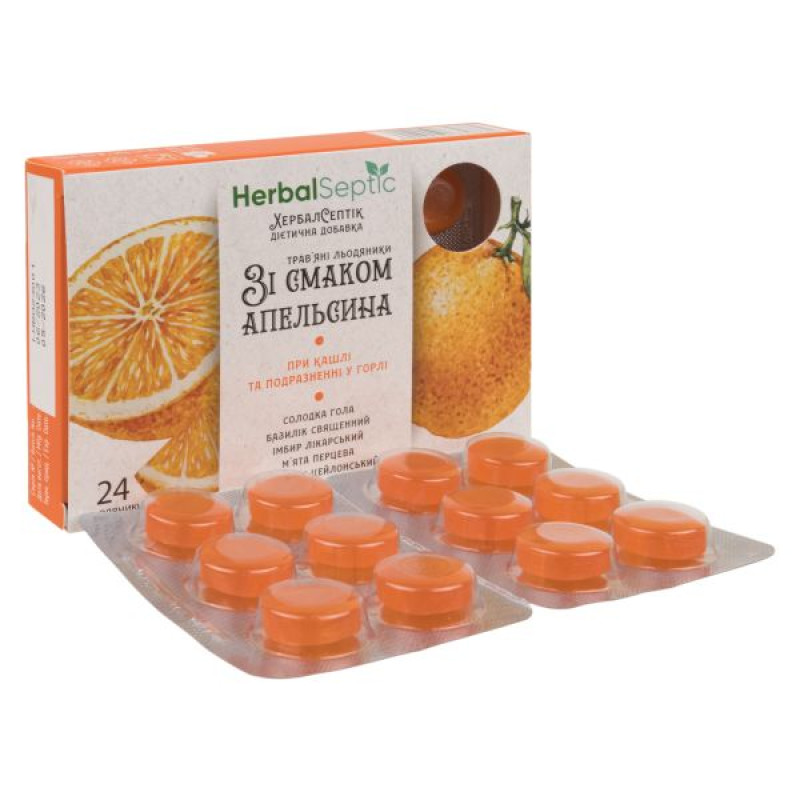
HerbalSeptic orange-flavored lollipops No. 24

Instructions for HerbalSeptic orange-flavored lollipops No. 24
Composition
One lollipop with a net weight of 2.5 g (g) (± 5%) contains extracts of:
- Licorice ( Glycyrrhiza glabra ) 10 mg (mg),
- Holy basil ( Ocimum sanctum ) 5 mg,
- Ginger ( Zingiber officinale ) 5 mg,
- Peppermint ( Mentha piperita ) 5 mg (mg),
- Ceylon cinnamon ( Cinnamomum zeylanicum ) 2 mg (mg).
Excipients: sugar, liquid glucose, orange flavoring, orange red C dye (mixture of dyes: sunset yellow E 110 and carmoisine E 122).
Nutritional value per 100 g (g): proteins 0.35 g (g), fats 0.65 g (g), carbohydrates 98.92 g (g).
Energy value (calories) per 100 g (g): 380 kcal (kcal) (1590 kJ (kJ)).
Release form
Orange-flavored lollipops.
Recommendations for use
It is recommended to use as an additional source of biologically active components during seasonal colds, coughs, irritation of the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract, coughs in smokers, and increased load on the vocal cords.
It is not a medicine.
Method of administration and dosage
Children over 6 years of age and adults should take 1 lollipop every 2 hours, but no more than 6 lollipops per day. The course of use is 4-5 days. The lollipops slowly dissolve in the mouth.
You should consult a doctor before use.
Should not be used as a substitute for a complete diet.
Do not exceed the indicated recommended dose for daily consumption.
Reservation
Pregnant and lactating women as prescribed by a doctor.
Contraindication
Individual sensitivity to product components; children under 6 years of age.
Storage conditions
Store in the original packaging in a dry place, protected from light and out of reach of children, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Packaging
12 lollipops in a blister; 2 blisters in a cardboard box.
Expiration date
3 years from date of manufacture. The batch number and the "Use by" date are indicated on the packaging. Do not use after the expiry date.
GMO-free.
Producer
Lozen Pharma Pvt Ltd, Raghav Estate, KSSIDS Industrial Estate, Shiggaon Road, Savanur – 581118, India.
Distributor / Importer / Claims Accepting Organization: Konark Intelmed LLC,
Ukraine, 61033, Kharkiv, Shevchenko St., 315, tel.: +38 (057) 714-38-02, 714-38-03.
Useful information about Ayurvedic plants
Licorice ( Glycyrrhiza glabra ). It can have expectorant, enveloping, diuretic, anti-inflammatory, antihistamine effects, participates in the regulation of water-salt metabolism in the body, can be used for cough, bronchitis, bronchial asthma and other inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract. Licorice root contains many active substances, such as: Glycyrrhizic acid: helps relieve inflammation, stimulate the activity of the adrenal glands. It can inhibit the biosynthesis of cholesterol, react with it and form an insoluble complex. Flavonoids: help relieve smooth muscle tension, inflammation, normalize the level of permeability of the walls of blood vessels. Saponins: help enhance the secretory function of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract and gastrointestinal tract, gently envelop, help protect against irritation, thin phlegm and facilitate coughing. May have anti-inflammatory and disinfectant effects.
