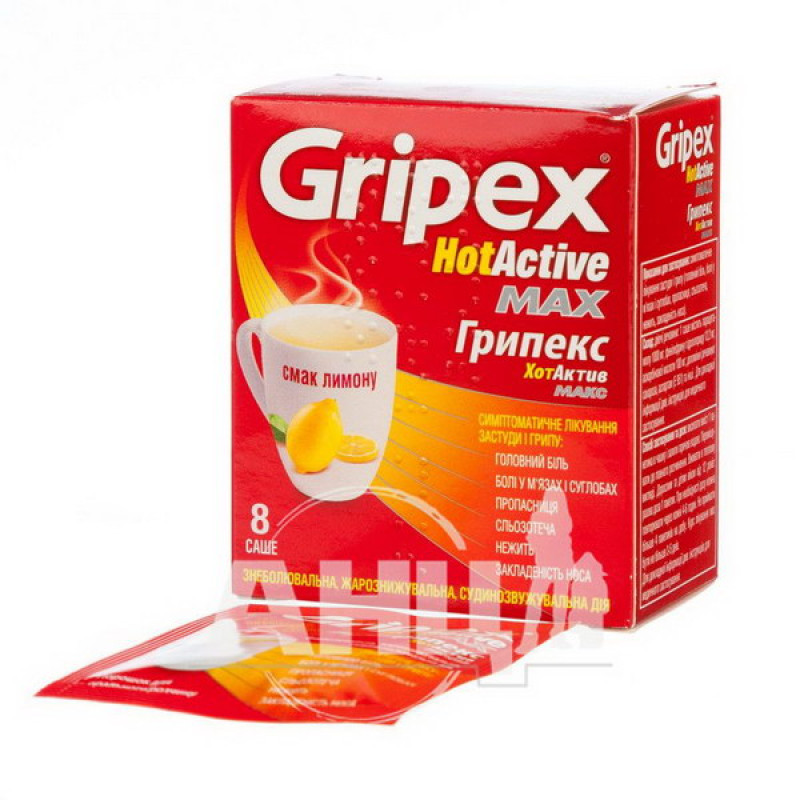
Gripex Hotaktiv Max powder for oral solution sachet 5 g No. 8

Pharmacological properties
The pharmacological effect of the drug is due to the action of all its components.
Paracetamol acts as an analgesic and antipyretic. The analgesic and antipyretic effect of paracetamol is associated with the drug's effect on the thermoregulation center in the hypothalamus and its ability to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis.
Paracetamol is rapidly absorbed in the digestive tract, binds to blood plasma proteins. T ½ is 1-4 hours. Metabolized in the liver with the formation of paracetamol glucuronide and sulfate. Excreted by the kidneys mainly in the form of conjugation products, less than 5% is excreted unchanged.
Phenylephrine hydrochloride stimulates postsynaptic α-adrenergic receptors. It constricts pulmonary vessels and increases pulmonary artery pressure. As a vasoconstrictor, it has an anticongestive effect: it reduces swelling and hyperemia of the nasal mucosa, the severity of exudative manifestations, and restores free breathing.
Phenylephrine hydrochloride has low bioavailability due to uneven absorption and the effect of monoamine oxidase in the gastrointestinal tract and liver during the first pass. It is excreted by the kidneys in the form of metabolites. Acidification of urine accelerates excretion from the body.
Caffeine is a central nervous system stimulant. It stimulates the respiratory center, which increases the rate and depth of oxygen saturation of the lungs, increases skeletal muscle tone, and lowers the threshold for hypercapnia. To obtain the same response from an analgesic without caffeine, a dose of approximately 40% higher than a single dose in combination with caffeine is required. Thus, caffeine is used as an adjuvant to paracetamol.
Caffeine, which is part of Gripex Start, Gripex Active and Gripex Active Max, and its water-soluble salts are rapidly absorbed in the intestines (including the colon). T ½ is about 5 hours, in some individuals - up to 10 hours. The main part is demethylated and oxidized. About 10% is excreted by the kidneys in unchanged form.
