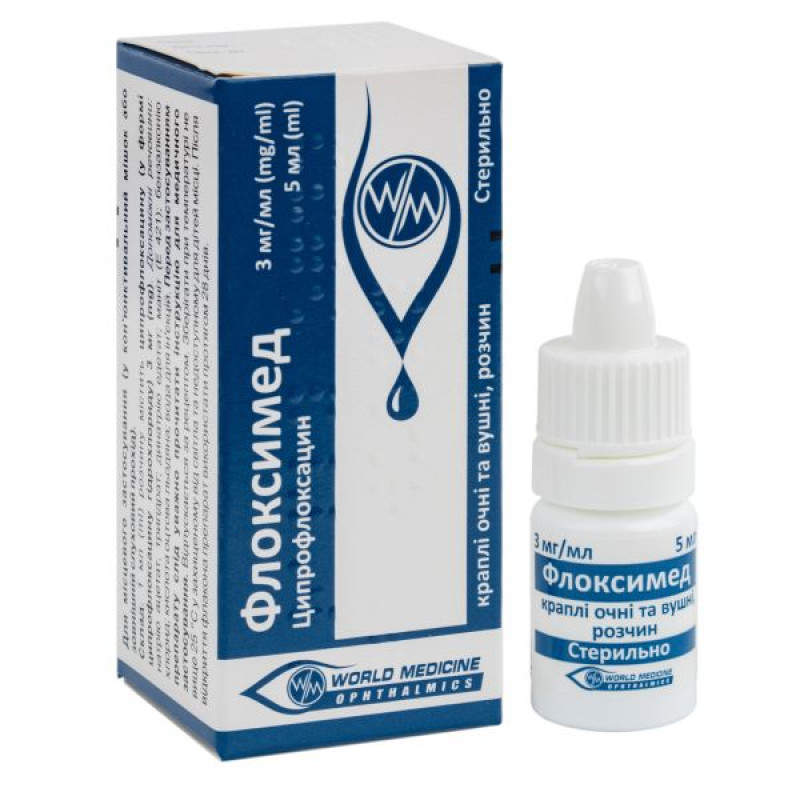
Floximed eye/ear drops 3 mg/ml dropper bottle 5 ml

Instructions for use: Floximed eye/ear drops 3 mg/ml, dropper bottle 5 ml
Composition
active ingredient: ciprofloxacin;
1 ml of solution contains ciprofloxacin (in the form of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride) 3 mg;
Excipients: sodium acetate trihydrate; disodium edetate; mannitol (E 421); benzalkonium chloride; glacial acetic acid; water for injections.
Dosage form
Eye and ear drops, solution.
Main physicochemical properties: transparent solution from colorless to greenish-yellow.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Means for use in ophthalmology and otology. Antimicrobial agents. ATX code S03A A07.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics.
Mechanism of action.
The drug contains ciprofloxacin from the quinolone class. The bactericidal effect of quinolones, which mainly affects the synthesis of bacterial DNA, is expressed by inhibiting DNA gyrase.
Ciprofloxacin has high in vitro activity against most gram-negative microorganisms, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa. It is also effective against aerobic gram-positive microorganisms, such as staphylococci and streptococci.
Sensitivity to microorganisms.
Application in ophthalmology.
Ciprofloxacin has been shown to be active against most strains of the following organisms in both in vitro studies and clinical use in ocular infections.
Aerobic gram-positive microorganisms: Staphylococcus aureus (including both methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant strains); Staphylococcus epidermidis; Staphylococcus spp., other coagulase-negative Staphylococcus spp., including S. haemolyticus and S. hominis; Corynebacterium spp.; Streptococcus pneumoniae; Viridans Group Streptococcus. |
Aerobic Gram-negative microorganisms: Acinetobacter spp.; Haemophilus influenzae; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Moraxella spp. (including M. catarrhalis). |
Application in otology.
