Darfen Kids oral suspension 100mg/5ml 200ml
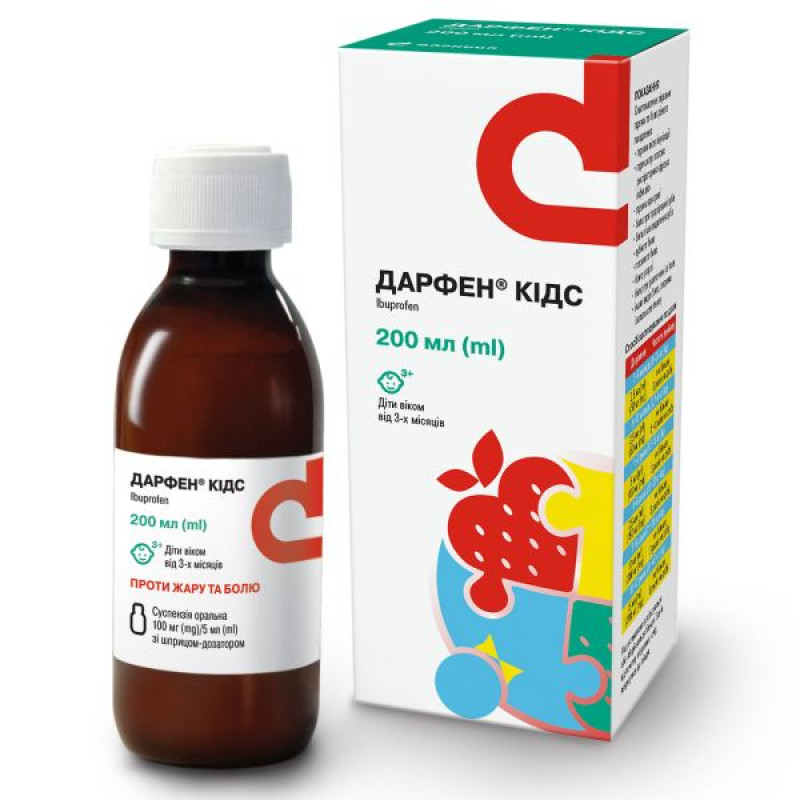

Instructions for use Darfen Kids oral suspension 100mg/5ml 200ml
Composition
active ingredient: ibuprofen;
5 ml of suspension contains 100 mg of ibuprofen;
excipients: sodium benzoate, anhydrous citric acid, sodium citrate, sodium saccharin, sodium chloride, hypromellose 15 CP, xanthan gum, liquid maltitol, glycerin (E 422), strawberry flavoring, purified water.
Dosage form
Oral suspension.
Main physicochemical properties: viscous suspension, free from foreign substances, white or almost white in color with a characteristic strawberry odor.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory and antirheumatic drugs. Propionic acid derivatives. Ibuprofen. ATC code M01A E01.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), a propionic acid derivative, which has been shown to act by inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis. In humans, ibuprofen reduces pain associated with inflammation, swelling, and fever. Ibuprofen has analgesic, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory effects. The onset of analgesic and antipyretic effects of ibuprofen has been shown to occur within 30 minutes. In addition, ibuprofen reversibly inhibits platelet aggregation.
Experimental data suggest that ibuprofen may inhibit the effect of low-dose acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) on platelet aggregation when these drugs are used concomitantly. In a study in which a single dose of ibuprofen 400 mg was taken within 8 hours before or within 30 minutes after immediate-release aspirin (81 mg), a reduced effect of acetylsalicylic acid on thromboxane formation or platelet aggregation was observed. However, the limitations of these data and the uncertainty regarding the extrapolation of ex vivo data to the clinical picture do not allow for firm conclusions to be drawn regarding the routine use of ibuprofen. Therefore, such clinically significant effects are considered unlikely with non-routine use of ibuprofen.