Chlorpheniramine maleate, which is part of Gripex Active, Gripex Active Max, is a blocker of H1-histamine receptors, which inhibits the reaction of smooth muscles to histamine. It has an antiallergic effect, reduces tearing, itching in the nose.
Chlorpheniramine maleate is a component that reduces the severity of the characteristic effects of histamine, which is especially important for the prevention and relief of many allergic symptoms. It is relatively slowly absorbed in the digestive tract, C max in blood plasma is achieved 2.5-6 hours after oral administration. Bioavailability is low and ranges from 25-50% of the dose taken. Chlorpheniramine maleate is metabolized during the first pass through the liver. The substance is extensively metabolized in the liver with the formation of metabolites desmethyl- and didesmethylchlorpheniramine. About 70% of it binds to blood proteins in plasma. Chlorpheniramine maleate is distributed in all organs and tissues, passes through the blood-brain barrier. The component in unchanged form and its metabolites are excreted mainly in the urine, excretion depends on the pH of the urine and the degree of excretion; only traces are found in the feces. The duration of action is 4-6 hours.
Ascorbic acid, which is part of Gripex Hotactiv, Gripex Hotactiv Max, is a vital vitamin that is added to the preparation to compensate for the loss of vitamin C that may occur at the beginning of a viral infection.
Ascorbic acid takes an active part in the redox reactions of the body. It stimulates tissue respiration, oxidative phosphorylation in the liver, activates proteolytic and microsomal enzymes, promotes the transition of folic acid to folinic acid. Ascorbic acid is required for the synthesis of steroid hormones and procollagen. It regulates the permeability of the vascular wall, blood clotting, promotes regeneration processes, as well as the formation of supporting tissues. Ascorbic acid helps activate the immune system, provides an increased need for vitamin C in influenza and colds, strengthens the body's defense mechanisms.
Dextromethorphan hydrobromide, which is part of Gripex Active Max, is a centrally acting antitussive. It suppresses the cough center by acting directly on it and increasing the threshold of the cough center to irritating agents. The pharmacokinetics of the combined drug depends on the pharmacokinetics of the active substances that make up its composition.
Dextromethorphan hydrobromide is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. It is metabolized in the liver and excreted in the urine in unchanged form and as demethylated metabolites, including dextrorphan, which suppresses cough. T ½ of dextromethorphan hydrobromide is 4 hours.
Indication
Gripex Active, Gripex Active Max. symptomatic treatment for symptoms of influenza and acute respiratory viral infections (hyperthermia, headache, runny nose) in adults and children over 12 years of age.
Gripex Hotactiv, Gripex Hotactiv Max. Symptomatic treatment for acute respiratory viral infections and flu (headache, muscle and joint pain, fever, tearing, rhinitis, nasal congestion).
Application
Adults and children aged 12 years and over:
Gripex Active, Gripex Active Max. The drug is intended for oral administration.
Gripex Hotactiv, Gripex Hotactiv Max. Pour the contents of 1 sachet into a cup and pour hot water. Stir until completely dissolved. Take warm.
A single dose of paracetamol is 10-15 mg/kg body weight, the maximum daily dose is 60 mg/kg. You should not take more than 4 doses within 24 hours.
Adults and children over 12 years old - 1 sachet. If necessary, the dose can be repeated every 4-6 hours. Do not take more than 4 sachets per day.
The interval between doses is at least 4 hours.
The course of treatment should not exceed 3-5 days. The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor. The maximum period of use for children without consulting a doctor is 3 days.
Do not exceed the recommended dose.
Do not take simultaneously with other medicines containing paracetamol.
Contraindication
Gripex Active and Gripex Active Max. The drug is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to any of its components.
Alcoholism, prostatic hyperplasia, severe forms of atherosclerosis, hypertension, acute pancreatitis and hepatitis, peripheral arterial thrombosis, decompensated heart failure, severe forms of coronary artery disease, cardiac conduction disorders, ventricular tachycardia, glaucoma, severe renal and hepatic dysfunction, bronchial asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, pheochromocytoma, hyperthyroidism, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, blood diseases, severe leukopenia, anemia, congenital hyperbilirubinemia, Dubin-Johnson syndrome, diabetes mellitus, increased intraocular pressure. Tendency to vasospasm, difficulty urinating, bladder neck obstruction. Stenosing gastric and duodenal ulcers, pyloroduodenal obstruction; epilepsy, increased excitability, sleep disorders, emphysema, acute myocardial infarction. Age 60 years. Concomitant use with tricyclic antidepressants, β-adrenergic blockers. Do not use with MAO inhibitors and within 2 weeks after discontinuation of MAO inhibitors.
