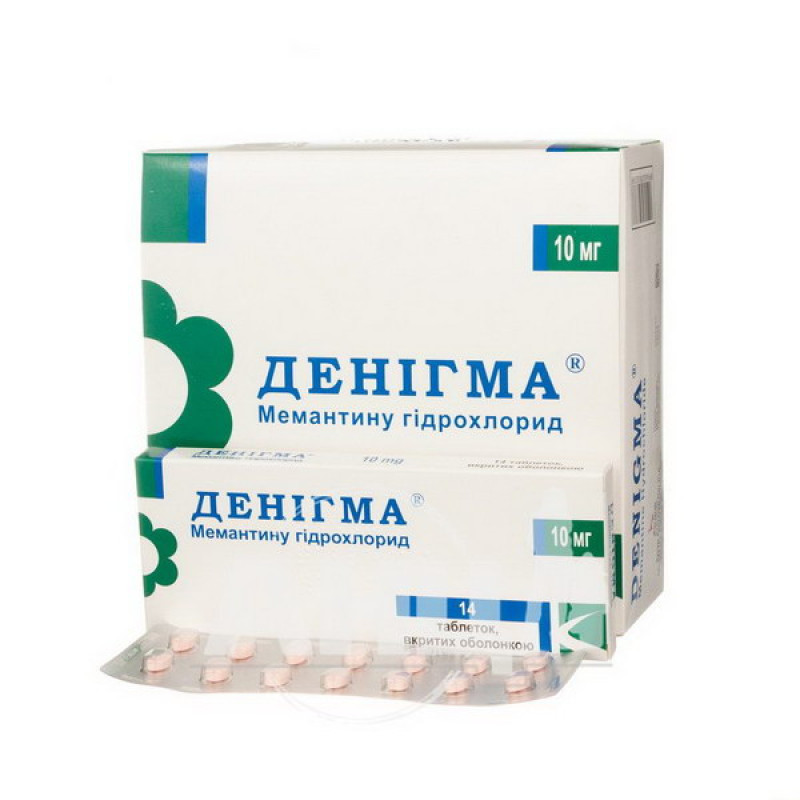
Denigma film-coated tablets 10 mg blister No. 140
Instructions for Denigma film-coated tablets 10 mg blister No. 140
Composition
active ingredient: memantine;
1 tablet contains 5 mg or 10 mg of memantine hydrochloride;
excipients: mannitol (E 421), microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, povidone K 30, colloidal anhydrous silica, magnesium stearate, Opadry Pink 03F84827 (talc, titanium dioxide (E 171), hypromellose, red iron oxide (E 172), polyethylene glycol).
Dosage form
Film-coated tablets.
Main physicochemical properties: oval pink tablets, coated, smooth on both sides.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Drugs used in dementia. ATX code N06D X01.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Disturbances in glutamatergic neurotransmission, especially involving NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) receptors, play an important role in the manifestation of symptoms and progression of neurodegenerative dementia.
Memantine is a potential-dependent, medium-affinity, non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist. Memantine modulates the effects of pathologically elevated levels of glutamate, which can lead to neuronal dysfunction.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption.
The absolute bioavailability of memantine is approximately 100%, the time to peak plasma concentration (Tmax) is 3 to 8 hours. There is no evidence of an effect of food intake on absorption.
Distribution.
A daily dose of 20 mg results in steady-state plasma concentrations of memantine ranging from 70 to 150 ng/ml (0.5-1 μmol) with significant interindividual variation. At daily doses of 5 to 30 mg, the ratio of the drug in cerebrospinal fluid to serum is 0.52. Approximately 45% of memantine is bound to plasma proteins.
Biotransformation.
In humans, about 80% of memantine circulates as the parent compound, the main metabolites do not have NMDA antagonistic properties. Cytochrome P450 involvement in metabolism in vitro has not been demonstrated.
Elimination.