Pharmacokinetics
Ibuprofen is rapidly absorbed after administration and is rapidly distributed throughout the body. Excretion is rapid and complete and occurs via the kidneys.
Maximum plasma concentrations are reached 45 minutes after oral administration in the fasted state. When administered with food, peak levels are observed after 1-2 hours. This time may vary for different dosage forms.
The half-life is approximately 2 hours.
In limited studies, ibuprofen has been found in breast milk at very low concentrations.
Indication
Symptomatic treatment of fever and pain of various origins in children aged 3 months to 12 years with a body weight of at least 5 kg (including fever after immunization, acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, teething pain, pain after tooth extraction, toothache, headache, sore throat, pain from sprains and other types of pain, including inflammatory genesis).
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to ibuprofen or to any of the excipients of the drug. History of hypersensitivity reactions (e.g. bronchospasm, bronchial asthma, rhinitis, angioedema or urticaria) after taking acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Gastric ulcer/bleeding in active form or history of recurrence (two or more severe episodes of confirmed ulcer or bleeding). History of gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation associated with the use of NSAIDs. Severe hepatic insufficiency, severe renal insufficiency or severe heart failure. Severe dehydration (caused by vomiting, diarrhea or insufficient fluid intake). Last trimester of pregnancy. Cerebrovascular or other bleeding. Unexplained hematopoietic or coagulation disorders. Hereditary fructose intolerance.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions
Ibuprofen, like other NSAIDs, should not be used in combination with:
− acetylsalicylic acid, as this may increase the risk of adverse reactions, unless acetylsalicylic acid (dose not exceeding 75 mg per day) has been prescribed by a doctor. Experimental data suggest that ibuprofen may inhibit the antiplatelet effect of low doses of acetylsalicylic acid when used concomitantly. However, the limited data and the uncertainty regarding the extrapolation of ex vivo data to the clinical picture do not allow for firm conclusions regarding the systematic use of ibuprofen. Therefore, such clinically significant effects are considered unlikely with non-systematic use of ibuprofen;
− other NSAIDs, including selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors. The simultaneous use of two or more NSAIDs should be avoided as this may increase the risk of side effects.
Ibuprofen should be used with caution in combination with the following drugs:
− Antihypertensives (ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers and angiotensin II antagonists) and diuretics: NSAIDs may reduce the effect of these drugs. In some patients with impaired renal function (e.g. dehydrated patients or elderly patients with compromised renal function), concomitant use of ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers or angiotensin II antagonists and cyclooxygenase inhibitors may lead to further deterioration of renal function, including possible acute renal failure, which is usually reversible. Therefore, this combination should be used with caution, especially in the elderly. Patients should be adequately hydrated and liver function should be monitored after initiation of concomitant therapy and periodically thereafter. Diuretics may increase the risk of nephrotoxicity of NSAIDs;
− corticosteroids: increased risk of ulcers and bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract;
− antiplatelet agents and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs): increased risk of gastrointestinal bleeding;
− cardiac glycosides, such as digoxin: NSAIDs may exacerbate cardiac dysfunction, reduce glomerular filtration rate and increase plasma levels of glycosides. Concomitant use of ibuprofen with digoxin may increase serum levels of these drugs. When used correctly (maximum 4 days), monitoring of serum digoxin levels is usually not necessary;
− Lithium: there is evidence of a potential increase in plasma lithium levels. With proper use (maximum 4 days), monitoring of serum lithium levels is usually not necessary;
− methotrexate: there is a possibility of increased plasma levels of methotrexate. The use of ibuprofen within 24 hours before or after the administration of methotrexate may lead to an increase in the concentration of methotrexate and an increase in its toxic effect;