Ciprofloxacin has high in vitro activity against most aerobic Gram-negative microorganisms, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa. It is also effective against aerobic Gram-positive microorganisms, such as staphylococci and streptococci. As shown in the table below, ciprofloxacin demonstrates a broad spectrum of in vivo activity (MIC90S ≤2 μg/ml) against pathogenic microorganisms isolated from patients with acute otitis externa in recent clinical studies.
| Type of bacteria | Isolates N= | IPCmin (μg/ml) | IPC50 (μg/ml) | IPC90 (μg/ml) | MICmax (μg/ml) |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 1089 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.25 | 16 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 221 | 0.13 | 0.50 | 1.0 | 128 |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | 257 | 0.06 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 128 |
| Staphylococcus caprae | 75 | 0.13 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 2.0 |
| Enterococcus faecalis | 53 | 0.50 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 |
| Enterobacter cloacae | 45 | 0.004 | 0.016 | 0.032 | 0.25 |
Ciprofloxacin is also active against pathogenic microorganisms isolated from patients with acute otitis media with the use of tympanostomy tubes.
| Type of bacteria | Isolates N= | IPCmin (μg/ml) | IPC50 (μg/ml) | IPC90 (μg/ml) | MICmax (μg/ml) |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae | 197 | 0.25 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 8.0 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 134 | 0.06 | 0.25 | 1.0 | >128 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 132 | 0.03 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 128 |
| Haemophilus influenzae | 122 | 0.004 | 0.008 | 0.016 | 0.25 |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | 103 | 0.06 | 1.0 | 64 | 64 |
| Moraxella catarrhalis | 37 | 0.008 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| Escherichia coli | 15 | 0.008 | 0.03 | 128 | >128 |
Limit values of diameters of zones of inhibition of growth of microorganisms.
Application in ophthalmology.
Ciprofloxacin has been shown to be active in vitro against most strains of the following microorganisms; however, the clinical significance of these findings in ophthalmic infections is unknown. The safety and efficacy of ciprofloxacin in the treatment of corneal ulcers or conjunctivitis caused by these microorganisms have not been established in adequate and well-controlled clinical trials.
The following bacteria are considered susceptible when assessed using systemic zone inhibition breakpoints. However, the relationship between systemic in vitro zone inhibition breakpoints and ophthalmic efficacy has not been established. Ciprofloxacin exhibits in vitro minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of 1 μg/mL or less (systemic zone inhibition breakpoints) against the majority (90%) of the following ocular pathogens.
Aerobic gram-positive microorganisms: Bacillus species. |
Aerobic Gram-negative microorganisms: Acinetobacter calcoaceticus; Enterobacter aerogenes; Escherichia coli; Haemophilus parainfluenzae; Klebsiella pneumoniae; Neisseria gonorrhoeae; Proteus mirabilis; Proteus vulgaris; Serratia marcescens. |
Others Peptococcus spp.; Propionibacterium acnes; Clostridium perfringens. |
Insensitive species
Some strains of Burkholderia cepacia and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia are resistant to ciprofloxacin, as are some anaerobic bacteria, especially Bacteroides fragilis.
Other information
The minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) does not typically exceed the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) by more than a factor of 2.
Application in otology.
Ciprofloxacin has been shown to be active in vitro against most strains of the following microorganisms; however, the clinical significance of these findings in ear infections is unknown. The safety and efficacy of ciprofloxacin in the treatment of acute otitis externa caused by these microorganisms have not been established in adequate and well-controlled clinical trials.
The following bacteria are considered susceptible when assessed using systemic zone inhibition breakpoints. However, the relationship between in vitro systemic zone inhibition breakpoints and otic efficacy has not been established. Ciprofloxacin exhibits in vitro minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of 1 μg/mL or less (systemic zone inhibition breakpoints) against most (90%) strains of the following pathogens.
Aerobic Gram-positive microorganisms Bacillus species; Corynebacterium species; Enterococcus faecalis; Staphylococcus aureus; Staphylococcus epidermidis; Staphylococcus caprae; Staphylococcus capitis; Staphylococcus haemolyticus; Streptococcus pneumoniae; Viridans Group Streptococcus. |
Aerobic gram-negative microorganisms Achromobacter xylosoxidans subsp. chylosoxidans; Acinetobacter baumanii; Acinetobacter junii; Acinetobacter Iwoffi; Acinetobacter radioresistant; genospecies of Acinetobacter 3; Citrobacter freundii; Citrobacter koseri; Enterobacter aerogenes; Enterobacter cloacae; Escherichia coli; Haemophilus influenzae; Klebsiella oxytoca; Klebsiella pneumoniae; Moraxella catarrhalis; Proteus mirabilis; Pseudomonas stutzeri; Serratia marcescens. |
Ciprofloxacin has also been shown to be active in vitro against most strains of the following microorganisms that cause otitis media:
Aerobic Gram-positive microorganisms Staphylococcus aureus; Staphylococcus epidermidis; Streptococcus pneumoniae. |
Aerobic Gram-negative microorganisms Escherichia coli; Haemophilus influenzae; Moraxella catarrhalis; Pseudomonas aeruginosa. |
Resistance to ciprofloxacin generally develops slowly. However, parallel resistance has been observed within this group of gyrase inhibitors.
