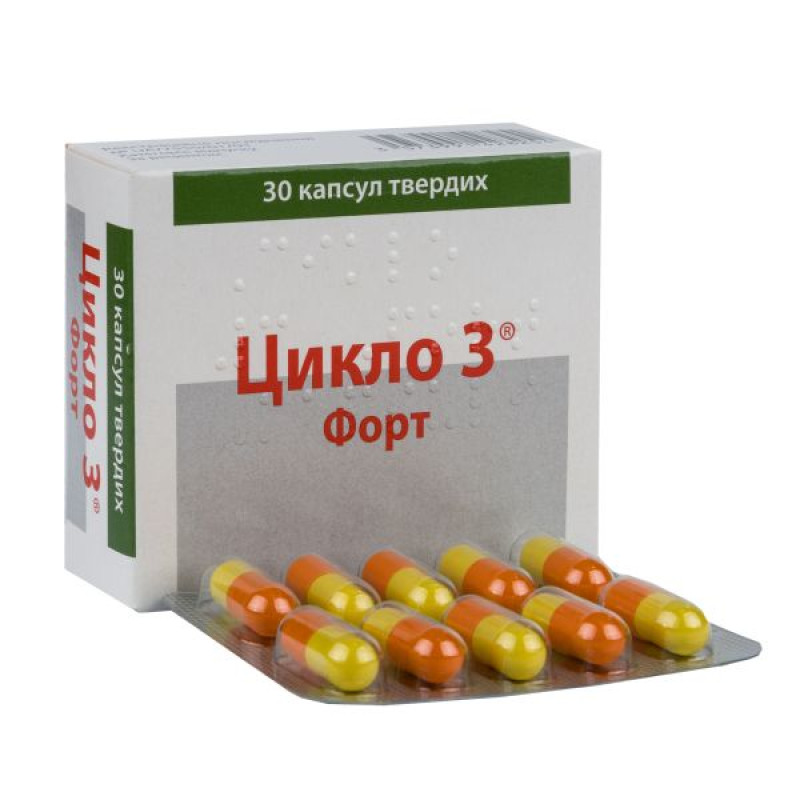
Cyclo 3 Fort hard capsules 400 mg blister No. 30

Instructions for Cyclo 3 Fort hard capsules 400 mg blister No. 30
Composition
active ingredients: ruscus aculeatus, hesperidin methyl chalcone, ascorbic acid;
1 capsule contains dry extract of nettle (Ruscus aculeatus) with a titrated content of sterol heterosides (150 mg), hesperidin methylchalcone (150 mg), ascorbic acid (100 mg);
excipients (capsule contents): talc, macrogol 6000, colloidal hydrophobic silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate;
Excipients (capsule shell): gelatin, sunset yellow dye (E 110), quinoline yellow dye (E 104), titanium dioxide (E 171).
Dosage form
The capsules are hard.
Main physicochemical properties: size No. 1 capsule with an opaque yellow body and an opaque orange cap, containing a more or less compacted yellowish powder.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Angioprotectors. Capillary stabilizing agents.
ATX code C05C X.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
The drug has venotonic, lymphotonic and angioprotective properties.
The venotonic effect of pine needle extract is due to adrenergic mechanisms at two levels, namely:
direct stimulation of postsynaptic alpha-adrenergic receptors of vascular wall smooth muscle cells;
indirect effect due to the release of noradrenaline from the granules of presynaptic nerve endings.
The intensity of the action of pine needle extract is proportional to temperature.
In in vitro studies on isolated perfused veins, needle extract rapidly (after 5–8 min) caused a pronounced, progressive and prolonged vessel contraction. In in vivo studies on animals, needle extract induced an increase in venous pressure. The intensity of this effect was comparable in healthy and pathologically altered veins.
The venotonic effect of the drug on human vessels was confirmed by stereomicroscopic examination of the dorsal veins of the wrist (Aeliga method).
The relationship between dosage and effect of the drug for a single dose was also established and the respective role of each component of the drug for vein tone was demonstrated.
The drug improves lymphatic circulation. Experiments on dogs have shown a significant and long-lasting increase in the speed of lymph flow in the thoracic duct.
Angioprotective effect. The drug reduces the permeability of human capillaries (as demonstrated by the Landis test) and increases capillary resistance (as confirmed by the method of petechiae induction in the skin under rarefaction). A significant increase in capillary resistance was observed already in the first hour after dosing. This effect is mainly due to the action of ascorbic acid.
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetic studies in animals have demonstrated that pine needle extract (labeled with the tritium isotope) and hesperidin methylchalcone (labeled with the
carbon 14C) are rapidly absorbed. The maximum concentration of both ingredients in the blood plasma is reached after approximately 2 hours. The components of the drug are excreted in the urine and feces (the latter is referred to as enterohepatic recirculation).
It is impossible to conduct appropriate studies of the pharmacokinetics of the drug in humans, however, pharmacodynamic tests allow an indirect assessment of the kinetics of the drug Cyclo 3® Fort. In stereomicroscopic studies of the dorsal veins of the wrist (Aeliga method), the maximum venotonic effect is observed 2 hours after taking the drug, with a return to the initial state after approximately 6 hours.
Indication
Symptomatic treatment of venous-lymphatic insufficiency (with manifestations such as heaviness in the limbs, pain, tired legs syndrome).
Hemorrhoid exacerbation (treatment of functional symptoms).
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to any component of the drug; severe kidney disease.
