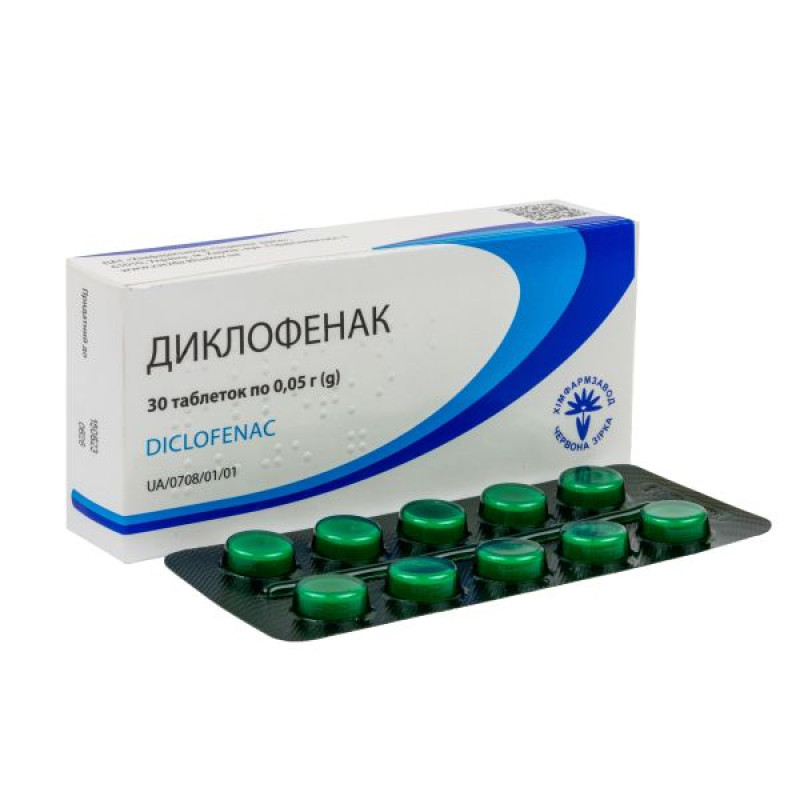
Diclofenac tablets 0.05 g blister No. 30

Instructions Diclofenac tablets 0.05 g blister No. 30
Composition
active ingredient: diclofenac;
1 tablet contains: diclofenac sodium (calculated as dry matter) 50 mg (0.05 g);
Excipients: microcrystalline cellulose, lactose monohydrate, potato starch, colloidal anhydrous silicon dioxide, calcium stearate.
Dosage form
Pills.
Main physicochemical properties: white tablets, with a score and a bevel.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory and antirheumatic drugs. Acetic acid derivatives and related compounds.
ATX code M01A B05.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics.
It has a pronounced anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and moderate antipyretic effect, the mechanism of action is associated with inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis. Inhibits platelet aggregation. Reduces pain at rest and during movement, morning stiffness, swelling of joints, improves their functional ability. In inflammatory processes that occur after operations and injuries, it quickly relieves both spontaneous pain and pain during movement.
Pharmacokinetics.
Diclofenac sodium is rapidly absorbed into the blood - the maximum concentration in the blood plasma is reached after 1-2 hours. The connection with blood plasma proteins is over 99%. It penetrates well into tissues and synovial fluid, where its concentration increases slowly, after 4 hours it reaches higher values than in the blood plasma. Food can slow down the rate of absorption, without affecting the completeness of absorption. Bioavailability is about 5%.
The half-life from blood plasma is 1-2 hours, from synovial fluid - 3-6 hours. About 35% is excreted in the form of metabolites with feces; about 65% is metabolized in the liver and excreted by the kidneys in the form of inactive derivatives, about 1% - in unchanged form.
Indication
Inflammatory and degenerative forms of rheumatic diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, osteoarthritis, spondyloarthritis);
pain syndromes in the spine;
rheumatic diseases of extra-articular soft tissues;
acute attacks of gout;
post-traumatic and postoperative pain syndromes accompanied by inflammation and swelling, for example, after dental and orthopedic interventions;
gynecological diseases accompanied by pain and inflammation, for example, primary dysmenorrhea or adnexitis;
as an adjuvant for severe inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs, which are accompanied by severe pain syndrome, for example, with pharyngotonsillitis, otitis.
According to general therapeutic principles, the underlying disease should be treated with basic therapy. Fever alone is not an indication for the use of the drug.
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any other component of the drug.
Acute stomach or intestinal ulcer; gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation.
History of gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation related to previous treatment with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Active ulcer/bleeding or history of recurrent ulcer/bleeding (two or more separate episodes of established ulceration or bleeding).
