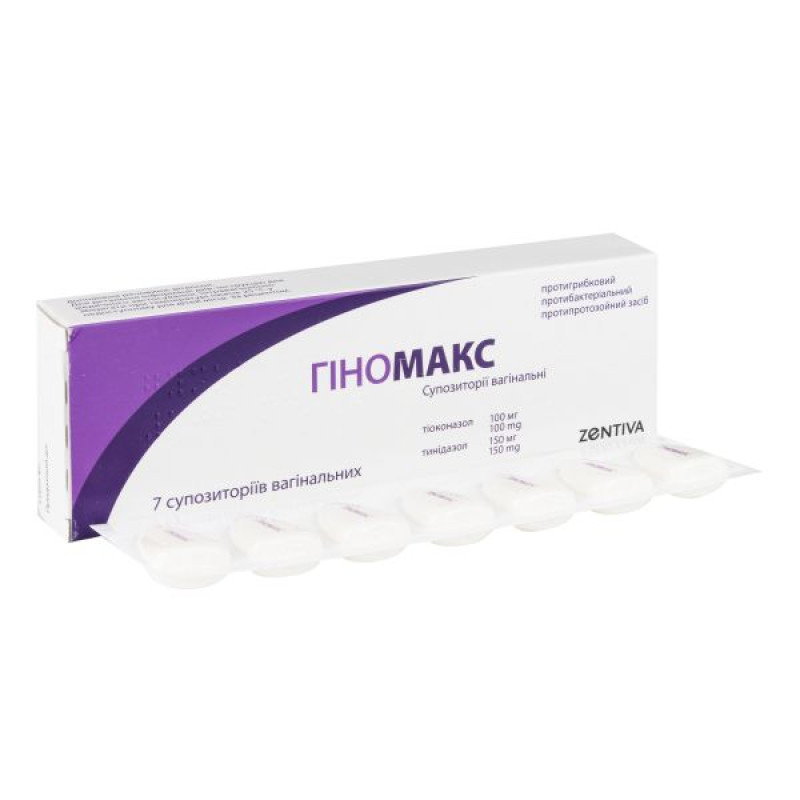
Gynomax vaginal suppositories 100 mg/150 mg No. 7
Instructions for use Gynomax vaginal suppositories 100 mg/150 mg No. 7
Composition
active ingredients: tioconazole and tinidazole;
1 vaginal suppository contains: tioconazole 100 mg and tinidazole 150 mg;
excipient: vitepsol.
Dosage form
Vaginal suppositories.
Main physicochemical properties: flat suppository from white to yellowish color with a smooth surface.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Antimicrobial and antiseptic agents used in gynecology, except combinations with corticosteroids. Combination of imidazole derivatives. ATX code G01A F20.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Tioconazole is a synthetic antifungal agent with high in vitro activity against yeast-like and other fungi (including dermatophytes). It is also effective against Trichomonas vaginalis, Gardnerella vaginalis, bacteria of the Bacteroides family, and some Gram-positive bacteria (including bacteria of the Staphylococcus and Streptococcus families). In clinical studies, tioconazole has been shown to be effective in the treatment of diseases caused by Candida Albicans and other Candida species (Torulopsis glabrata), and vaginal infections caused by Trichomonas vaginalis.
Tioconazole acts by altering the permeability of the fungal cell membrane. Ergosterol is an important component of the fungal cell membrane. Tioconazole inhibits ergosterol synthesis by interacting with 14α-demetalase, a cytochrome P450 enzyme that converts lanosterol to ergosterol. Inhibition of ergosterol synthesis leads to increased cell permeability and, consequently, to leakage of intracellular phosphorus and potassium compounds through the cell membrane.
Tinidazole is effective against most protozoa and anaerobic bacteria. Its antiprotozoal effect extends to Trichomonas vaginalis, Entamoeba histolytica and Giardia lamblia. Tinidazole is effective against Gardnerella vaginalis and most anaerobic bacteria (Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides melaninogenicus, bacteria of the Bacteroides family, bacteria of the Clostridium family, bacteria of the Eubacterium family, Peptostreptococcus and Veillonella).
The mechanism of action of tinidazole is not fully understood. Reduction of the nitro group occurs via the ferredoxin system and due to the low redox potential, which is released only by anaerobic bacteria. This may be the reason that the absorption of tinidazole is more active in anaerobes than in aerobes, although tinidazole penetrates the cell membranes of both types of microorganisms. The reduction process creates reactive intermediates and a diffusion gradient that enhances the uptake of tinidazole.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Tinidazole.
The absorption of tinidazole after intravaginal administration is approximately 10%.
The mean peak plasma concentration was 1.0 μg/ml; in 6 healthy volunteers, the time to reach this level (tmax) was 8.7 hours after administration of a vaginal suppository containing 500 mg tinidazole.
Tioconazole.
When administered intravaginally, tioconazole is absorbed in low concentrations by the mucosa. The mean peak plasma concentration after administration of a single dose of 300 mg tioconazole ointment to women with candidal vulvovaginitis was 18 μg/mL.
Distribution
Tinidazole.