Gripex Hotactiv, Gripex Hotactiv Max. Hypersensitivity to any of the components of the drug, congenital hyperbilirubinemia, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, severe liver or kidney dysfunction, acute hepatitis, severe hypertension, severe cardiovascular diseases, including conduction disorders, severe atherosclerosis, severe coronary artery disease, states of increased excitement, sleep disorders, epilepsy, blood diseases, Gilbert's syndrome, leukopenia, anemia, thrombosis, thrombophlebitis, hyperthyroidism, severe forms of diabetes mellitus, acute pancreatitis, alcoholism, glaucoma, prostatic hypertrophy with difficulty urinating, combined use with MAO inhibitors and within 2 weeks after discontinuation of MAO inhibitors, contraindicated in patients taking tricyclic antidepressants, β-adrenoceptor blockers or other antihypertensive drugs, drugs that suppress or increase appetite, and amphetamine-like psychostimulants, phenylketonuria. Age up to 12 years.
Side effects
In most cases, the drug is well tolerated. Side effects caused by the active components of the drug are observed less frequently, usually due to prolonged use of the drug in high doses.
Paracetamol.
Gastrointestinal tract: rarely - nausea, vomiting, decreased appetite, constipation, diarrhea or flatulence, epigastric discomfort. With prolonged use of the drug in high doses - pain in the epigastric region, hepatotoxic effect; hepatonecrosis (when used in high doses).
From the blood and lymphatic system: very rarely - hemolytic anemia, bruising or bleeding, methemoglobinemia (cyanosis, shortness of breath, heart pain), thrombocytopenia, in isolated cases - aplastic anemia, pancytopenia, sulfhemoglobinemia, neutropenia, agranulocytosis, leukopenia.
Respiratory system: bronchospasm in patients sensitive to acetylsalicylic acid and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
From the urinary system: renal colic, aseptic pyuria, interstitial glomerulonephritis, very rarely - nephrotoxic effect, papillary necrosis, urination disorders, dysuria.
On the part of the immune system: anaphylaxis, hypersensitivity reactions, including skin itching, rash on the skin and mucous membranes (usually generalized rash, erythematous, urticaria), angioedema, erythema multiforme exudative (including Stevens-Johnson syndrome), toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell's syndrome).
On the part of the hepatobiliary system: impaired liver function, increased activity of liver enzymes, usually without the development of jaundice.
Other: in rare cases - hypoglycemia, up to hypoglycemic coma, general weakness, increased sweating, visual impairment, dry eyes. Increased creatinine clearance, increased sodium and calcium excretion, nasal congestion, possibly a false increase in uric acid in the blood, determined by the Bittner method; slight increase in 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid, vanillylmandelic acid and catecholamines in the urine.
From the side of the central nervous system: rarely - headache, feeling of fear, general weakness, dizziness, in isolated cases - psychomotor agitation and disorientation, insomnia, anxiety, irritability or nervousness, tremor, confusion, depressive states, tingling and heaviness in the limbs, tinnitus, epileptic seizures, coma, anxiety, hallucinations, dyskinesia.
From the cardiovascular system: in rare cases - palpitations, tachycardia, arrhythmia, increased blood pressure (especially in patients with hypertension).
Gastrointestinal tract: rarely - nausea, vomiting, exacerbation of peptic ulcer disease.
Phenylephrine hydrochloride.
From the nervous system: rarely - headache, insomnia, dizziness, confusion.
From the cardiovascular system: in rare cases - tachycardia, reflex bradycardia, shortness of breath, heart pain, increased blood pressure (especially in patients with hypertension), arrhythmia.
Chlorpheniramine maleate.
Gastrointestinal tract: nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, dry mouth or throat.
On the part of the organ of vision: very rarely - mydriasis, accommodation disorders, increased intraocular pressure.