Bacterial susceptibility testing has shown that most organisms resistant to ciprofloxacin are also resistant to other fluoroquinolones. The incidence of strains with acquired resistance to ciprofloxacin in clinical studies was low.
Due to its specific mode of action, there is no cross-resistance between ciprofloxacin and other antibacterial agents with different chemical structures, such as beta-lactam antibiotics, aminoglycosides, tetracyclines, macrolides and peptides, as well as sulfonamides, trimethoprim and nitrofuran derivatives. Thus, microorganisms resistant to these drugs may be sensitive to ciprofloxacin.
Preclinical safety data.
Ciprofloxacin and other quinolones cause arthropathy in young animals of most species tested after oral administration. At 30 mg/kg ciprofloxacin, there was minimal joint damage. This dose is 270 times the recommended clinical dose for the treatment of a 10 kg child in the ear with 0.27 mg ciprofloxacin in each ear twice daily. In a one-month study in young dogs (beagles) with topical application of ciprofloxacin eye drops, no joint damage was observed. There was also no evidence that topical application had any effect on the joints. In addition, in 634 children who received oral ciprofloxacin, no skeletal toxicity was observed in clinical and radiographic studies.
Reproduction studies conducted in rats and mice at doses 50 times the maximum human daily ophthalmic dose and 900 times the recommended otic dose (when treating a 10 kg child or a 50 kg adult with 0.27 mg or 0.36 mg ciprofloxacin respectively in each ear twice daily) revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to ciprofloxacin.
Ciprofloxacin was not teratogenic in rabbits when administered orally at doses of 30 and 100 mg/kg, although significant maternal toxicity was observed at both doses. No maternal toxicity, embryotoxicity or teratogenic effects were observed after intravenous administration of doses up to 20 mg/kg.
Pharmacokinetics.
Systemic absorption of ciprofloxacin after topical ocular administration is low. Plasma ciprofloxacin levels after seven days of topical administration ranged from unquantifiable (<1.25 ng/ml) to 4.7 ng/ml. The mean maximum plasma ciprofloxacin concentration obtained after topical ocular administration was approximately 450-fold lower than that observed after a single oral dose of ciprofloxacin, 250 mg.
In children with otorrhea with a tympanostomy tube or with a perforated eardrum, topical application of ciprofloxacin to the ear resulted in unquantifiable plasma ciprofloxacin concentrations at a detection limit of 5 ng/mL. In chinchillas, ciprofloxacin was distributed in plasma and middle ear fluid after intramuscular injection and absorbed into the inner ear after topical application to the middle ear.
The systemic pharmacokinetic properties of ciprofloxacin are well studied.
Ciprofloxacin is well distributed in body tissues, with tissue levels generally higher than plasma levels. The volume of distribution at steady state is 1.7–2.71 l/kg. Plasma protein binding is 16–43%. The plasma half-life of ciprofloxacin is 3–5 hours. After single oral doses ranging from 250 to 750 mg in adult patients with normal renal function, 15–50% of the dose is excreted in the urine as unchanged drug and 10–15% as metabolites within 24 hours. Both ciprofloxacin and its four primary metabolites are excreted in the urine and feces. The renal clearance of ciprofloxacin is generally 300–479 ml/min. Approximately 20–40% of the dose is excreted in the feces as unchanged drug and metabolites within 5 days.
Indication
Corneal ulcers and superficial infections of the eye(s) and its adnexa caused by strains of bacteria susceptible to ciprofloxacin.
Acute otitis externa, as well as acute otitis media with drainage through a tympanostomy tube, caused by strains of bacteria sensitive to ciprofloxacin.
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to ciprofloxacin, other quinolones, or to any of the excipients of the drug.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions
Interaction studies have not been conducted.
Since ciprofloxacin has low systemic concentrations when used topically in the ophthalmologic or otologic sense, interactions with other drugs are unlikely.
If several topical eye medications are used at the same time, wait at least 5 minutes between applications. Eye ointments should be applied last.