− cyclosporine: increased risk of nephrotoxicity;
− mifepristone: NSAIDs should not be used earlier than 8-12 days after mifepristone administration, as they may reduce its effectiveness;
− tacrolimus: possible increased risk of nephrotoxicity with concomitant use of NSAIDs with tacrolimus;
− zidovudine: increased risk of hematological toxicity with concomitant use of zidovudine and NSAIDs. There is evidence of an increased risk of hemarthrosis and hematoma in HIV-infected patients with hemophilia when treated concomitantly with zidovudine and ibuprofen;
− Quinolone antibiotics: Animal data suggest that NSAIDs may increase the risk of seizures associated with the use of quinolone antibiotics. Patients taking NSAIDs and quinolones may be at increased risk of developing seizures;
− Sulfonylurea drugs: possible potentiation of the effect. Clinical studies have shown an interaction between NSAIDs and antidiabetic drugs (sulfonylureas). Although no interactions between ibuprofen and sulfonylureas have been described to date, monitoring of blood glucose levels is recommended as a precautionary measure when these drugs are used concomitantly;
- phenytoin: possible increase in serum levels of phenytoin. With proper use (maximum 4 days), monitoring of serum levels of phenytoin is usually not necessary;
− probenecid and sulfinpyrazone: medicines containing probenecid or sulfinpyrazone may delay the elimination of ibuprofen;
− potassium-sparing diuretics: simultaneous use of ibuprofen and potassium-sparing diuretics may lead to hyperkalemia (it is recommended to monitor serum potassium levels);
− Voriconazole and fluconazole (CYP2C9 inhibitors): Concomitant use of ibuprofen with CYP2C9 inhibitors may increase the exposure of ibuprofen (CYP2C9 substrate). A study with voriconazole and fluconazole has shown an increase in the exposure of S(+)-ibuprofen by approximately 80-100%. When ibuprofen is co-administered with strong CYP2C9 inhibitors, a reduction in the dose of ibuprofen is recommended, especially when high doses of ibuprofen are required with voriconazole or fluconazole.
Application features
Side effects associated with ibuprofen can be minimized by using the lowest effective dose necessary to treat symptoms for the shortest period of time.
Elderly patients have an increased frequency of adverse reactions to NSAIDs, especially gastrointestinal bleeding and perforation, which can be fatal. Elderly patients are at increased risk of adverse reactions. Long-term use of NSAIDs in the elderly is not recommended. If long-term therapy is necessary, patients should be regularly monitored.
Caution should be exercised in patients with the following conditions:
− systemic lupus erythematosus, as well as mixed connective tissue disease − due to an increased risk of aseptic meningitis;
− congenital disorder of porphyrin metabolism, such as acute concomitant porphyria;
− history of hypertension and/or heart failure, as fluid retention and edema have been reported in association with NSAID therapy;
− renal failure – due to the possibility of worsening kidney function;
− liver dysfunction;
− use immediately after extensive surgical interventions;
− hay fever, nasal polyps or chronic obstructive airways disease due to an increased risk of allergic reactions. These include asthma attacks (so-called analgesic asthma), angioedema or urticaria;
− patients with a history of allergic reactions to other substances, − due to an increased risk of hypersensitivity reactions to ibuprofen.
Effects on the respiratory system.
Bronchospasm may occur in patients who suffer from bronchial asthma or allergic diseases or have a history of these diseases.
Other NSAIDs.
The concomitant use of ibuprofen with other NSAIDs, including selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors, should be avoided as this increases the risk of adverse reactions.
Systemic lupus erythematosus and mixed connective tissue disease.
Ibuprofen should be used with caution in systemic lupus erythematosus and mixed connective tissue disease due to an increased risk of aseptic meningitis.
Effects on the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular systems.
Patients with a history of hypertension and/or heart failure should start treatment with caution (consultation with a doctor is necessary), since cases of fluid retention, hypertension and edema have been reported with ibuprofen therapy, as with other NSAIDs.