Holy Basil ( Ocimum sanctum ). Basil has been used as a primary herb in Ayurveda for thousands of years. It is often used for colds, headaches, stomach ailments, and various types of poisoning. Studies show that basil contains a high amount of eugenol (1-hydroxy-2-methoxy-4-allyl-benzyl), which may give basil its analgesic properties. It also helps lower cholesterol levels and has a beneficial effect on blood glucose levels due to its antioxidant properties.
Peppermint ( Mentha piperita ). Peppermint leaves contain essential oil, which includes menthol, pinenes, limonene, phellandrene, cineole and other terpenoids, as well as flavonoids, ursolic and oleanolic acid, betaine, carotene, hesperidin, tannins, organic acids, trace elements. Peppermint is a component of many products with a different spectrum of action. Peppermint leaves can be taken in the form of infusions for insomnia, hysteria and neuralgia; they help stimulate cardiac activity, improve blood circulation and can be used for atherosclerosis. Mint is actively used for diseases of the upper respiratory tract, gastrointestinal tract: gastritis, colitis, flatulence, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting and constipation. It also helps to suppress the vital activity of a number of spore-forming bacteria and Staphylococcus aureus.
Ceylon cinnamon ( Cinnamomum zeylanicum ). Ceylon cinnamon oil contains eugenol (up to 10%), beta-caryophyllene, cinnamaldehyde, linalool, methylhavicol, phellandrene, and also contains a special substance - cinnamic acid aldehyde. The effect of cinnamon on the body is based on the fact that the oil irritates the skin and mucous membranes, helps to increase blood circulation and increase body temperature. Scientists have established the fact that cinnamon ether destroys pathogenic fungi of the genus Candida. It can be used for weight loss, normalization of metabolic processes and burning of excess subcutaneous fat, helps to normalize intestinal function and can be used for fermentation, gas formation and bloating.
According to the materials:
- Maznev N. I. Golden book of medicinal plants / N. I. Maznev. – 15th ed., add. - M.: LLC "ID RIPOL Klassik", LLC Izdatelstvo "DOM. XXI century", 2008. 621 p. (Maznev N. I. The Golden Book of Medicinal Plants / N. I. Maznev. – 15th ed., supplement. - M.: LLC "ID RIPOL Classic", LLC "DOM. XXI century", 2008. 621 p.)
- Maznev N. I. Travnyk / N. I. Maznev. - M.: LLC "Gamma Press 2000", 2001. - 512 p. with ill. (Maznev N. I. Travnik / N. I. Maznev. - M.: LLC "Gamma Press 2000", 2001. - 512 pp. with illustrations)
- Tovstukha E. S. Phytotherapy / E. S. Tovstukha. – K.: Zdorovya, 1990. – 304 p., ill., 6.55 sheets ill.
- Chuhno T. Big encyclopedia of medicinal plants / T. Chuhno. - M.: Eksmo, 2007. - 1024 p. (T. Chuhno. Big encyclopedia of medicinal plants / T. Chuhno. - Moscow: Eksmo, 2007. - 1024 p.)
- Botanical Pathways article with clinical trials details Indian J Exp Biol. 1999 Mar; 37 (3): 248-52. (Botanical Pathways article with clinical trials details Indian J Exp Biol. 1999 Mar; 37 (3): 248-52.)
- Prakash P, Gupta N. Therapeutic uses of Ocimum sanctum Linn (Tulsi) with a note on eugenol and its pharmacological actions: a short review. Effect of Ocimum sanctum Leaf Powder on Blood Lipoproteins, Glycated Proteins and Total Amino Acids in Patients with Non-insulin-dependent Diabetes Mellitus. Journal of Nutritional & Environmental Medicine. V. RAI MSC, UV MANI MSC PHD FICN AND UM IYER MSC PHD. Volume 7, Number 2 / June 1, 1997. p. 113–118. (Prakash P, Gupta N. Therapeutic uses of Ocinum sanctum Linn (Tulsi) with a note on eugenol and its pharmacological actions: a brief review. Effect of Ocinum sanctum leaf powder on blood lipoproteins, glycated proteins and total amino acids in patients with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Journal of Nutrition and Environmental Medicine. V. RAI EMS, Y. V. MANI EMS PCHD EFCI AND Y. M. AYIAR EMS PCHD. Vol. 7, No. 2 / 1 June 1997, pp. 113-118.)
- Evaluation of Hypoglycemic and Antioxidant Effect of Ocimum Sanctum, Jyoti Sethi, Sushma Sood, Shashi Seth, and Anjana Talwar. Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry, 2004, 19 (2) 152–155.
- Muravyova D. A. Tropical and subtropical medicinal plants. – M. Medicine, 1983. – 336 p.
- Dudchenko L. G. Kozyakov A. S. Kryvenko V. V. Spicy-aromatic and spicy-flavoring plants: Handbook / Editor-in-chief K. M. Sytnyk. – K. Naukova Dumka, 1989. – 304 p.
The information is provided for informational purposes only and should not be used for self-treatment.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.