Application features
General.
The drug is intended for topical use (in the conjunctival sac or in the external auditory canal). It should not be injected or swallowed.
Serious and sometimes fatal (anaphylactic) hypersensitivity reactions have been reported in patients treated with quinolones, some after the first dose. Some reactions were accompanied by cardiovascular failure, loss of consciousness, tinnitus, swelling of the throat or face, dyspnea, urticaria, and pruritus. Only a few of these had a history of hypersensitivity reactions.
Serious cases of acute hypersensitivity to ciprofloxacin may require emergency treatment. Oxygen therapy and airway patency should be administered as clinically indicated.
The drug should be discontinued at the first sign of skin rash or any other sign of a hypersensitivity reaction.
As with all antibacterial agents, prolonged use of ciprofloxacin may result in overgrowth of non-susceptible bacterial strains or fungi. In the event of superinfection, appropriate therapy should be instituted.
Tendonitis and rupture have been reported with systemic fluoroquinolone therapy, including ciprofloxacin, particularly in the elderly and in patients receiving concomitant corticosteroids. Therefore, the drug should be discontinued at the first sign of tendonitis (see section 4.8).
For eye drops.
Clinical experience with the use of ciprofloxacin eye drops in children under 1 year of age, especially newborns, is quite limited.
The drug is not recommended for use in newborns with neonatal blenorrhea of gonococcal and chlamydial origin, as it has not been evaluated in this category of patients. Newborns with neonatal blenorrhea should receive treatment appropriate to their condition.
If clinically indicated, the patient should be examined using a slit lamp.
In patients with corneal ulcers, frequent use of ciprofloxacin has been associated with the development of a white precipitate in the eye (drug residue), which disappeared after continued use. The presence of the precipitate does not require discontinuation of the drug and does not adversely affect the clinical course of the healing process.
The medicine contains benzalkonium chloride, which may cause irritation and discolouration of soft contact lenses. It is not recommended to wear contact lenses during treatment of an eye infection. If you wear contact lenses, they should be removed and you should wait 15 minutes after instillation before putting them back in.
After instillation of eye drops, tight eyelid closure for 2 minutes or nasolacrimal occlusion for 2 minutes is recommended. This reduces systemic absorption of agents administered into the eye, which reduces the likelihood of systemic side effects.
For ear drops.
The efficacy and safety of ciprofloxacin drops in children under 1 year of age have not been evaluated.
When instilling the drug into the ear, frequent medical monitoring should be carried out to allow for timely implementation of other therapeutic measures.
The product contains benzalkonium chloride, which may cause skin irritation.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding
Pregnancy.
There are no adequate data from the use of topical ciprofloxacin in pregnant women. Animal studies do not indicate direct harmful effects with respect to reproductive toxicity. It is preferable to avoid the use of the drug during pregnancy.
Breast-feeding.
Ciprofloxacin has been detected in breast milk after oral administration. It is not known whether ciprofloxacin is excreted in breast milk after topical application to the eye or ear. The drug should be used with caution during breastfeeding.
Fertility.
No human studies have been conducted to evaluate the effect of topical ciprofloxacin on fertility. Oral administration to animals does not indicate a direct harmful effect on fertility.
Ability to influence reaction speed when driving vehicles or other mechanisms
Ciprofloxacin topical has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive or use machines. Temporary blurred vision or other visual disturbances may affect the ability to drive or use machines. If blurred vision occurs during instillation, the patient should wait until vision clears before driving or using machines.
There are no data on the effect of the drug on the ability to drive vehicles or other mechanisms.
Method of administration and doses
Application in ophthalmology.
Dosage.
Adolescents and adults, including elderly patients.
Corneal ulcers.
The medicine should be used at the following intervals, including at night:
on the 1st day, instill 2 drops into the conjunctival sac(s) of the affected eye(s) every 15 minutes for the first 6 hours, then 2 drops every 30 minutes for the first day;
on the 2nd day, instill 2 drops into the conjunctival sac(s) of the affected eye(s) every hour;
From day 3 to day 14, instill 2 drops into the conjunctival sac(s) of the affected eye(s) every 4 hours.
In case of corneal ulcer, treatment may last more than 14 days; the dosage regimen and duration of treatment are determined by the doctor.
Bacterial superficial infections of the eye and its adnexa.
