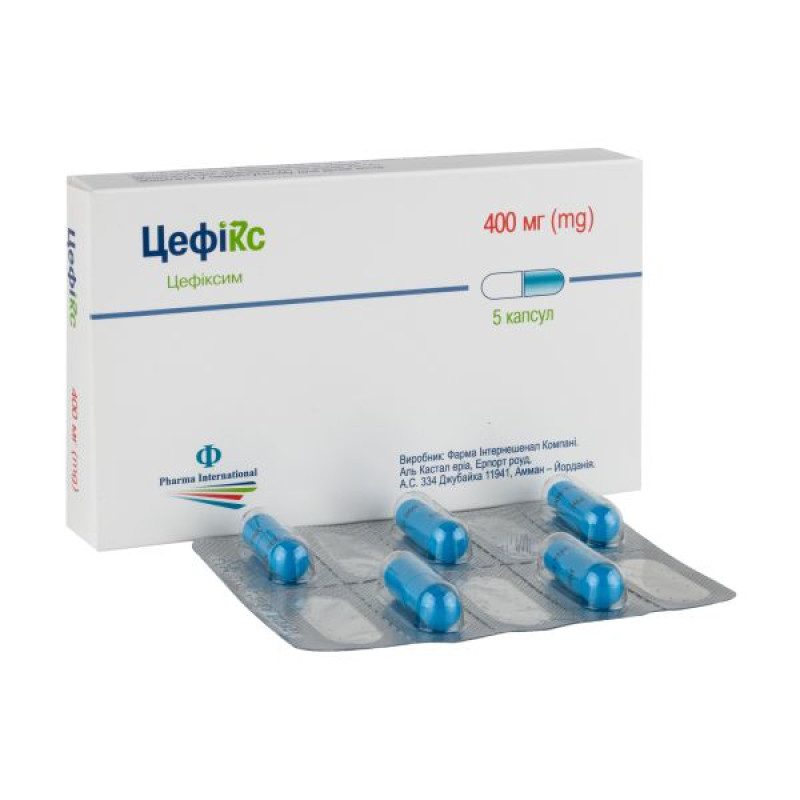
Cefix capsules 400 mg No. 5
Instructions for Cefix capsules 400 mg No. 5
Composition
active ingredient: cefixime;
1 capsule contains cefixime (in the form of trihydrate) 400 mg;
Excipients: microcrystalline cellulose, sodium lauryl sulfate, magnesium stearate, croscarmellose sodium, hydrogenated vegetable oil.
composition of the capsule shell:
capsule shell: FD&C Blue No. 1 (E 133), titanium dioxide (E 171), gelatin, purified water;
capsule shell: FD&C Blue No. 1 (E 133), titanium dioxide (E 171), gelatin, purified water.
Dosage form
Capsules.
Main physicochemical properties: white to yellowish powder in hard gelatin capsules with a blue cap with the inscription "PhI" and a blue body with the inscription "Cefix 400 mg", size 0E.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Antibacterials for systemic use. Other beta-lactam antibiotics. Third generation cephalosporins. ATX code J01D D08.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Cefixime is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic for internal use. In vitro, it exhibits significant bactericidal activity against a wide range of gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. Clinically effective in the treatment of infections caused by the most common pathogenic microorganisms, including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, E.coli, Proteus Mirabilis, Klebsiella species, Haemophilus influenzae (beta-lactamase-positive and -negative), Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis (beta-lactamase-positive and -negative) and Enterobacter species. It has a high degree of stability in the presence of beta-lactamases.
