma;
age over 60 years.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions
Concomitant use of caffeine-sodium benzoate with:
MAO inhibitors, furazolidone, procarbazine and selegiline - may cause the development of dangerous cardiac arrhythmias or a pronounced increase in blood pressure;
barbiturates, primidone, anticonvulsants (hydantoin derivatives, especially phenytoin) - increased metabolism and increased caffeine clearance;
ketoconazole, disulfiram, ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, enoxacin, pipemidic acid - may cause a slowdown in the elimination of caffeine and an increase in its concentration in the blood;
cimetidine, hormonal contraceptives, isoniazid – increased effects of caffeine;
fluvoxamine – increased levels of caffeine in blood plasma;
mexiletine – reduction of caffeine excretion by 50%;
nicotine – increases the rate of caffeine excretion;
methoxsalen – reducing the excretion of caffeine from the body with possible enhancement of its effect and development of toxic effects;
clozapine – increased concentration of clozapine in the blood;
theophylline and other xanthines – decreased clearance of these drugs, increased risk of additive pharmacodynamic and toxic effects;
β-blockers – may lead to mutual inhibition of therapeutic effects;
Thyroid-stimulating agents – increase in thyroid effect;
opioid analgesics, anxiolytics, hypnotics and sedatives - reduced effect of these drugs;
lithium preparations – increased urinary excretion of lithium;
calcium preparations – reduced absorption of these drugs;
cardiac glycosides – accelerated absorption, enhanced action and increased toxicity of cardiac glycosides;
analgesics-antipyretics – enhancing their effect;
ergotamine – improving the absorption of ergotamine from the digestive tract;
xanthine derivatives, α- and β-adrenomimetics, psychostimulants - potentiation of their effects.
Beverages and medications containing caffeine, when used together with the drug, may lead to excessive stimulation of the central nervous system. High doses of caffeine may cause tremors and palpitations. Patients should avoid excessive consumption of coffee or tea.
Application features
When using the drug, excessive consumption of coffee, strong tea, other tonic drinks, alcohol and medications containing caffeine should be avoided.
In case of prolonged use of the drug, the development of mental dependence is possible. Abrupt cessation of treatment leads to increased inhibition of the central nervous system (drowsiness, depression).
The effect of the drug largely depends on the type of nervous system and can manifest itself as both excitation and inhibition of higher nervous activity.
Caffeine can cause a false increase in uric acid in the blood, as determined by the Bittner method.
Caffeine may increase levels of 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA), vanillylmandelic acid (VMA), and catecholamines in urine, which may lead to false-positive diagnostic results for pheochromocytoma and neuroblastoma.
Use the drug with caution in patients with a history of gastric and duodenal ulcers.
This medicine contains lactose. Patients with rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, the Lapp lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption should not take this medicine.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding
The drug is contraindicated for use during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
The ability to influence the reaction speed when driving or working with other mechanisms
Until the patient's individual response to the drug is determined, one should refrain from driving or operating other mechanisms, given that adverse reactions from the central nervous system may occur during treatment.
Method of administration and doses
Apply orally 2-3 times a day. A single dose for adults is 100-200 mg.
The highest single dose is 500 mg, the highest daily dose is 1 g.
Children over 12 years of age should be prescribed a dose of 100 mg 2-3 times a day.
The highest daily dose for children is 500 mg.
The dose of the drug and the course of treatment are determined by the doctor individually depending on the severity of the disease and the effectiveness of the therapy.
Children
Caffeine sodium benzoate in tablet form is not recommended for use in children under 12 years of age.
Overdose
Symptoms: gastralgia, agitation, anxiety, motor restlessness, confusion, delirium, dehydration, tachycardia, arrhythmias, hyperthermia, increased frequency of urination, headache, increased tactile or pain sensitivity, tremor or muscle twitching; nausea and vomiting, sometimes with blood; tinnitus, convulsions (in acute overdose - tonic-clonic seizures).
Treatment: gastric lavage, administration of enterosorbents, support of pulmonary ventilation and oxygenation; in case of convulsions - intravenous diazepam, phenobarbital or phenytoin; maintenance of fluid and salt balance; hemodialysis. There is no specific antidote.
Side effects
Nervous system: agitation, anxiety, tremor, restlessness, headache, dizziness, muscle twitching, convulsions, increased reflexes, tachypnea, insomnia; with sudden withdrawal - increased inhibition of the central nervous system with the appearance of a feeling of increased fatigue, drowsiness, muscle tension, depression.
Cardiovascular system: feeling of pressure in the chest, feeling of palpitations, tachycardia, arrhythmias, increased blood pressure.
Digestive tract: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, exacerbation of peptic ulcer disease.
Urinary system: increased urinary frequency, increased creatinine clearance, increased sodium and calcium excretion.
Immune system: possible manifestations of hypersensitivity reactions, including skin rashes, itching, urticaria, angioedema, bronchospasm, anaphylactic shock, Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Laboratory indicators: possible false increase in blood uric acid, determined by the Bittner method, hypoglycemia/hyperglycemia, slight increase
5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA), vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) and catecholamines in urine.
Others: nasal congestion, with prolonged use - a decrease in the effect of caffeine, which is associated with the formation of new adenosine receptors, drug dependence.
Expiration date
4 years.
Storage conditions
In the original packaging at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Keep out of reach of children.
Packaging
10 tablets in a blister, 1 blister in a pack; 10 tablets in a blister.
Vacation category
According to the recipe.
Producer
Public Joint Stock Company "Research and Production Center "Borshchagov Chemical and Pharmaceutical Plant".
Limited Liability Company "Agropharm".
Location of the manufacturer and its business address
Ukraine, 03134, Kyiv, Myru St., 17.
Ukraine, 08200, Kyiv region, Irpin, Centralna st., 113-A.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.