From the cardiovascular system: in rare cases - tachycardia.
From the side of the central nervous system: rarely - drowsiness, headache, tremor.
From the urinary system: very rarely - urinary retention and stranguria (difficulty urinating).
The excipient sunset yellow FCF (E110) may cause allergic reactions.
Special instructions
Gripex Active and Gripex Active Max. Before prescribing the drug, it is necessary to make sure that the main cause of the cough is determined and that reducing the intensity of the cough will not increase the risk of clinical or physiological complications. Use with caution in chronic cough resulting from smoking or pulmonary emphysema, when the cough is accompanied by excessive sputum secretion, in patients with congenital prolonged QT interval or in cases of long-term use of drugs that can prolong the QT interval.
It is necessary to consult a doctor about the possibility of using the drug in patients with impaired kidney and liver function. Before using the drug, it is necessary to consult a doctor if the patient uses warfarin or similar drugs that have an anticoagulant effect.
During treatment, alcohol consumption should be avoided, as it enhances the sedative effect of chlorpheniramine maleate and the hepatotoxicity of paracetamol.
It should be noted that patients with alcoholic liver disease are at increased risk of hepatotoxic effects of paracetamol; the drug may affect the results of laboratory tests for blood glucose and uric acid.
Patients with severe infections such as sepsis, accompanied by decreased glutathione levels, are at increased risk of metabolic acidosis when taking paracetamol. Symptoms of metabolic acidosis include deep, rapid or difficult breathing, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite. You should seek immediate medical attention if these symptoms occur.
Patients who take analgesics daily for mild arthritis should consult a doctor.
Do not exceed the indicated doses.
Do not take the drug with other medicines containing paracetamol.
If symptoms persist, you should consult a doctor.
If the headache becomes persistent, you should see a doctor.
Caffeine weakens the effect of sleeping pills and narcotics. During treatment, it is not recommended to drink excessive amounts of drinks containing caffeine (such as coffee, tea). This can lead to sleep problems, tremors, and an unpleasant feeling behind the sternum due to palpitations.
Phenylephrine may cause increased heart rate, dizziness, or palpitations; patients should be warned about this.
Use with caution in liver and kidney diseases, hypertension, and compensated heart failure.
The use of the drug may cause a positive analytical result in doping control.
Gripex Hotactiv, Gripex Hotactiv Max. It is necessary to consult a doctor about the possibility of using the drug in patients with impaired kidney and liver function.
The risk of overdose occurs in patients with non-cirrhotic alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol consumption should be avoided during treatment.
It should be noted that patients with alcoholic liver disease are at increased risk of hepatotoxic effects of paracetamol; the drug may affect the results of laboratory tests for blood glucose and uric acid.
Patients who take analgesics daily for mild arthritis should consult a doctor.
Before using the drug, it is necessary to consult a doctor if the patient is using warfarin or similar drugs with an anticoagulant effect.
Use of the drug in fasting individuals may pose a risk of liver damage.
Use with caution in elderly patients, with difficulty urinating, Raynaud's disease (which may manifest as pain in the fingers and toes in response to cold or stress). Do not exceed recommended doses. Phenylephrine, which is part of the drug, can cause angina attacks.
If, on the recommendation of a doctor, the drug is used for a long period, it is necessary to monitor the functional state of the liver and peripheral blood.
Do not use in patients with rare hereditary conditions of fructose intolerance, glucose-galactose malabsorption or sucrase-isomaltase insufficiency.
The drug contains aspartame, a derivative of phenylalanine, which is dangerous for patients with phenylketonuria.
Patients with severe infections such as sepsis, which are accompanied by a decrease in glutathione levels, are at increased risk of metabolic acidosis when taking paracetamol. Symptoms of metabolic acidosis include deep, rapid or difficult breathing, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite. You should seek immediate medical attention if these symptoms occur.
Do not exceed the indicated doses.
If the headache becomes persistent, you should see a doctor.
If the signs of the disease do not disappear within 3 days of treatment or, conversely, the state of health worsens, you should consult a doctor.