Clinical trial data and epidemiological data suggest that the use of ibuprofen, especially at high doses (2400 mg per day) and in long-term treatment, may be associated with a small increased risk of arterial thrombotic events (e.g. myocardial infarction or stroke). Epidemiological studies do not suggest that the use of low doses of ibuprofen (e.g. ≤ 1200 mg per day) increases the risk of myocardial infarction.
Effect on the kidneys.
Long-term use of analgesics, especially in combination with other painkillers, can lead to chronic kidney damage with the risk of kidney failure (analgesic nephropathy).
Caution should be exercised in patients with renal insufficiency due to the possibility of worsening renal function.
There is a risk of kidney failure in children and adolescents with dehydration.
Effect on the liver.
Liver dysfunction.
Effect on the gastrointestinal tract.
NSAIDs should be used with caution in patients with a history of gastrointestinal diseases (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease) as their condition may be exacerbated. Such patients should seek medical advice.
There are reports of cases of gastrointestinal bleeding, perforation, ulcers, which can be fatal, occurring at any stage of treatment with NSAIDs, regardless of the presence of warning symptoms or the presence of severe gastrointestinal disorders in history.
The risk of gastrointestinal bleeding, ulceration or perforation is dose-dependent (increasing with increasing doses of NSAIDs), in the presence of a history of peptic ulcer disease, especially complicated by bleeding or perforation, and in elderly patients. Adverse reactions may occur even with short-term therapy.
These patients should be started on the lowest available dose. Combination therapy with protective agents (e.g. misoprostol or proton pump inhibitors) is recommended for these patients, as well as for patients requiring concomitant low-dose acetylsalicylic acid or other medicinal products that may increase the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
Patients with a history of toxic gastrointestinal lesions, especially the elderly, should report any unusual gastrointestinal symptoms to their physician.
Caution should be exercised when treating patients who are concomitantly taking medications that may increase the risk of ulceration or bleeding, such as oral corticosteroids, anticoagulants (e.g. warfarin), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors or antiplatelet agents (e.g. acetylsalicylic acid).
If gastrointestinal bleeding or ulceration occurs in patients receiving ibuprofen, treatment should be discontinued immediately.
On the skin and subcutaneous tissue.
Severe acute hypersensitivity reactions (e.g. anaphylactic shock) have been observed very rarely. At the first signs of a hypersensitivity reaction after taking ibuprofen, therapy should be discontinued and a doctor should be consulted immediately.
In exceptional cases, chickenpox can cause severe skin and soft tissue infections. The effect of NSAIDs on the worsening of these infections cannot be excluded, therefore it is recommended to avoid the use of ibuprofen in case of chickenpox.
Masking the symptoms of underlying infections.
NSAIDs can mask symptoms of infection and fever.
Darfen® Kids may mask the symptoms of an infectious disease, which may delay the initiation of appropriate treatment and thereby complicate the course of the disease. This has been observed in bacterial community-acquired pneumonia and bacterial complications of chickenpox. When ibuprofen is used for fever or to relieve pain in an infection, monitoring for the infectious disease is recommended. In outpatient settings, the patient should consult a doctor if symptoms persist or worsen.
Ibuprofen may temporarily inhibit platelet aggregation. Therefore, it is recommended to carefully monitor the condition of patients with blood clotting disorders.
With prolonged use of ibuprofen, liver function tests, kidney function, and hematological function/blood count should be regularly checked.
Prolonged use of any painkiller for headache may worsen this condition. In such cases, a doctor should be consulted and treatment should be discontinued. The possibility of medication overuse headache should be considered in patients who suffer from frequent or daily headaches despite (or because of) regular use of headache medication.
The concomitant use of alcohol and NSAIDs may increase adverse reactions associated with the active substance, especially those affecting the gastrointestinal tract or central nervous system (CNS).
Before taking this medicine, you should consult a doctor: pregnant women, women trying to get pregnant, elderly people, smokers.
Important information about excipients.
Due to the content of liquid maltitol, this medicinal product may have a mild laxative effect. The energy value of 1 g of maltitol is 2.3 kcal. It should not be prescribed to patients with rare hereditary disorders of fructose tolerance.