Tinidazole is almost completely distributed in all tissues and body fluids, and also penetrates the blood-brain barrier. The known volume of distribution is about 50 liters. The binding of tinidazole to plasma proteins is 12%. Tinidazole penetrates the placental barrier and is excreted in breast milk.
Tioconazole.
In most clinical studies, after intravaginal administration of a single dose of 300 mg tioconazole, it was determined that its concentrations in vaginal fluid provide inhibition of the growth of Candida albicans for 2–3 days.
It is not known whether tioconazole is excreted in breast milk.
Biotransformation
Tinidazole.
Tinidazole is partially metabolized by oxidation, hydroxylation, and coagulation.
Tinidazole is biotransformed mainly by cytochrome CYP3A4.
Tioconazole.
The main metabolite of tioconazole is the glucuronide conjugate.
Tioconazole is not metabolized in vaginal fluid, but the portion of the drug that is absorbed systemically after intravaginal administration is metabolized. One reported metabolite is formed by N-glucuronidation of the nitrogen on the imidazole ring, the other is formed by O-dethienylation of the chlorothienyl group, hydration in alcohol, and glucuronidation.
Breeding
Tinidazole.
The half-life of tinidazole is about 12–14 hours. Tinidazole is excreted by the liver and kidneys. Tinidazole is mainly excreted unchanged in the urine (about 20–25% of the administered dose). Approximately 12% of the drug is excreted in the feces.
Tioconazole.
After intravaginal administration of the drug, tioconazole is eliminated from plasma, usually within 72 hours.
After oral administration of tioconazole, 25–27% of the dose is excreted in the urine as metabolites, and 59% of the dose is excreted in the feces (mainly unchanged).
Indication
Treatment of candidal vulvovaginitis caused by pathogens of the Candida albicans family, bacterial vaginosis caused by pathogens of the Gardnerella vaginalis family and anaerobic bacteria, trichomonas vaginitis caused by Trichomonas vaginalis, as well as vaginitis caused by mixed infection.
Contraindication
- Hypersensitivity to the active ingredients or their derivatives.
- Drinking alcoholic beverages during treatment or within 3 days after treatment.
- Taking disulfiram during treatment or within 2 weeks after treatment.
- Porphyria.
- Epilepsy.
- Severe liver dysfunction.
- First trimester of pregnancy.
- Breastfeeding period.
- Organic diseases of the nervous system.
- Violations of hematopoiesis, including a history.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions
Due to the absorption of tinidazole, the following interactions with other drugs are observed.
Acenocoumarol, anisindione, dicumarol, phenindione, phenprocoumon, warfarin: increased risk of bleeding.
Cholestyramine: reduced effectiveness of tinidazole.
Cimetidine: increased concentration of tinidazole in blood plasma.
Cyclosporine: increased cyclosporine levels.
Disulfiram: central nervous system side effects (e.g. psychotic reactions).
Fluorouracil: increased fluorouracil concentration in the blood and signs of possible intoxication (granulocytopenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, stomatitis, vomiting).
Fosphenytoin: increased toxicity of fosphenytoin and/or decreased blood concentrations of tinidazole.
Ketoconazole: increased concentration of tinidazole in the blood.
Lithium: increased blood lithium concentrations and signs of lithium intoxication (weakness, tremor, polydipsia, confusion).
Phenobarbital: decreased blood concentration of tinidazole.
Phenytoin: increased risk of phenytoin intoxication and/or decreased blood concentrations of tinidazole.
Rifampicin: decreased plasma concentrations of tinidazole.
Tacrolimus: increased tacrolimus levels.
CYP3A4 inducers/inhibitors: reduced efficacy of tinidazole or increased risk of adverse reactions (CYP3A4 inhibitors such as cimetidine and ketoconazole may prolong the half-life, as well as reduce the blood clearance of tinidazole and increase the plasma concentration of tinidazole).
Oxycodone: Concomitant administration of tinidazole and oxycodone may increase the plasma concentration of oxycodone and reduce the clearance of this substance.
Application features
For intravaginal use only. Do not swallow or insert into other areas.
Like other drugs with a similar structure, tinidazole should not be used in patients with impaired hematopoiesis, including a history of it. Transient leukopenia and neutropenia may develop.
Patients should refrain from drinking alcohol during treatment and for at least 3 days after the end of treatment due to the increased risk of disulfiram-like reactions.
Should not be used in girls who have not had sexual intercourse.
It is not recommended to use GYNOMAX during menstruation due to decreased effectiveness and difficulties in use.
Suppositories should not be used with contraceptives such as diaphragms and condoms, as the suppository base may interact with rubber in an undesirable way.
Other intravaginal products (e.g. tampons, douches or spermicides) should not be used concurrently with treatment.
When treating patients with trichomonas vaginitis, simultaneous treatment of the sexual partner is necessary.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Since the effects of the active ingredients of GYNOMAX on the fetus and newborn are unknown, women using this drug should avoid pregnancy by using effective methods of contraception.
Tinidazole crosses the placental barrier.
Animal studies are insufficient to assess the effects of the drug on pregnancy, embryonic/intrauterine development, parturition, and postnatal development. The potential risk to humans is unknown.
