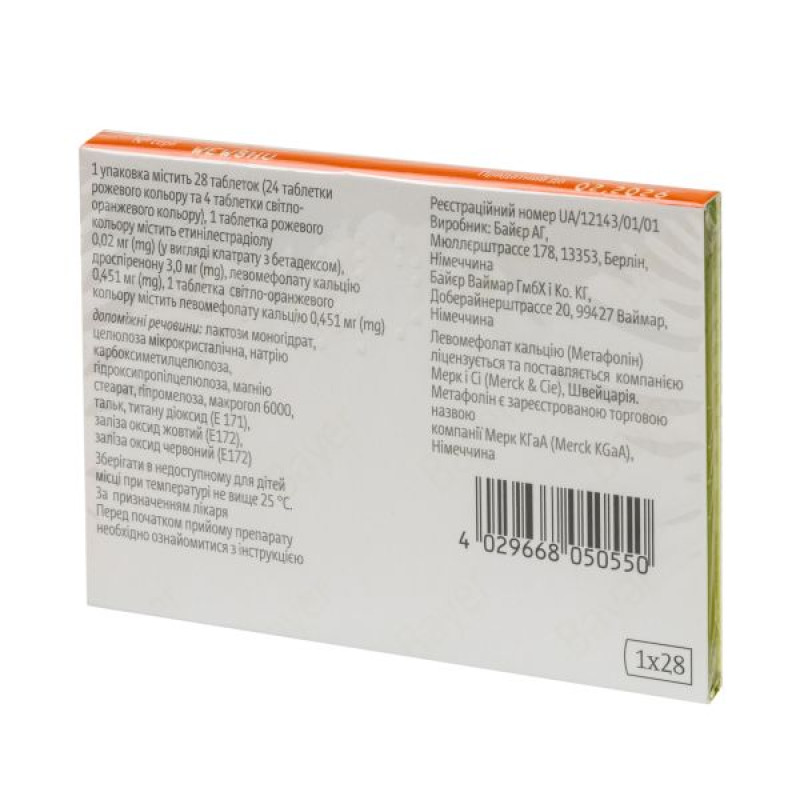
Jazz Plus film-coated tablets blister pack No. 28

Instructions Jazz Plus film-coated tablets blister pack No. 28
Composition
active ingredients: ethinylestradiol, drospirenone, calcium levomefolate;
1 pack contains 28 tablets (24 pink tablets and 4 light orange tablets);
1 pink tablet contains ethinylestradiol 0.02 mg (as clathrate with betadex) and drospirenone 3 mg, calcium levomefolate 0.451 mg;
excipients: lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, sodium carboxymethylcellulose, hydroxypropylcellulose, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, macrogol 6000, talc, titanium dioxide (E 171), red iron oxide (E 172);
1 light orange tablet contains 0.451 mg of calcium levomefolate;
excipients: lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, sodium carboxymethylcellulose, hydroxypropylcellulose, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, macrogol 6000, talc, titanium dioxide (E 171), yellow iron oxide (E 172), red iron oxide (E 172).
Dosage form
Film-coated tablets.
Main physicochemical properties:
Film-coated tablets containing hormones are round, biconvex, pink in color, with “Z+” embossed on one side in a regular hexagon; film-coated tablets containing levomefolate only are round, biconvex, light orange in color, with “M+” embossed on one side in a regular hexagon.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Hormonal contraceptives for systemic use.
ATX code G03A A12.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Mechanism of action
Combined oral contraceptives (COCs) reduce the risk of pregnancy mainly by inhibiting ovulation. Other possible mechanisms include changes in the nature of cervical mucus, which makes it difficult for sperm to penetrate, and changes in the endometrium, which reduce the likelihood of implantation.
Pharmacodynamic properties
Drospirenone is an analogue of spironolactone, which has antimineralocorticoid and antiandrogenic properties. The estrogenic component of the drug Jazz Plus is ethinyl estradiol.
Contraceptive effect
No specific studies of the pharmacodynamic properties of Jazz Plus have been conducted.
Two studies evaluated the effect of 3 mg drospirenone/0.02 mg ethinylestradiol on ovarian suppression, as measured by follicle size by transvaginal ultrasound and serum hormone levels (progesterone and estradiol), during two treatment cycles (21-day active tablet period plus 7-day tablet-free interval). Suppression of ovulation was observed in more than 90% of the subjects. One study compared the ovarian suppression of 3 mg drospirenone/0.02 mg ethinylestradiol in two different regimens (24-day active tablet period plus 4-day tablet-free interval and 21-day active tablet period plus 7-day tablet-free interval) over two treatment cycles. During the first treatment cycle, ovulation was not observed in any of the women (0/49, 0%) who received the drug in the 24-day regimen and was observed in one woman (1/50, 2%) who took the drug in the 21-day regimen. After intentional non-adherence to the dosage regimen (three missed active tablets in the first three days of the cycle) during the second treatment cycle, ovulation was observed in 1 patient (1/49, 2%) in the 24-day regimen group and in 4 patients (4/50, 8%) in the 21-day regimen group.
Acne
Acne is a skin condition that has many causes, including androgenic stimulation of sebum production. Although the combination of drospirenone and ethinylestradiol increases sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) and reduces free testosterone, no relationship has been established between these changes and a reduction in the severity of facial acne in otherwise healthy women with this skin condition. The effect of drospirenone's antiandrogenic activity on acne is unknown.