Inflammatory bowel disease (e.g., Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis).
Kidney failure.
Liver failure.
Severe heart failure (CH III-IV).
Congestive heart failure (NYHA II-IV).
Ischemic heart disease in patients with angina pectoris or previous myocardial infarction.
Cerebrovascular disease in patients who have had a stroke or have episodes of transient ischemic attacks.
Peripheral artery disease.
Treatment of postoperative pain in coronary artery bypass grafting (or the use of a cardiopulmonary bypass machine).
Diclofenac, like other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, is contraindicated in patients who develop attacks of bronchial asthma, angioedema, urticaria or acute rhinitis, nasal polyps and other allergic symptoms in response to the use of ibuprofen, acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs.
Hematopoiesis disorders.
Special safety measures.
When using Diclofenac, careful medical supervision is necessary for patients with complaints indicating gastrointestinal diseases or who have a history of gastric or intestinal ulcers; patients with ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease, as well as patients with impaired liver function.
With prolonged use of Diclofenac, as with other NSAIDs, systematic monitoring of peripheral blood counts is indicated.
Diclofenac, like other NSAIDs, may temporarily inhibit platelet aggregation. Therefore, careful monitoring of relevant laboratory parameters is necessary in patients with impaired hemostasis.
When taking Diclofenac, you should avoid drinking alcoholic beverages. If you are taking Diclofenac before surgery, you should inform your doctor or dentist.
It has been established that premature discontinuation of the drug may lead to a recurrence of painful phenomena.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions
The following interactions include those observed with diclofenac in the form of gastro-resistant tablets and/or other dosage forms of diclofenac.
Lithium: Diclofenac may increase plasma lithium concentrations when used concomitantly. Monitoring of serum lithium levels is recommended.
Digoxin: Diclofenac may increase the plasma concentration of digoxin when used concomitantly. Monitoring of serum digoxin levels is recommended.
Diuretics and antihypertensives: As with other NSAIDs, concomitant use of diclofenac with diuretics and antihypertensives (e.g. β-blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors) may lead to a reduction in their antihypertensive effect by inhibiting the synthesis of vasodilator prostaglandins. Therefore, such a combination should be used with caution and patients, especially the elderly, should be closely monitored for blood pressure. Patients should be adequately hydrated and monitoring of renal function is recommended after initiation of concomitant therapy and regularly thereafter, especially with diuretics and ACE inhibitors due to the increased risk of nephrotoxicity.
Drugs known to cause hyperkalemia: Concomitant treatment with potassium-sparing diuretics, cyclosporine, tacrolimus, or trimethoprim may be associated with increases in serum potassium, and patients should be monitored more frequently.
Anticoagulants and antithrombotic agents. Concomitant use may increase the risk of bleeding, therefore caution is advised. Although clinical studies do not indicate an effect of diclofenac on the activity of anticoagulants, there is some evidence of an increased risk of bleeding in patients receiving diclofenac and anticoagulants concomitantly. Therefore, close monitoring of such patients is recommended to ensure that no changes in the dosage of anticoagulants are necessary. As with other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, diclofenac in high doses may temporarily inhibit platelet aggregation.
Other NSAIDs, including selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors, and corticosteroids. Concomitant use of diclofenac and other NSAIDs or corticosteroids may increase the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding or ulceration. The concomitant use of two or more NSAIDs should be avoided.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs): Concomitant use of NSAIDs and SSRIs may increase the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
Antidiabetic drugs. Clinical studies have shown that diclofenac can be used together with oral antidiabetic drugs without changing their therapeutic effect. However, there are some reports of the development of both hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia in such cases, which necessitated the need to change the dose of antidiabetic drugs during the use of diclofenac. For this reason, as a precautionary measure, it is recommended to monitor blood glucose levels during combination therapy.
Methotrexate. Diclofenac may inhibit the renal tubular clearance of methotrexate, leading to increased methotrexate levels. Caution should be exercised when NSAIDs, including diclofenac, are administered less than 24 hours before methotrexate, as this may increase the blood concentration of methotrexate and increase its toxicity. Serious toxicity has been reported when methotrexate and NSAIDs, including diclofenac, were administered within 24 hours of each other. This interaction is mediated by accumulation of methotrexate as a result of impaired renal excretion in the presence of NSAIDs.
Cyclosporine. The effect of diclofenac, like other NSAIDs, on prostaglandin synthesis in the kidneys may enhance the nephrotoxicity of cyclosporine, and therefore it should be used in lower doses than in patients not taking cyclosporine.