Interactions
The simultaneous use of the drug with other medicines containing paracetamol or other active substances that are part of the drug Gripex Active Max should be avoided.
The peculiarities of the drug interaction are due to the properties of its components.
The drug potentiates the effect of MAO inhibitors, sedatives and ethanol. In addition, MAO inhibitors and furazolidone, when used simultaneously with the drug, can cause an excited state, hypertensive crisis and hyperpyrexia (due to chlorpheniramine maleate). When taken simultaneously with antidepressants, antiparkinsonian drugs, neuroleptics, an atropine-like effect may occur (manifested by dry mouth, urinary retention, constipation).
The risk of glaucoma increases with the simultaneous use of Gripex with corticosteroids. Paracetamol, which is part of the drug, reduces the effectiveness of diuretics, and also increases the risk of hepatotoxic reactions when used simultaneously with barbiturates, DIPHENYL, carbamazepine, rifampicin and other inducers of liver enzymes, as well as anticonvulsants. The rate of absorption of paracetamol may increase with simultaneous use with metoclopramide and domperidone and decrease with simultaneous use with cholestyramine. Simultaneous use of paracetamol with azidothymidine may lead to the development of neutropenia. The anticoagulant effect of warfarin and other coumarins is enhanced with prolonged regular use of paracetamol. The risk of bleeding increases. Taking single doses does not have a significant effect. Simultaneous use of paracetamol with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs increases the risk of kidney complications. With the simultaneous use of paracetamol with hepatotoxic agents, the toxic effect of the drugs on the liver increases.
Barbiturates reduce the severity of the antipyretic effect of paracetamol. Anticonvulsants (including phenytoin, barbiturates, carbamazepine), which stimulate the activity of liver microsomal enzymes, can enhance the toxic effect of paracetamol on the liver due to an increase in the degree of conversion of the drug to hepatotoxic metabolites. Simultaneous use of paracetamol in high doses with isoniazid increases the risk of developing hepatotoxic syndrome.
One of the components of the drug - phenylephrine hydrochloride - has an adrenomimetic effect when used with tricyclic antidepressants; simultaneous use with haloman increases the risk of ventricular arrhythmia. Gripex reduces the hypotensive effect of guanethidine, which, in turn, enhances the α-adrenostimulating effect of phenylephrine hydrochloride. Phenylephrine can cause adverse reactions when combined with indomethacin and bromocriptine (severe hypertension). The use of phenylephrine hydrochloride with sympathomimetic amines, digoxin and cardiac glycosides increases the risk of arrhythmia and myocardial infarction. Rauwolfia alkaloids reduce the therapeutic effect of phenylephrine hydrochloride. β-blockers (phentolamine), phenothiazines, furosemide and other diuretics prevent vasoconstriction. Phenylephrine may reduce the effectiveness of β-blockers and antihypertensive drugs (reserpine, methyldopa, etc.) with an increased risk of hypertension and other adverse reactions from the cardiovascular system.
Chlorpheniramine enhances the anticholinergic effect of atropine, antispasmodics, tricyclic antidepressants, inhibitors, antiparkinsonian drugs. Chlorpheniramine enhances the effect of CNS depressants (tranquilizers, barbiturates), antiparkinsonian drugs.
Do not use simultaneously with alcohol. Chlorpheniramine, when used simultaneously with alcohol, enhances the effects of each other.
Maprotiline (a tetracyclic antidepressant) and other anticholinergic drugs may enhance the anticholinergic effects of these drugs or antihistamines such as chlorpheniramine.
Caffeine enhances the effect (improves bioavailability) of analgesics-antipyretics, potentiates the effects of xanthine derivatives, alpha- and beta-adrenomimetics, psychostimulants. Cimetidine, hormonal contraceptives, isoniazid enhance the effect of caffeine. Caffeine reduces the effect of opioid analgesics, anxiolytics, hypnotics and sedatives, is an antagonist of anesthetics and other drugs that depress the CNS, a competitive antagonist of adenosine drugs, ATP. With simultaneous use of caffeine with ergotamine, the absorption of ergotamine in the digestive tract improves, with thyroid-stimulating agents - the thyroid effect increases. Caffeine reduces the concentration of lithium in the blood.