The medicinal product contains sodium compounds. Caution should be exercised when used in patients on a controlled sodium diet.
Ability to influence reaction speed when driving vehicles or other mechanisms
When used in accordance with the recommended doses and duration of treatment, the medicinal product is not expected to affect the ability to drive or operate other mechanisms.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding
Pregnancy.
Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis may adversely affect pregnancy and/or embryonal/fetal development. Epidemiological data suggest an increased risk of miscarriage, congenital heart defects and gastroschisis following exposure to prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors in early pregnancy. The risk is thought to increase with dose and duration of therapy. The absolute risk of cardiovascular malformations increased from less than 1% to approximately 1.5%.
Ibuprofen should not be taken during the first two trimesters of pregnancy unless, in the opinion of the physician, the potential benefit to the patient outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. If ibuprofen is used by a woman attempting to conceive or who is pregnant in the first or second trimester, the lowest possible dose should be used for the shortest possible period of time.
During the third trimester of pregnancy, all prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors may pose the following risks:
for the fetus: cardiopulmonary toxicity (characterized by premature closure of the ductus arteriosus and pulmonary hypertension); renal dysfunction, which may progress to renal failure, accompanied by oligohydramnios;
for the mother and the newborn, at the end of pregnancy: possible increase in bleeding time, antiplatelet effect, which can develop even at very low doses; inhibition of uterine contractions, leading to delay or prolongation of labor. Possible increased risk of edema in the mother. Therefore, ibuprofen is contraindicated during the third trimester of pregnancy.
Breastfeeding. Ibuprofen and its metabolites pass into breast milk in low concentrations. There is currently no information on the negative effects on the infant, therefore, for short-term treatment of pain and fever at recommended doses, it is usually not necessary to interrupt breastfeeding.
Fertility: There is some evidence that drugs that inhibit cyclooxygenase/prostaglandin synthesis may impair female fertility by affecting ovulation. This effect is reversible upon discontinuation of treatment.
Therefore, the use of ibuprofen is not recommended for women who have difficulty becoming pregnant.
Method of administration and doses
Side effects can be minimized by using the lowest effective dose necessary to control symptoms for the shortest period of time.
For oral use. The recommended daily dose of the drug is 20-30 mg/kg body weight, divided into equal doses, depending on age and body weight, with an interval between doses of 6-8 hours. To ensure accurate dosing, the package contains a syringe-doser. The recommended dose should not be exceeded. For short-term use only.
Child's age Body weight (kg) | Recommended dose | Frequency of administration per day |
| 3-6 months (5-7.6 kg) | 2.5 ml of suspension (50 mg) | no more than 3 times |
| 6-12 months (7.7-9 kg) | 2.5 ml of suspension (50 mg) | no more than 3−4 times |
| 1-3 years (10-16 kg) | 5 ml of suspension (100 mg) | no more than 3 times |
| 4−6 years (17−20 kg) | 7.5 ml of suspension (150 mg) | no more than 3 times |
| 7−9 years (21−30 kg) | 10 ml of suspension (200 mg) | no more than 3 times |
| 10−12 years (31−40 kg) | 15 ml of suspension (300 mg) | no more than 3 times |
Do not use on children under 3 months of age unless recommended by a doctor.
Do not use this medicine for children weighing less than 5 kg.
For children aged 3 to 6 months: If symptoms persist for more than 24 hours after the start of treatment or worsen (after 3 doses), you should consult a doctor immediately.
If symptoms persist for more than 3 days after starting treatment or worsen in children aged 6 months to 12 years, a doctor should be consulted.
In case of fever after immunization (children aged 3-6 months), the recommended daily dose is 2.5 ml of suspension (50 mg), if necessary - another 2.5 ml of suspension (50 mg) after 6 hours, but not more than 5 ml of suspension (100 mg) within 24 hours. If symptoms persist, you should consult a doctor.