Tacrolimus: There is a possible increased risk of nephrotoxicity when NSAIDs are used with tacrolimus, which may be mediated through the renal antiprostaglandin effects of the NSAID and the calcineurin inhibitor.
Quinolone antibacterials. Convulsions may occur in patients receiving concomitant quinolones and NSAIDs. This may occur in patients with or without a prior history of epilepsy or seizures. Therefore, caution should be exercised when considering the use of a quinolone in patients already receiving NSAIDs.
Phenytoin: When phenytoin is used concomitantly with diclofenac, monitoring of phenytoin plasma concentrations is recommended due to the expected increase in phenytoin exposure.
Cardiac glycosides. Concomitant use of cardiac glycosides and NSAIDs in patients may exacerbate heart failure, reduce glomerular filtration rate (GFR), and increase plasma glycoside levels.
Mifepristone: NSAIDs should not be used for 8-12 days after mifepristone administration, as NSAIDs may reduce the effect of mifepristone.
Potent CYP2C9 inhibitors: Caution is advised when co-administering diclofenac with potent CYP2C9 inhibitors (e.g. voriconazole), which may lead to a significant increase in maximum plasma concentrations and exposure to diclofenac due to inhibition of diclofenac metabolism.
Application features
General
To minimize adverse effects, treatment should be initiated at the lowest effective dose for the shortest period of time to control symptoms.
The concomitant use of diclofenac with systemic NSAIDs such as selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors should be avoided due to the lack of any evidence of a synergistic effect and due to potential additive side effects.
Caution is required in elderly patients. In particular, it is recommended to use the lowest effective dose in frail elderly patients or those with low body weight.
As with other NSAIDs, allergic reactions - including anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions - may occur, even without prior exposure to diclofenac.
Due to its pharmacodynamic properties, diclofenac, like other NSAIDs, may mask the signs and symptoms of infection.
Diclofenac contains lactose. Patients with rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, the Lapp lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption should not take diclofenac.
Effects on the digestive tract
Gastrointestinal bleeding (hemorrhage, melena), ulceration or perforation, which can be fatal, have been reported with all NSAIDs, including diclofenac, and may occur at any time during treatment with or without warning symptoms or a previous history of serious gastrointestinal events. These events are usually more severe in the elderly. If gastrointestinal bleeding or ulceration occurs in patients receiving diclofenac, the drug should be discontinued.
As with other NSAIDs, including diclofenac, patients presenting with symptoms suggestive of gastrointestinal (GI) disorders should be monitored closely and caution exercised. The risk of GI bleeding, ulceration or perforation increases with increasing dose of NSAIDs, including diclofenac.
Elderly people have an increased frequency of adverse reactions to NSAIDs, especially gastrointestinal bleeding and perforation, which can be fatal.
To reduce the risk of such gastrointestinal toxicity in patients, treatment should be initiated and maintained at the lowest effective dose. For such patients, as well as those requiring concomitant use of medicinal products containing low doses of acetylsalicylic acid (ASA/aspirin) or other medicinal products likely to increase the risk of gastrointestinal adverse effects, combination therapy with protective agents (e.g. proton pump inhibitors or misoprostol) should be considered. Patients with a history of gastrointestinal toxicity, particularly the elderly, should report any unusual abdominal symptoms (especially gastrointestinal bleeding). Caution is also warranted in patients receiving concomitant medicinal products that may increase the risk of ulceration or bleeding, such as systemic corticosteroids, anticoagulants (e.g. warfarin), antithrombotic agents (e.g. ASA) or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.
Effect on the liver
Close medical supervision is necessary if diclofenac is prescribed to patients with impaired liver function, as their condition may worsen. As with other NSAIDs, including diclofenac, the level of one or more liver enzymes may increase.
During long-term treatment with Diclofenac, regular monitoring of liver function and liver enzyme levels should be performed as a precautionary measure. If liver function abnormalities persist or worsen and if clinical signs or symptoms suggestive of progressive liver disease or if other manifestations (e.g. eosinophilia, rash) occur, Diclofenac should be discontinued. Diseases such as hepatitis may occur without prodromal symptoms. Caution is advised when diclofenac is used in patients with hepatic porphyria, as it may precipitate an attack.
Since cases of fluid retention and edema have been reported with NSAIDs, including diclofenac, special attention should be paid to patients with impaired cardiac or renal function, a history of hypertension, elderly patients, patients receiving concomitant therapy with diuretics or drugs that significantly affect renal function, and patients with a significant decrease in extracellular fluid volume for any reason, for example, before or after major surgery. In such cases, monitoring of renal function is recommended as a precautionary measure. Discontinuation of therapy usually leads to a return to the state that existed before treatment.