Most strains of enterococci (Streptococcus faecalis, group D Streptococci) and Staphylococci (including coagulase-positive, coagulase-negative and methicillin-resistant strains) are resistant to cefixime. In addition, most strains of Pseudomonas, Bacteroides fragilis, Listeria monocytogenes and Clostridia are resistant to cefixime.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption. The absolute bioavailability of cefixime after oral administration is 22-54%. Since the presence of food does not significantly affect absorption, cefixime can be administered without regard to food intake. Peak serum levels after administration of recommended doses for adults or children range from 1.5 to 3 μg/ml. There is little or no accumulation of cefixime with repeated dosing. The pharmacokinetics of cefixime were compared in healthy elderly subjects (aged > 64 years) and young volunteers (aged 11-35 years) after administration of 400 mg cefixime once daily for 5 days. Mean Cmax and AUC values were slightly higher in elderly subjects. Elderly subjects can be administered the same doses as adults.
Distribution: Cefixime is almost completely bound to albumin, with an average free fraction of approximately 30%.
Metabolism: Metabolites of cefixime have not been isolated from human serum or urine.
Excretion: Cefixime is excreted mainly unchanged in the urine. The predominant mechanism is glomerular filtration.
There are no data on the penetration of cefixime into breast milk.
Indication
Infectious and inflammatory diseases caused by microorganisms sensitive to the drug:
– upper respiratory tract infections (including otitis media) and other upper respiratory tract infections (sinusitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis of bacterial etiology) in case of known or suspected resistance of the pathogen to other commonly used antibiotics, or in case of risk of treatment failure;
– lower respiratory tract infections (including acute bronchitis and exacerbation of chronic bronchitis);
– urinary tract infections (including cystitis, cystourethritis, uncomplicated pyelonephritis).
Clinically effective in the treatment of infections caused by the most common pathogenic microorganisms, including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, E.coli, Proteus Mirabilis, Klebsiella species, Haemophilus influenzae (beta-lactamase positive and -negative), Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis (beta-lactamase positive and -negative) and Enterobacter species. Has a high degree of stability in the presence of beta-lactamases.
Most strains of enterococci (Streptococcus faecalis, group D Streptococci) and Staphylococci (including coagulase-positive, coagulase-negative and methicillin-resistant strains) are resistant to cefixime. In addition, most strains of Pseudomonas, Bacteroides fragilis, Listeria monocytogenes and Clostridia are resistant to cefixime.
Contraindication
Confirmed hypersensitivity to cephalosporin antibiotics or to other components of the drug; hypersensitivity to penicillins; porphyria.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions
As with other cephalosporins, increases in prothrombin time have been reported in some patients, therefore caution should be exercised in patients receiving anticoagulant therapy.
Cefixime should be used with caution in patients receiving coumarin-type anticoagulants, such as warfarin potassium. Since cefixime may potentiate the effects of anticoagulants, an increase in prothrombin time with or without clinical bleeding may occur.
When cefixime is used in combination with potentially nephrotoxic substances (aminoglycosides, colistin, polymyxin, viomycin) or potent diuretics (ethacrynic acid, furosemide), there is an increased risk of developing renal failure.
Salicylic acid increases the level of free cefixime by 50% due to displacement of cefixime from protein binding sites. This effect is concentration-dependent.
Carbamazepine may cause an increase in cefixime plasma concentrations, so it is advisable to monitor this indicator.
Nifedipine increases the bioavailability of cefixime, but the clinical interaction has not been determined.
Potentially, like other antibiotics, the use of the drug may result in a decrease in estrogen reabsorption and a decrease in the effectiveness of combined oral contraceptives.
During treatment with cefixime, a false-positive reaction for glucose in the urine is possible when using copper sulfate tablets, Benedict's or Fehling's solutions. It is recommended to use a glucose oxidase test to determine glucose in the urine.
Cephalosporin antibiotics may cause a false-positive direct Coombs test. Therefore, it should be kept in mind that a positive Coombs test may be caused by this drug.
Application features
Severe cutaneous adverse reactions such as toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS syndrome) have been reported in some patients with cefixime. If severe cutaneous adverse reactions occur, cefixime should be discontinued and appropriate treatment should be initiated.
Cases of drug-induced haemolytic anaemia, including severe cases with fatal outcomes, have been reported with cephalosporins. Haemolytic anaemia has also been reported following repeated use of cephalosporins (including cefixime).
Effect on kidney function.