Patients with sensitive stomachs should take the medicine with meals.
Shake before use.
Special categories of patients.
Renal impairment: No dose reduction is required in patients with mild to moderate renal impairment (for patients with severe renal impairment, see section "Contraindications").
Hepatic impairment: No dose reduction is required in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment (for patients with severe hepatic impairment, see section "Contraindications").
In case of taking a dose exceeding the recommended dose, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Children
The medicine should be used in children aged 3 months to 12 years with a body weight of at least 5 kg.
Overdose
In children, symptoms of overdose may occur when taking ibuprofen doses exceeding 400 mg/kg. In adults, dose reactions are less pronounced. The half-life in overdose is 1.5-3 hours.
Symptoms. In most patients, the use of clinically significant amounts of NSAIDs caused only nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain or, less commonly, diarrhea. Tinnitus, headache and gastrointestinal bleeding may also occur. In more severe poisoning, toxic CNS lesions in the form of vertigo, dizziness, drowsiness, sometimes - an excited state and disorientation or coma are possible. Sometimes patients develop convulsions. In severe poisoning, hyperkalemia and metabolic acidosis may occur, as well as an increase in prothrombin time/international normalized ratio (INR) - presumably due to interaction with blood clotting factors circulating in the bloodstream. Acute renal failure, liver damage, hypotension, respiratory depression and cyanosis, loss of consciousness may occur. In patients with bronchial asthma, exacerbation of the course of asthma is possible. Nystagmus and visual impairment are possible.
Treatment. There is no specific antidote. Treatment should be symptomatic and supportive, and include maintaining a patent airway, monitoring cardiac function and vital signs until the patient is stable. Consider oral administration of activated charcoal or gastric lavage if the patient has taken a potentially toxic dose within 1 hour. If ibuprofen has already been absorbed, alkaline agents may be used to help eliminate acidic ibuprofen in the urine. For frequent or prolonged seizures, intravenous antihistamines (e.g. diazepam or lorazepam) should be administered. Bronchodilators should be administered in cases of exacerbation of bronchial asthma. Medical advice should be sought immediately.
Adverse reactions
The list of adverse reactions includes all adverse reactions known to occur with ibuprofen, including those observed with high doses, in long-term therapy in patients with rheumatism.
The frequency reported, which goes beyond very rare reports, refers to short-term use of doses (maximum 1200 mg ibuprofen per day) for oral dosage forms.
The most frequently observed adverse reactions are gastrointestinal. Most adverse reactions are dose-related, in particular the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding depends on the dose and duration of treatment. Gastrointestinal ulcers, perforation or gastrointestinal bleeding, sometimes fatal, may occur, especially in elderly patients. Nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, abdominal distension, constipation, dyspepsia, abdominal pain, melena, haematemesis, ulcerative stomatitis, exacerbation of colitis and Crohn's disease have been reported after the use of ibuprofen. Gastritis has been observed less frequently.
Edema, hypertension, and heart failure have been reported to be associated with NSAID treatment.
Clinical trial data and epidemiological data suggest that the use of ibuprofen, especially at high doses of 2400 mg per day and with long-term treatment, may be associated with a slightly increased risk of arterial thrombotic complications (e.g. myocardial infarction or stroke).
There have been reports of exacerbations of inflammation associated with infection, such as necrotizing fasciitis, coinciding with the use of NSAIDs. This may be related to the mechanism of action of NSAIDs.
If signs of infection develop or worsen while taking ibuprofen, the patient is advised to seek immediate medical attention. It is necessary to determine whether antimicrobial/antibiotic therapy is indicated.
With long-term therapy, it is necessary to regularly perform blood tests.
The patient should immediately consult a doctor and stop taking ibuprofen if any of the symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions occur, which may develop even with the first use of the drug. In such cases, immediate medical attention is required.