Effects on the skin
Serious skin reactions (some of which were fatal) have been reported very rarely in association with the use of NSAIDs, including diclofenac, including exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Patients appear to be at greatest risk of developing these reactions early in the course of therapy: the onset of the reaction occurs in most cases within the first month of treatment. Diclofenac should be discontinued at the first appearance of skin rash, mucosal lesions or any other sign of hypersensitivity.
SLE and mixed connective tissue diseases
Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and mixed connective tissue diseases may be at increased risk of developing aseptic meningitis.
Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular effects
For patients with a history of hypertension and/or mild to moderate congestive heart failure, appropriate monitoring and advice is necessary, as fluid retention and oedema have been reported in association with the use of NSAIDs, including diclofenac.
Clinical trial data and epidemiological data suggest that the use of diclofenac, especially at high doses (150 mg/day) and with long-term treatment, may be associated with a small increased risk of arterial thrombotic events (e.g. myocardial infarction or stroke).
Patients with uncontrolled hypertension, mild to moderate congestive heart failure, stable ischemic heart disease, peripheral arterial disease and/or cerebrovascular disease should only be treated with diclofenac after careful evaluation.
Diclofenac should be prescribed to patients with significant risk factors for cardiovascular events (e.g. hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, smoking) only after careful clinical evaluation. Since the cardiovascular risks of Diclofenac may increase with increasing dose and duration of treatment, it should be used for the shortest possible period and at the lowest effective dose. The patient's need for Diclofenac should be periodically reviewed for symptom relief and response to therapy. Use with caution in patients over 65 years of age.
Effect on hematological parameters
With prolonged use of this drug, as with other NSAIDs, monitoring of complete blood counts is recommended.
Diclofenac may temporarily inhibit platelet aggregation. Patients with impaired hemostasis, hemorrhagic diathesis or hematological disorders should be carefully monitored.
History of asthma
Patients with asthma, seasonal allergic rhinitis, swelling of the nasal mucosa (i.e. nasal polyps), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or chronic respiratory infections (especially associated with allergic rhinitis-like symptoms) are more likely to experience reactions to NSAIDs, such as exacerbation of asthma (so-called analgesic intolerance/analgesic asthma), angioedema or urticaria. Therefore, special precautions (emergency medical attention) are recommended for such patients. This also applies to patients with allergic reactions to other substances, such as rash, itching or urticaria.
Like other drugs that inhibit prostaglandin synthetase activity, diclofenac sodium and other NSAIDs can provoke the development of bronchospasm when used in patients suffering from bronchial asthma or in patients with a history of bronchial asthma.
Fertility in women
Diclofenac may impair female fertility and is not recommended in women attempting to conceive. In women who may have difficulty conceiving or who are undergoing investigation of infertility, discontinuation of Diclofenac should be considered.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding
During pregnancy, use is contraindicated. If it is necessary to prescribe the drug to a mother who is breastfeeding, the issue of stopping breastfeeding should be decided. Like other NSAIDs, diclofenac may adversely affect female fertility, therefore it is not recommended to prescribe the drug to women planning a pregnancy. In women who have problems with conception or are undergoing infertility studies, the advisability of canceling the drug diclofenac should be considered.
Ability to influence reaction speed when driving vehicles or other mechanisms
You should refrain from driving or performing potentially dangerous activities that require increased attention and speed of reaction, because visual disturbances, dizziness, vertigo, drowsiness, central nervous system disorders, lethargy or increased fatigue may occur while taking the drug.
Method of administration and doses
For oral use.
The drug should be used in the lowest effective doses for the shortest period of time, taking into account the treatment objectives of each individual patient.
Take the tablets during or after meals, without chewing, with water.
The dose of the drug and the duration of use are prescribed by the doctor depending on the nature and course of the disease, the patient's response to the drug, and the therapeutic effect.
Adults and children aged 14 and over.
The initial dose is usually 100-150 mg per day. With mild symptoms, as well as with long-term therapy, a dose of 75-100 mg/day is sufficient. The daily dose should be divided into 2-3 doses. With primary dysmenorrhea, the daily dose should be selected individually, usually it is 50-150 mg. The initial dose may be 50-100 mg, but if necessary, it can be increased over several menstrual cycles to the maximum, which is 200 mg per day. The drug should be started after the first pain symptoms appear and continued for several days, depending on the dynamics of symptom regression.
For children aged 14 to 18, the drug is used at a dose of 75 to 150 mg per day in two or three doses.