Cefixime should be used with caution in patients with significant renal impairment (see "Method of administration and dosage. Dosage in renal failure").
As with other cephalosporins, cefixime may cause acute renal failure, including tubulointerstitial nephritis as the underlying pathological condition. If acute renal failure occurs, cefixime should be discontinued and appropriate therapy and/or measures should be taken.
In case of simultaneous use of cefixime in high doses with aminoglycosides, polymyxin B, colistin, loop diuretics (furosemide, ethacrynic acid), it is necessary to carefully monitor renal function. After prolonged use of cefixime, it is necessary to check the state of hematopoiesis function.
Hypersensitivity reactions.
Due to cross-reactions of hypersensitivity, before starting treatment, it is necessary to establish whether the patient has a history of severe hypersensitivity reactions to cephalosporin or penicillin antibiotics. Cefixime should be administered with particular caution to patients with hypersensitivity to penicillin antibiotics, since there is a risk of anaphylactic reactions. If an allergic reaction to cefixime develops, the drug should be discontinued. Allergic reactions (especially anaphylaxis) observed with the use of beta-lactam antibiotics can be severe and, in rare cases, fatal (see "Adverse reactions").
Colitis/overgrowth of non-susceptible microorganisms.
When using the drug, adverse reactions from the digestive tract may occur, therefore cefixime should be prescribed with caution to patients with a history of bleeding, digestive tract diseases, especially such as ulcerative colitis, regional colitis or enteritis, as well as with impaired liver function.
Prolonged use of cefixime may lead to overgrowth of non-susceptible microorganisms, including disruption of the normal intestinal microflora, which may lead to overgrowth of Candida albicans and the development of oral candidiasis (see "Adverse reactions").
Pseudomembranous colitis.
Broad-spectrum antibiotics, especially when used for long periods of time, can cause pseudomembranous colitis. Symptoms of pseudomembranous colitis may develop during or after antibiotic treatment is stopped.
The occurrence of severe diarrhea during treatment with the drug may be a consequence of the development of pseudomembranous colitis. In these cases, the use of cefixime should be discontinued and appropriate examination should be performed.
Effect on the blood system.
Neutropenia and agranulocytosis may occur with beta-lactam antibiotics, especially with prolonged treatment. If neutropenia develops, cefixime treatment should be discontinued.
With long-term use of the drug (more than 10 days), blood tests should be monitored.
Impact on serological test results.
Cefixime may cause false-positive Coombs' test results. Cefixime may also cause false-positive urine glucose tests (see Adverse Reactions).
Spectrum of antibacterial activity.
For infections caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus, the course of treatment should be at least 10 days to prevent acute rheumatic fever.
Cephalosporins increase the toxicity of alcohol, so it is not recommended to drink alcoholic beverages during treatment with cefixime.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
There are no data on the use of the drug during pregnancy. Cefixime crosses the placenta.
Breastfeeding should be discontinued during treatment with the drug.
The drug should not be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding, except in cases of extreme necessity as prescribed by a doctor.
Ability to influence reaction speed when driving vehicles or other mechanisms
In general, it does not affect, but the possibility of adverse reactions from the central nervous system (for example, dizziness) should be taken into account, which may lead to a decrease in the speed of psychomotor reactions, in which case you should refrain from driving or working with other complex mechanisms.
Method of administration and doses
Food intake does not affect the absorption of cefixime. The duration of treatment depends on the severity of the disease and is set individually. Usually the course of treatment is 7 days, if necessary - 14 days. In infections caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, the course of treatment should be at least 10 days. In the treatment of uncomplicated cystitis, the course of treatment is 3 days.
Adults and children aged 12 years and over with a body weight of more than 50 kg:
The recommended dose is 400 mg (1 capsule) once a day.
For the treatment of uncomplicated urethral or cervical gonococcal infections, a single dose of 400 mg is recommended.
Elderly patients:
Administer the drug at the recommended adult dose. Renal function should be monitored and the dose adjusted in severe renal impairment (see Dosage in renal impairment).