If severe epigastric pain, melena, or bloody vomiting occurs, discontinue use of the drug and consult a doctor immediately.
Adverse reactions that have occurred with ibuprofen are listed below by system organ class and frequency. The frequency of adverse reactions is defined as follows: very common (≥ 1/10), common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10), uncommon (≥ 1/1,000 to < 1/100), rare (≥ 1/10,000 to < 1/1,000), very rare (< 1/10,000) and not known (cannot be estimated from the available data). Within each frequency grouping, adverse reactions are presented in order of decreasing seriousness.
On the part of the organs of vision:
frequency unknown: with prolonged treatment, visual disturbances and optic neuritis may occur.
From the side of the organs of hearing and vestibular apparatus:
frequency unknown: dizziness may occur with prolonged treatment;
Rare: ringing in the ears.
From the respiratory system, chest organs and mediastinum:
frequency unknown: airway reactivity including asthma, bronchospasm or dyspnoea1.
From the gastrointestinal tract:
common: abdominal pain, nausea, dyspepsia, diarrhea, flatulence, constipation, heartburn, vomiting and minor gastrointestinal bleeding, which in exceptional cases may lead to anemia;
infrequently: gastric and duodenal ulcers, perforations or gastrointestinal bleeding, melena, hematemesis, sometimes fatal (especially in the elderly), ulcerative stomatitis, gastritis, exacerbation of colitis and Crohn's disease;
very rare: esophagitis, formation of diaphragmatic intestinal strictures, pancreatitis.
From the liver and biliary tract:
very rare: liver dysfunction, liver damage, especially with long-term therapy, liver failure, acute hepatitis.
From the kidneys and urinary system:
Rare: acute renal failure, especially with long-term use of NSAIDs, in combination with increased serum urea levels, papillonecrosis;
very rare: edema formation, especially in patients with arterial hypertension or renal insufficiency, nephrotic syndrome, interstitial nephritis, which may be accompanied by acute renal failure.
From the nervous system:
uncommon: headache, dizziness, insomnia, agitation, irritability or fatigue;
very rare: aseptic meningitis2.
From the psyche:
very rare: psychotic reactions, depression; with prolonged use: hallucinations, confusion.
From the cardiovascular system:
very rare: heart failure, palpitations, edema, myocardial infarction,
arterial hypertension, vasculitis.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders:
very rare: blood disorders (anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, agranulocytosis). The first signs are fever, sore throat, superficial ulcers in the mouth, flu-like symptoms, severe exhaustion, nasal and skin bleeding, hematomas.
On the part of the immune system:
uncommon: hypersensitivity reactions1, urticaria and pruritus;
Very rare: severe hypersensitivity reactions, symptoms of which may include swelling of the face, tongue and larynx, shortness of breath, tachycardia, hypotension (anaphylactic reaction, angioedema or severe shock). Exacerbation of asthma.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders:
uncommon: various skin rashes1;
frequency unknown: acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, rash accompanied by eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS syndrome).
General disorders:
frequency unknown: malaise and fatigue.
Laboratory indicators:
Rare: decreased hemoglobin level.
Infections and invasions.
very rare: exacerbation of inflammation associated with infection (e.g. development of necrotizing fasciitis. In exceptional cases, chickenpox can cause severe infectious complications of the skin and soft tissues).
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions.
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after the marketing authorisation of a medicinal product is an important procedure. It allows for continued monitoring of the benefit-risk balance of the medicinal product in question. Healthcare professionals should report any suspected adverse reactions via the national reporting system.
Expiration date
3 years. After first opening the bottle – 6 months.
Storage conditions
Store in original packaging at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Packaging
200 ml in a bottle; 1 bottle complete with a dosing syringe in a pack.
Vacation category
Without a prescription.
Producer
Famar Nederland BV/Famar Nederland BV
Location of the manufacturer and its business address
Industrieweg 1, Bladel, 5531 AD, Netherlands.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.