Memantine is eliminated monoexponentially with a t1/2 of 60 to 100 hours. In volunteers with normal renal function, the total clearance (Cltot) is 170 ml/min/1.73 m2. The renal phase of memantine pharmacokinetics also includes tubular reabsorption.
The rate of renal elimination of memantine in alkaline urine may be reduced by 7-9 times. Alkalinization of urine may occur as a result of profound changes in diet, such as changing from a meat-rich diet to a vegetarian diet or as a result of intensive use of antacids.
Linearity.
Pharmacokinetics are linear in the dose range of 10-40 mg.
Pharmacodynamic/pharmacokinetic relationship.
At a dose of 20 mg memantine per day, the level of content in the cerebrospinal fluid corresponds to the ki value (inhibition constant) of memantine, which is 0.5 μmol in the frontal cortex of the human brain.
Indication
Alzheimer's disease from mild to severe forms.
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any component of the drug.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions
Concomitant use of memantine and amantadine should be avoided due to the risk of pharmacotoxic psychosis. Both compounds are chemically related NMDA antagonists. The same may be true for ketamine and dextromethorphan. One published report also noted the possible risk of the combination of memantine and phenytoin.
The mechanism of action suggests that the effects of L-dopa, dopaminergic agonists and anticholinergics may be potentiated by concomitant use of NMDA antagonists such as memantine. The effects of barbiturates and neuroleptics may be attenuated. Concomitant administration of memantine and antispasmodics, dantrolene or baclofen may modify their effects and require dose adjustment.
Other drugs such as cimetidine, ranitidine, procainamide, quinidine, quinine and nicotine, which use the same renal cation transport system as amantadine, may also be able to interact with memantine, leading to a potential risk of increased plasma levels.
When memantine is co-administered with hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) or any combination with HCTZ, a decrease in serum HCTZ levels is possible.
There have been isolated reports of increased international normalized ratio (INR) with memantine in patients taking warfarin. Although a causal relationship has not been established, careful monitoring of prothrombin time or INR is necessary in patients taking concomitant oral anticoagulants.
In pharmacokinetic studies in healthy subjects, no significant interaction effects of memantine with glyburide/metformin, donepezil, or galantamine were observed.
Memantine is not an inhibitor of CYP 1A2, 2A6, 2C9, 2D6, 2E1, 3A, flavin-containing monooxygenase, epoxide hydrolase, or sulfation in vitro.
Application features
Concomitant use with N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) antagonists such as amantadine, ketamine or dextromethorphan should be avoided. These compounds act on the same receptor system as memantine and therefore side effects (mainly related to the central nervous system) may be more frequent or more pronounced.
Several factors that may increase urine pH may warrant close monitoring. These include major dietary changes, such as changing from a meat-rich diet to a vegetarian diet, or heavy use of antacids. In addition, urine pH may be elevated due to conditions such as renal tubular acidosis (RTA) or severe urinary tract infections caused by Proteus bacteria.
In most clinical trials, patients with recent myocardial infarction, decompensated congestive heart failure (New York Heart Association grades III-IV), and uncontrolled hypertension were excluded from the study. As a result, only limited data are available and patients with these conditions require close monitoring.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding
There are no data on the effects of memantine during pregnancy. Experimental studies in animals indicate the possibility of intrauterine growth retardation at exposure concentrations identical to or slightly higher than those used in humans. The potential risk for humans is unknown. Memantine should not be used during pregnancy unless clearly necessary.
It is not known whether memantine is excreted in breast milk, but it is possible given the lipophilicity of the substance. Women taking memantine should refrain from breastfeeding.
Ability to influence reaction speed when driving vehicles or other mechanisms
Moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease usually impairs the ability to drive and use machines. Furthermore, memantine has a minor to moderate effect on the reaction time, so outpatients should be warned to exercise caution when driving or operating machinery.
Method of administration and doses
Treatment should be initiated and continued under the supervision of a physician. Therapy should only be initiated in the presence of a caregiver who will monitor the patient's intake of the drug.
The tablets should be taken once a day at the same time each day. The tablets can be taken with or without food.
Adults.