The recommended maximum daily dose of Diclofenac is 150 mg.
Elderly patients.
Although the pharmacokinetics of diclofenac are not altered to any clinically significant extent in the elderly, NSAIDs should be used with caution in patients who are generally more susceptible to adverse reactions. In particular, the lowest effective dose is recommended for debilitated elderly patients or patients with low body mass; patients should also be monitored for gastrointestinal bleeding during treatment with NSAIDs.
Children
This dosage form should not be prescribed to children under 14 years of age. The drug should be used in children over 14 years of age provided that the prescribed dosage can be achieved.
Overdose
Symptoms.
There is no typical clinical picture of diclofenac overdose. Overdose may cause symptoms such as headache, nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, gastrointestinal bleeding, diarrhea, dizziness, disorientation, agitation, coma, drowsiness, tinnitus, or convulsions. Acute renal failure and liver damage are possible in cases of severe intoxication.
Treatment.
Treatment of acute poisoning with NSAIDs, including diclofenac, consists of supportive and symptomatic therapy. This applies to the treatment of manifestations such as arterial hypotension, renal failure, convulsions, gastrointestinal disorders, respiratory depression. It is unlikely that such specific therapeutic measures as forced diuresis, dialysis or hemoperfusion will be effective in removing NSAIDs, including diclofenac, since the active substances of these drugs are largely bound to blood proteins and undergo intensive metabolism. Activated charcoal can be used after taking potentially toxic doses, and after taking potentially life-threatening doses - induction of vomiting, gastric lavage.
Adverse reactions
From the hematopoietic and lymphatic systems: thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, anemia, including hemolytic anemia and aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis.
Immune system disorders: hypersensitivity, fever, anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions (including hypotension and shock); angioedema (including facial edema).
Mental disorders: disorientation, depression, insomnia, irritability, nightmares, psychotic disorders.
Nervous system: headache, dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, paresthesia, memory impairment, convulsions, anxiety, tremor, aseptic meningitis, taste disorders, stroke, cerebral circulation disorders, confusion, hallucinations, sensory disturbances, general malaise.
From the organs of vision: visual disturbances, blurred vision, diplopia, optic neuritis.
From the side of the organs of hearing and labyrinth: vertigo, tinnitus, hearing disorders.
Cardiovascular system: general weakness, palpitations, shortness of breath, increased pulse rate, increased respiratory rate (RR), chest pain, heart failure, myocardial infarction, hypertension, hypotension, vasculitis.
From the digestive tract: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dyspepsia, heartburn, bloating, loss of appetite, taste disturbances, abdominal pain, flatulence, anorexia, gastritis, gastrointestinal bleeding (hemorrhage, melena, diarrhea with blood), stomach and intestinal ulcers, accompanied or not accompanied by bleeding or perforation (sometimes fatal, especially in the elderly), colitis (including hemorrhagic colitis and exacerbation of ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease), constipation, stomatitis (including ulcerative stomatitis), glossitis, esophageal dysfunction, diaphragmatic stenosis of the intestine, pancreatitis, gastric erosion, gastroenteropathy with malabsorption syndrome, maldigestion, polyserositis.
Hepatobiliary system: increased transaminase levels, hepatitis, jaundice, liver disorders, fulminant hepatitis, liver necrosis, liver failure.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: rash (punctate, maculopapular, papular), hyperemia, urticaria, blistering rash, eczema, erythema, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Lyell's syndrome (toxic epidermal necrolysis), exfoliative dermatitis, hair loss, photosensitivity reaction, purpura, including allergic, itching.
Renal and urinary disorders: acute renal failure, hematuria, proteinuria, nephrotic syndrome, interstitial nephritis, renal papillary necrosis.
General disorders and administration site conditions: edema.
Reproductive system and breast disorders: impotence.
Clinical trial data and epidemiological data suggest an increased risk of thrombotic complications (e.g. myocardial infarction or stroke) associated with the use of diclofenac, particularly at high therapeutic doses (150 mg per day) and with long-term use.
Expiration date
3 years.
Storage conditions
Store in original packaging at a temperature not exceeding 25 0C.
Keep out of reach of children.
Incompatibility.
Unknown.
Packaging
10 tablets in blisters.
10 tablets in a blister; 1 or 3 blisters in a cardboard pack.
Vacation category
According to the recipe.
Manufacturer/Applicant
PJSC "Chempharmaceutical Plant "Chervona Zirka".
Location of the manufacturer and its address of place of business/location of the applicant and/or representative of the applicant.
61010, Ukraine, Kharkiv, 1 Hordienkivska St.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.