Iron storage disorders (thalassemia, hemochromatosis, sideroblastic anemia) due to the presence of ascorbic acid in the composition of the drug.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions
Absorption of ascorbic acid is reduced with simultaneous use of oral contraceptives, consumption of fruit or vegetable juices, alkaline drinks. Ascorbic acid when taken orally increases the absorption of penicillin, tetracycline, iron, reduces the effectiveness of heparin and indirect anticoagulants, increases the risk of crystalluria during treatment with salicylates. Simultaneous administration of vitamin C and deferoxamine increases tissue toxicity of iron, especially in the heart muscle, which can lead to decompensation of the circulatory system. Vitamin C can be taken only 2 hours after the injection of deferoxamine. Long-term administration of large doses by persons treated with disulfiram inhibits the disulfiram-alcohol reaction. Large doses of vitamin C reduce the effectiveness of tricyclic antidepressants, neuroleptics - phenothiazine derivatives, tubular reabsorption of amphetamine, and disrupt the excretion of mexiletine by the kidneys. Ascorbic acid increases the total clearance of ethyl alcohol. Quinoline drugs, calcium chloride, salicylates, corticosteroids, with prolonged use, reduce the reserves of ascorbic acid in the body.
Application features
If diarrhea develops, the drug should be discontinued.
Use in hemorrhoids: treatment with Cyclo 3® Fort cannot be a substitute for specific therapy of proctological diseases. Treatment with the drug should be short. If the symptoms do not disappear quickly, it is necessary to conduct a thorough proctological examination of the patient and prescribe appropriate treatment.
If nausea or stomach pain occurs, the drug should be taken with food.
When taking high doses and long-term use of ascorbic acid, it is necessary to monitor kidney function and blood pressure, as well as pancreatic function. The drug should be used with caution in patients with a history of kidney disease or diabetes mellitus.
In case of urolithiasis, the daily dose of ascorbic acid should not exceed 1 g. Large doses of the drug should not be prescribed to patients with increased blood clotting.
Since ascorbic acid increases iron absorption, its use in high doses can be dangerous for patients with hemochromatosis, thalassemia, polycythemia, leukemia and sideroblastic anemia. Patients with high iron levels in the body should not use the drug. Absorption of ascorbic acid may be impaired in intestinal dyskinesias, enteritis and achilia. Ascorbic acid as a reducing agent can affect the results of laboratory tests, for example, when determining the blood glucose content, bilirubin, transaminase activity, lactate dehydrogenase, etc. Since ascorbic acid has a mild stimulating effect, it is not recommended to take the drug at the end of the day.
The medicine contains a dye (E 110) and may cause allergic reactions.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding
There are limited data on the use of the drug in pregnant women. Animal studies do not indicate direct or indirect harmful effects with respect to reproductive toxicity. Preclinical data from conventional studies of safety pharmacology, repeated dose toxicity, genotoxicity and reproductive function did not reveal any special hazard for humans. Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted (however, in mice treated with hesperidin methylchalcone alone, no carcinogenic effect was observed after 96 weeks of oral administration (5% of the diet, i.e. 20 g/kg body weight)). As a precautionary measure, it is preferable to avoid the use of the drug during pregnancy.
It is not known whether metabolites of the medicinal product are excreted in human milk. A risk to the newborn/infants cannot be excluded. As a precautionary measure, the medicinal product should not be used during breast-feeding.
There are no data on fertility.
Ability to influence reaction speed when driving vehicles or other mechanisms
No specific studies were conducted.
Method of administration and doses
For venous-lymphatic insufficiency: 2–3 capsules per day.
In proctology: 4–5 capsules per day.
Capsules are taken orally with a glass of water.
Children
Not used.
Overdose
No cases of overdose have been reported. However, excessive doses of ascorbic acid may lead to hemolytic anemia in patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency.
Possible increase in adverse reactions. When using ascorbic acid in a dose of more than 1 g per day, irritation of the mucous membrane of the digestive tract, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea are possible.
On the part of the urinary system: with prolonged use of ascorbic acid in high doses, damage to the glomerular apparatus of the kidneys, crystalluria, formation of urate, cystic and/or oxalate stones in the kidneys and urinary tract is possible.
In case of overdose, symptomatic treatment is prescribed.
Adverse reactions
Adverse reactions are presented according to the following classification: very common (≥ 1/10), common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10), uncommon (≥ 1/1,000 to < 1/100), rare (≥ 1/10,000 to < 1/1,000), very rare (< 1/10,000).
From the nervous system:
- infrequently: insomnia;
- rarely: nervousness.
From the side of the organs of hearing and labyrinth:
From the vascular system:
- rarely: peripheral coldness, venous pain.
Gastrointestinal disorders:
- often: diarrhea, sometimes severe (associated with the risk of weight loss and disturbance of water and electrolyte balance with continued treatment), quickly disappears after discontinuation of the drug (see section "Special instructions for use"); abdominal pain;
- infrequently: dyspepsia, nausea;
- rarely: gastrointestinal disorders, aphthous stomatitis.
From the hepatobiliary system:
- rarely: increased alanine aminotransferase levels.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders:
- uncommon: erythema, itching.
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders:
- infrequently: muscle spasms, pain in the extremities.
Adverse reactions with unknown frequency.
Gastrointestinal disorders:
- in some cases (or in some patients) reversible, predominantly lymphocytic, microscopic colitis has been identified;
- stomach pain.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders:
- maculopapular erythema, urticaria.
On the part of the immune system: allergic reactions, including skin rash, angioedema; sometimes - anaphylactic shock in the presence of sensitization.
Expiration date
2 years.
Storage conditions
Store in the original packaging out of the reach of children at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Packaging
10 capsules in a blister. 3 blisters in a cardboard box.
Vacation category
According to the recipe.
Producer
Pierre Fabre Medicine Production.
Pierre Fabre Medicament Production.
Location of the manufacturer and address of its place of business
Progipharm production site, Rue du Lycee, 45500 Gien, France / site Progipharm, Rue du Lycee, 45500 Gien, France.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.