The standard dose of the drug is 1–2 drops in the conjunctival sac(s) of the affected eye(s) 4 times a day.
For severe infections, the dose may be 1–2 drops every 2 hours for the first two days during the daytime.
As a rule, treatment lasts 7–14 days.
Children
The dosage for children over 1 year of age is the same as for adults.
A clinical study in newborns and children under 1 month of age found that ciprofloxacin is clinically and microbiologically effective for the treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis in this category of patients when administered 3 times a day for 4 days.
Patients with impaired liver and kidney function.
The use of ciprofloxacin eye drops in this category of patients has not been studied.
Method of application.
To prevent contamination of the dropper tip and solution, care must be taken not to touch the eyelids, surrounding areas, or other surfaces with the tip of the dropper bottle.
After instillation, tight eyelid closure or nasolacrimal occlusion is recommended. This reduces systemic absorption of drugs administered into the eye, which reduces the likelihood of systemic side effects.
If several topical eye medications are used at the same time, wait at least 5 minutes between applications. Eye ointments should be applied last.
Application in otology.
Dosage.
Adults, including elderly patients.
The medicine should be applied at a dose of 4 drops into the ear canal 2 times a day.
In general, the duration of treatment should not exceed 5–10 days. In some cases, treatment can be extended, but in this case it is recommended to check the sensitivity of the local flora.
In case of simultaneous treatment with other topical medications, an interval of 10–15 minutes should be observed between their application.
Children.
The drug should be used in a dose of 3 drops in the ear canal 2 times a day. The safety and efficacy of ciprofloxacin have been studied in children aged 1 to 12 years. The safety and efficacy of use in children under 1 year of age have not been established.
Patients with impaired liver and kidney function.
The use of ciprofloxacin ear drops in this category of patients has not been studied.
Method of application
The external auditory canal should be thoroughly cleaned. To prevent vestibular stimulation, it is recommended to administer a solution at room temperature or body temperature.
The patient should be in a supine position on the opposite side of the affected ear. It is advisable to stay in this position for 5–10 minutes. Also, after local cleaning, a moistened gauze or hygroscopic cotton swab can be inserted into the ear canal for 1–2 days, but it must be moistened to be saturated with the drug 2 times a day.
To prevent contamination of the dropper tip and solution, care must be taken not to touch the auricle or external ear canal, surrounding areas, or other surfaces with the tip of the dropper bottle.
Children.
Application in ophthalmology.
The medicine should be used in children from birth.
The safety and efficacy of ciprofloxacin eye drops were evaluated in 230 children aged 0 to 12 years. No serious adverse reactions associated with the use of the drug in this patient population were reported.
Application in otology.
The medicine should be used in children over 1 year of age.
The safety and efficacy of ciprofloxacin ear drops were evaluated in 193 children aged 1 to 12 years. No serious adverse reactions associated with the use of the drug in this patient population were reported.
Safety and effectiveness in children under 1 year of age have not been established.
Overdose
Symptoms.
Given the characteristics of this medicinal product, intended for topical use, no toxic effect is expected when used in ophthalmology/otology at recommended doses, as well as in the event of accidental ingestion of the contents of 1 vial.
Treatment.
In case of local overdose, the eye(s) should be rinsed with warm water. If necessary, symptomatic and supportive therapy should be administered.
Adverse reactions
In clinical trials, the most common adverse reactions were corneal deposits, ocular discomfort, dysgeusia when ciprofloxacin was applied to the eye, and otorrhea and ear itching when applied to the ear.
The following adverse reactions are classified as follows: very common (≥1/10), common (≥1/100 to <1/10), uncommon (≥1/1000 to <1/100), rare (≥1/10,000 to <1/1000), very rare (<1/10,000) or not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data). Within each grouping, adverse reactions are presented in order of decreasing seriousness. Adverse reactions have been reported in clinical trials and during post-marketing experience.