The maximum daily dose is 20 mg. In order to reduce the risk of adverse reactions, the maintenance dose should be determined by gradually increasing the dosage by 5 mg per week during the first 3 weeks as follows:
Week 1 (day 1-7): take 5 mg per day for a week;
Week 2 (day 8-14): take 10 mg per day for a week;
Week 3 (days 15-21): take 15 mg per day for a week;
starting from week 4: take 20 mg per day every day.
The recommended maintenance dose is 20 mg per day.
The duration of treatment should be determined individually by a physician experienced in the diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer's disease. The tolerability and dosage of memantine should be assessed regularly, preferably within three months of starting treatment. Thereafter, the clinical effect of memantine and the patient's response to treatment should be assessed regularly in accordance with current clinical guidelines. Maintenance treatment may be continued as long as the therapeutic effect remains favourable and the patient's tolerance of memantine is good. Discontinuation of memantine should be considered if signs of therapeutic effect disappear or the patient's tolerance of treatment deteriorates.
Elderly patients.
The recommended dose for patients aged 65 years and over is 20 mg per day (2 tablets of 10 mg once a day), as indicated above.
Kidney dysfunction.
For patients with mild renal impairment (creatinine clearance 50-80 ml/min), no dose reduction is required. For patients with moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance 30-49 ml/min), the daily dose should be reduced to 10 mg. The dose may be increased to 20 mg per day according to the standard regimen if there are no adverse reactions after at least 7 days of treatment. For patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance 5-29 ml/min), the daily dose should be reduced to 10 mg.
Liver dysfunction.
No dose adjustment is required for patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment (Child Pugh A, B). The use of memantine in patients with severe hepatic impairment is not recommended.
Children
The drug should not be used in children due to insufficient data on safety and efficacy.
Overdose
Experience is limited.
Relatively large overdoses (200 mg and 105 mg per day for 3 days, respectively) were either associated with symptoms of fatigue, weakness and/or diarrhea, or were asymptomatic. Overdoses up to 140 mg or an unknown dose have been associated with symptoms of central nervous system disorders, such as confusion, lethargy, drowsiness, dizziness, agitation, aggression, hallucinations, gait disturbances and/or gastrointestinal disorders (vomiting and diarrhea).
After taking 2000 mg of memantine, the patient developed coma for 10 days, later - diplopia and agitation. After symptomatic treatment and plasmapheresis, the patient recovered without sequelae.
Treatment.
Symptomatic, no specific antidote exists. Standard clinical procedures should be used to remove the active substance from the body, such as gastric lavage, administration of activated charcoal, methods of acidifying the urine reaction, forced diuresis.
In case of excessive general stimulation of the central nervous system, symptomatic treatment measures should be used with caution.
Adverse reactions
Infections and infestations: fungal diseases.
Immune system disorders: hypersensitivity.
Psychiatric: drowsiness, confusion, hallucinations, psychotic reactions, depression, suicidal ideation, suicide.
From the nervous system: dizziness, balance disorders, gait disturbances, seizures.
Cardiac disorders: heart failure.
Vascular disorders: arterial hypertension, venous thrombosis/thromboembolism.
Respiratory system: shortness of breath.
From the digestive tract: constipation, vomiting, pancreatitis.
Liver and gallbladder: increased liver function tests, hepatitis.
General disorders: headache, fatigue.
Expiration date
3 years.
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Packaging
14 tablets in a blister, 1 blister in a cardboard box No. 14 or 10 cardboard boxes in a cardboard box No. 140 (14x10).
Vacation category
According to the recipe.
Producer
KUSUM HEALTHCARE PVT LTD
KUSUM HEALTHCARE PVT LTD.
Location of the manufacturer and address of its place of business
SP-289 (A), RIICO Industrial Area, Chopanki, Bhiwadi, Dist. Alwar (Rajasthan), India.
SP-289 (A), RIICO Industrial area, Chopanki, Bhiwadi, Dist. Alwar (Rajasthan), India.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.