Dextromethorphan hydrobromide. The use of dextromethorphan hydrobromide with enzyme inhibitors, including amiodarone, fluoxetine, haloperidol, paroxetine, propafenone, and thioridazine, may affect mental abilities. Ototoxic and photosensitizing drugs may increase side effects when used concomitantly.
Overdose
Signs and symptoms of overdose of individual components of the drug Gripex can be divided as follows:
Symptoms of paracetamol overdose. Overdose is usually caused by paracetamol and is manifested by pallor of the skin, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, hepatonecrosis, increased activity of hepatic transaminases and prothrombin index. In case of overdose, increased sweating, psychomotor agitation or depression of the central nervous system, drowsiness, impaired consciousness, heart rhythm disturbances, tachycardia, extrasystole, tremor, hyperreflexia, convulsions are possible. Liver damage may become apparent 12-48 hours after overdose. Glucose metabolism disorders and metabolic acidosis may occur. In severe poisoning, liver failure may progress and lead to the development of toxic encephalopathy with impaired consciousness, in some cases - with a fatal outcome. Acute renal failure with acute tubular necrosis may present with severe back pain, hematuria, and proteinuria and may occur even in the absence of severe liver damage. Arrhythmia and pancreatitis have also been reported. Liver damage may occur in adults who have ingested ≥10 g of paracetamol and in children who have ingested paracetamol at a dose of 150 mg/kg body weight. Ingestion of ≥5 g of paracetamol may result in liver damage in patients with risk factors (long-term treatment with carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone, rifampicin, St. John's wort or other drugs that induce liver enzymes, regular intake of excessive amounts of ethanol; glutathione cachexia, digestive disorders, cystic fibrosis, HIV infection, starvation, cachexia).
Symptoms of caffeine overdose. Caffeine in large doses can cause headache, epigastric pain, vomiting, diuresis, rapid breathing, extrasystole, tachycardia or arrhythmia, and affect the central nervous system (dizziness, insomnia, nervous excitement, irritability, affective state, anxiety, tremor, convulsions). Clinically significant symptoms of caffeine overdose are also associated with liver damage by paracetamol.
Symptoms of overdose associated with potentiation of the parasympatholytic action of the antihistamine component and the sympathomimetic action of phenylephrine. Drowsiness, after which a disturbance is possible (especially in children); visual impairment; nausea, vomiting, headache; circulatory disorders; comatose state; change in behavior; hypertension; bradycardia, atropine-like psychosis. Overdose due to the action of phenylephrine can cause increased sweating, psychomotor agitation or depression of the central nervous system, pallor, dizziness, insomnia, heart rhythm disturbances, tachycardia, extrasystole, tremor, hyperreflexia, irritability, anxiety. In severe cases, impaired consciousness, hallucinations, convulsions and arrhythmias may occur.
In case of an overdose of chlorpheniramine maleate, the state may vary from depressed to excited (restlessness and convulsions). In case of an overdose of chlorpheniramine maleate, atropine-like symptoms are possible, including mydriasis, photophobia, dryness of the skin and mucous membranes, increased body temperature, intestinal atony, central nervous system depression, which is accompanied by respiratory failure and impaired cardiovascular function.
Treatment. In case of overdose, immediate medical attention is required. The patient should be taken to a clinic immediately, even if there are no early symptoms of overdose. Symptoms may be limited to nausea and vomiting or may not reflect the severity of the overdose or the risk of organ damage. Treatment with activated charcoal should be considered if the overdose of paracetamol was taken within 1 h. The concentration of paracetamol in the blood plasma should be measured ≥4 h after ingestion (earlier concentrations are unreliable). Treatment with N-acetylcysteine can be used within 24 h of paracetamol ingestion, but the maximum protective effect occurs when it is used within 8 hours of ingestion. The effectiveness of the antidote decreases sharply after this time. If necessary, the patient should be given N-acetylcysteine intravenously, according to the established dose list. In the absence of vomiting, oral methionine can be used as a suitable alternative in remote areas outside the hospital. Naloxone is used to prevent the toxic effects of dextromethorphan on the central nervous system.
Storage conditions
Keep out of the reach of children at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.