The drug is contraindicated in the first trimester of pregnancy. The possibility of prescribing the drug during the second and third trimesters should be assessed by a doctor, taking into account the benefit/risk ratio. The drug should not be used during pregnancy unless clearly necessary.
Breastfeeding should be discontinued during treatment, as tinidazole passes into breast milk. Breastfeeding can be resumed 72 hours after the end of treatment.
It is not known whether tioconazole passes into breast milk. Breastfeeding should be discontinued because most drugs pass into breast milk.
In a 60-day reproductive toxicity study, tinidazole at a dose of 600 mg/kg/day reduced fertility and promoted the development of histopathological changes in the testes of male animals. Doses of 300 and 600 mg/kg/day caused spermatogenic effects. The maximum dose of the drug that did not lead to the development of observable undesirable effects in the testes and sperm was 100 mg/kg/day. These effects are characteristic of the 5-nitroimidazole class of drugs.
No effect on fertility was observed in male animals when tioconazole was administered orally at doses up to 150 mg/kg/day. However, there is evidence of preimplantation loss in female rats at oral doses above 35 mg/kg/day.
The ability to influence the reaction speed when driving vehicles or other mechanisms.
It is not known whether GINOMAX affects the ability to drive and use other mechanisms.
Method of administration and doses
For intravaginal use only. GYNOMAX should be inserted deep into the vagina in the supine position.
Administer 1 suppository at night before bedtime for 7 days. Alternative regimen: administer 1 suppository twice daily for 3 days.
Do not swallow or inject into other areas.
Additional information about special population groups:
Renal/hepatic failure
No significant changes in the pharmacokinetic parameters of tinidazole were observed in patients with severe renal impairment (CrCL < 22 mL/min). Therefore, dose adjustment is not required in patients with this condition.
Tinidazole clearance is significantly increased during hemodialysis, and the half-life is reduced from 12 hours to 4.9 hours. 43% of available tinidazole was removed during a 6-hour dialysis session. If tinidazole is to be used prior to hemodialysis, it is recommended that half the recommended dose of tinidazole be administered after hemodialysis. There are no data on the pharmacokinetics of tinidazole in patients with hepatic impairment. Caution should be exercised when prescribing the recommended dose of tinidazole to patients with hepatic impairment.
Elderly people
People over 65 years of age are prescribed the same dose as adults.
Children
Do not use on children.
Overdose
Systemic side effects may occur with large amounts of the drug, but life-threatening side effects are not expected with intravaginal use.
There is no specific antidote for tinidazole. In case of overdose, symptomatic and supportive treatment should be initiated. Gastric emptying may be considered.
Since the systemic absorption rate of tioconazole is very low, overdose is not possible with topical application.
Side/adverse effects of overdose are unknown.
Adverse reactions
The frequency of the following undesirable effects is defined according to the following classification: very common (> 1/10); common (> 1/100 - < 1/10); uncommon (> 1/1000 to < 1/100), rare (> 1/10000 to < 1/1000); very rare (< 1/10000), unknown (cannot be estimated from the available data).
No adverse effects have been reported with vaginal administration of GYNOMAX. Some of the adverse effects that may occur with systemic administration of tinidazole are listed below. Since blood concentrations of tinidazole are much lower with intravaginal administration, the effects are expected to be less severe.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders
Not known: leukopenia (transient phenomenon), neutropenia.
On the part of the immune system
Not known: allergic reactions.
From the nervous system
Common: weakness, fatigue, malaise, headache, dizziness.
Not known: ataxia, coma (rare), confusion (rare), depression (rare), drowsiness, insomnia, sleep disorders, vertigo, peripheral neuropathy, seizures, overexcitation, disorientation.
From the digestive system
Common: metallic/bitter taste in the mouth, nausea, anorexia, loss of appetite, flatulence, dyspepsia, abdominal cramps, epigastric discomfort, vomiting, constipation.
Not known: stomach pain, diarrhea, coated tongue, stomatitis, tongue discoloration, dry oral mucosa, pseudomembranous colitis.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Not known: pruritus, urticaria, angioedema, skin rash.
Renal and urinary disorders
Common: dark urine.
General disorders and administration site conditions
Not known: burning during urination and at the injection site, local swelling and irritation, itching, vaginal discharge, dyspareunia, nocturia, vaginal pain.
In case of undesirable manifestations, adverse reactions or in case of lack of therapeutic effect, it is necessary to report to the address ZENTIVA UKRAINE LLC, 02002, Kyiv, Brovarskyi Avenue, 5 "I", tel./fax: +38 044 517-75-00, e-mail address PV-Ukraine@zentiva.com
Expiration date
3 years.
Storage conditions
Store below 25°C out of the reach of children.
Packaging
7 vaginal suppositories in strips in a cardboard package with labeling in Ukrainian.
Vacation category
According to the recipe.
Producer.
Exceltis Ilac Sanai ve Tijaret Anonim Shirketi.
Location of the manufacturer and its business address.
Çerkezkoy Organiz Sanayi Belgese, Gaziosmanpaşa Mah. Fati Boulevard No. 19/2, Çerkezkoy, 59500 Tekirdag, Turkey.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.