Dosage in renal failure:
Cefixime should be administered with caution to patients with renal insufficiency. The dose is adjusted taking into account creatinine clearance (CC). If CC is greater than or equal to 60 ml/min, prescribe the standard dose, if CC is 21–60 ml/min or for patients on hemodialysis – 75% of the standard dose with the same intervals between administration, if CC is less than 20 ml/min or for patients on peritoneal dialysis, prescribe ½ of the standard dose with the same intervals between administration. Neither hemodialysis nor peritoneal dialysis remove a significant amount of cefixime from the body.
If it is necessary to use the drug in a dose of less than 400 mg, it is recommended to prescribe the drug in another dosage form (for example, suspension).
Children
Children under 12 years of age are recommended to use the drug in a different dosage form.
Overdose
Symptoms: increased manifestations of adverse reactions, such as: dizziness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
Treatment: gastric lavage, use of antihistamines and glucocorticoids; oxygen therapy. Hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis only slightly contribute to the removal of cefixime from the body. Therapy is symptomatic.
There are no specific antidotes for the treatment of overdose.
Adverse reactions
Adverse reactions caused by cefixime are minor and occur rarely. The following disorders are possible:
From the nervous system: headache, dizziness, dysphoria, hyperactivity.
From the side of the organs of hearing and vestibular apparatus: hearing loss.
From the respiratory system: dyspnea.
From the blood and lymphatic system: eosinophilia, granulocytopenia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, thrombocytosis, neutropenia, hemolytic anemia, hypoprothrombinemia (bleeding and bruising without apparent cause), thrombophlebitis, prolongation of thrombin and prothrombin time, agranulocytosis.
On the part of the digestive tract: stomach and intestinal cramps, abdominal pain, diarrhea*, nausea, vomiting, candidiasis of the oral mucosa, pseudomembranous colitis, dry mouth, dyspepsia, flatulence, dysbacteriosis, in rare cases - stomatitis, glossitis.
Metabolism and nutrition disorders: anorexia.
From the hepatobiliary system: hepatitis, cholestasis, transient increase in liver transaminases and alkaline phosphatase activity, hyperbilirubinemia, cholestatic jaundice, icterus of the sclera, icterus of the skin.
Renal and urinary disorders: acute renal failure, including interstitial nephritis as the underlying pathological condition, hematuria.
Immune system and skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: hypersensitivity reactions including: rash, pruritus, angioedema, anaphylactic shock, anaphylactic reactions; serum sickness-like reactions; drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS); facial edema, skin hyperemia, urticaria, erythema multiforme or Stevens-Johnson syndrome, serum sickness, purpura, arthralgia, fever, maculopapular and vesiculobullous rashes, fungal dermatitis, epithelial desquamation, dry skin, hair loss, sunburn, toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Infections and infestations: vaginal candidiasis (vaginal itching or discharge).
Laboratory data: Most laboratory changes are transient and have no clinical significance. Increased blood urea nitrogen, increased serum creatinine, false-positive Coombs test results, and positive urine ketones in nitroprusside tests but not nitrofurantoin may occur. Cefixime may cause false-positive urine glucose tests, so enzyme tests, liver function tests, and kidney function tests should be used.
General disorders: increased sweating, increased fatigue, weakness, inflammation of the mucous membranes.
* Diarrhea is usually associated with higher doses. Moderate to severe diarrhea has been reported; discontinuation of therapy is warranted. Cefixime should be discontinued if severe diarrhea occurs.
Expiration date
3 years.
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 ºС.
Keep out of reach of children.
Packaging
5 capsules in a blister; 1 blister in a cardboard box.
Vacation category
According to the recipe.
Producer
Pharma International.
Location of the manufacturer and its business address
Al Kastal, Airport Road, A.S. 334, Al Jubaiha 11941, Amman, Jordan.
Applicant
Pharma International.
Applicant's location
A.S. 334 Al-Jubayha 11941 Amman, Jordan.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.