Side effects observed after the use of ciprofloxacin in the eye.
| Infections and infestations | Rarely – barley, rhinitis |
| On the part of the immune system | Rarely – hypersensitivity |
| From the nervous system | Often – dysgeusia Uncommon – headache Rarely – dizziness |
| From the organs of vision | Common: corneal deposits, ocular discomfort, ocular hyperemia Uncommon: keratopathy, corneal infiltrates, corneal discoloration, photophobia, decreased visual acuity, eyelid edema, blurred vision, eye pain, dry eye, eye swelling, eye itching, foreign body sensation in the eye, lacrimation increased, eye discharge, eyelid margin scaling, eyelid peeling, conjunctival edema, eyelid erythema Rare: ocular toxicity, punctate keratitis, keratitis, conjunctivitis, corneal dysfunction, corneal epithelial defect, diplopia, ocular hypoaesthesia, asthenopia, eye irritation, eye inflammation, conjunctival hyperaemia |
| From the side of the organs of hearing and labyrinth | Rarely – ear pain |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | Rarely – hypersecretion of the paranasal sinuses |
| From the digestive tract | Uncommon – nausea Rarely – diarrhea, abdominal pain |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | Rarely – dermatitis |
| Musculoskeletal system | unknown – tendon injury |
| General disorders | Rarely – drug intolerance |
| Laboratory studies | Rarely – abnormal laboratory test results |
Children.
The safety and efficacy of ciprofloxacin eye drops were evaluated in 230 children aged 0 to 12 years. No serious adverse reactions associated with the use of ciprofloxacin in this patient population were reported.
Side effects observed after using ciprofloxacin in the ear
| From the nervous system | Uncommon: tearfulness, headache |
| From the side of the organs of hearing and labyrinth | Uncommon: ear pain, ear congestion, otorrhea, ear itching Unknown – ringing in the ears |
| from the skin and subcutaneous tissues | Infrequently – dermatitis |
| General disorders | Uncommon – hyperthermia |
Children.
The safety and efficacy of ciprofloxacin ear drops were determined in 193 children aged 1 to 12 years. No serious adverse reactions associated with the use of ciprofloxacin in this patient population were reported.
Description of the listed adverse reactions.
Reactions such as (generalized) rash, toxic epidermolysis, exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and urticaria have occurred very rarely with topical application of fluoroquinolones.
In isolated cases, blurred vision, decreased visual acuity, and signs of drug residue have been observed when ciprofloxacin was applied to the eye.
In patients with corneal ulcers, frequent use of ciprofloxacin has been associated with the development of a white precipitate in the eye (drug residue), which disappeared after continued use. The presence of the precipitate does not require discontinuation of the drug and does not adversely affect the clinical course of the healing process.
Rarely, the components of the medicinal product may cause a hypersensitivity reaction when applied to the ear. However, as with any substance applied to the skin, there is always the possibility of an allergic reaction to any of the excipients of the medicinal product.
Serious and in some cases fatal (anaphylactic) hypersensitivity reactions, sometimes after the first dose, have been reported in patients receiving systemic quinolone therapy. Some reactions have been accompanied by cardiovascular collapse, loss of consciousness, tingling, swelling of the throat or face, dyspnea, urticaria, and pruritus.
Tendon ruptures of the shoulder, hand, Achilles tendon, or other tendons requiring surgical repair or resulting in long-term disability have been reported in patients receiving systemic fluoroquinolones. Studies and post-marketing experience with systemic fluoroquinolones suggest that the risk of such ruptures may be increased in patients receiving corticosteroids, particularly in the elderly, and in patients with high tendon loads, including the Achilles tendon. To date, clinical and post-marketing data have not demonstrated a clear association between topical ciprofloxacin and musculoskeletal and connective tissue adverse reactions.
Moderate to severe phototoxicity has been observed in patients receiving systemic quinolones. However, phototoxicity reactions to ciprofloxacin are uncommon.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions that occur after the marketing authorisation of a medicinal product is extremely important. This allows for continuous monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via the national reporting system.
Expiration date
3 years.
After opening the bottle, use the drug within 28 days.
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C in a place protected from light and out of the reach of children.
Packaging
5 ml in a dropper bottle; 1 dropper bottle in a cardboard box.
Vacation category
According to the recipe.
Producer
WORLD MEDICINE ILACH SAN. VE TIJ. A.Sh./WORLD MEDICINE ILAC SAN. VE TIC. AS
Location of the manufacturer and address of its place of business
15 Temmuz Mahallesi Cami Yolu Caddesi No:50 Gunesli Bagcilar/Istanbul, Turkey/15 Temmuz Mahallesi Cami Yolu Caddesi No:50 Gunesli Bagcilar/Istanbul, Turkey.
Applicant
WORLD MEDICINE LLC, Ukraine/WORLD MEDICINE, LLC, Ukraine.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.