Folate. Two studies examined the effects of Jazz Plus on plasma and red blood cell folate levels. A randomized, double-blind, active-controlled, parallel-group study compared plasma and red blood cell folate levels in US women (patients) during 24 weeks of treatment with Jazz Plus 0.451 mg calcium levomefolate with Jazz alone. The pharmacodynamic effects on plasma and erythrocyte folate levels and the profile of circulating folate metabolites were assessed during 24 weeks of treatment with 0.451 mg of calcium levomefolate or 0.4 mg of folic acid (equimolar dose of 0.451 mg of calcium levomefolate) in combination with 3 mg of drospirenone/0.03 mg of ethinyl estradiol (Yarina®) followed by 20 weeks of open-label use of Yarina® alone (elimination phase).
In a 24-month animal carcinogenicity study, oral doses of 10 mg/kg/day of drospirenone or 1+0.01; 3+0.03 and 10+0.1 mg/kg/day of drospirenone and ethinyl estradiol, which represented 0.1-2 times the exposure (AUC of drospirenone) in women receiving contraceptives, an increase in the incidence of Gardermoa carcinoma was observed in the group receiving high doses of drospirenone monotherapy. In a similar study in another animal species, oral doses of 10 mg/kg/day of drospirenone or 0.3+0.003; 3+0.03 and 10+0.1 mg/kg/day of drospirenone and ethinylestradiol, which was 0.8-10 times the exposure in women receiving contraceptives, determined an increase in the incidence of benign and total (benign and malignant) adrenal pheochromocytomas in the group receiving high-dose drospirenone monotherapy. In vivo and in vitro mutagenicity studies of drospirenone revealed no evidence of mutagenic activity.
Long-term animal studies to determine the carcinogenic potential of levomefolate have not been conducted. Mutagenicity studies of levomefolate conducted in vivo and in vitro have not revealed any evidence of mutagenic activity.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
The drugs Jazz Plus and Jazz are bioequivalent with respect to drospirenone and ethinyl estradiol.
The absolute bioavailability of drospirenone after a single tablet intake is approximately
76%. The absolute bioavailability of ethinylestradiol is approximately 40%, which is the result of presystemic conjugation and the first-pass effect. The absolute bioavailability of Jazz Plus, which contains a combination of drospirenone and ethinylestradiol stabilized with betadex in the form of a clathrate (molecular complex), has not been studied. Ethinylestradiol has the same bioavailability when used as a clathrate with betadex and when taken as a free steroid. Serum concentrations of drospirenone and ethinylestradiol reached a maximum level 1-2 hours after taking Jazz Plus.
The pharmacokinetics of drospirenone after single doses in the range of 1 to 10 mg are dose-dependent. With daily use of Jazz, steady-state concentrations of drospirenone were reached after 8 days. An almost 2- to 3-fold increase in serum Cmax and AUC (0-24 hours) of drospirenone was observed after multiple doses of Jazz (see Table 1).
For ethinylestradiol, steady-state conditions were observed during the second half of the treatment course. With daily use of Jazz, serum Cmax and AUC (0-24 hours) for ethinylestradiol increased by almost 1.5-2 times (see Table 1).
Calcium levomefolate is structurally identical to L-5-methyltetrahydrofolate.
(L-5-methyl-THF), a metabolite of vitamin B9. The average initial concentration in individuals who do not consume foods enriched with folic acid, but have a normal diet, is 15 nmol/l. When calcium is administered orally, levomefolate is absorbed and accumulates in the body. The peak plasma concentration is about 50 nmol/l and is reached within 0.5-1.5 hours after a single dose of levomefolate calcium at a dose of 0.451 mg.
Steady-state conditions for total plasma folate levels after administration of 0.451 mg of calcium levomefolate are reached in approximately 8-16 weeks, depending on baseline values. Steady-state concentrations of calcium levomefolate in erythrocytes are reached somewhat later, due to the longer life cycle of erythrocytes, which is approximately 120 days.
Table 1. Pharmacokinetic parameters of the drug "Jazz" (3 mg of drospirenone and 0.02 mg of ethinyl estradiol)
| Drospirenone | |||||
| Course/day | Number of patients | Cmax a (ng/ml) | Tmaxb (h | AUC(0-24h)a (ng*h/ml) | T1/2a (hours) |
| 1/1 | 23 | 37.4 (25) | 1.5 (1-2) | 268 (19) | Not applicable |
| 1/21 | 23 | 70.3 (15) | 1.5 (1-2) | 763 (17) | 30.8 (22 |
| Ethinylestradiol | |||||
| Course/day | Number of patients | Cmaxa (ng/ml) | Tmaxb (h | AUC(0-24h)a (ng*h/ml) | T1/2a (hours) |
| 1/1 | 23 | 32.8 (45) | 1.5 (1-2) | 108 (52) | Not applicable |
| 1/21 | 23 | 45.1 (35) | 1.5 (1-2) | 220 (57) | Not applicable |
a) geometric mean (geometric coefficient of variation)
b) median (range).
The impact of food
The rate of absorption of drospirenone and ethinylestradiol after a single dose of preparations similar to Jazz Plus was lower when taken after a meal (high in fat), with mean serum concentrations (Cmax) decreasing by almost 40% for both active substances. However, the extent of absorption of drospirenone remained unchanged. In contrast, the extent of absorption of ethinylestradiol was reduced by almost 20% when taken after a meal.
The effect of food on the absorption of calcium levomefolate when using the drug Jazz Plus has not been studied.
Distribution
Drospirenone does not bind to GHB or corticosteroid-binding globulin (CBG), but binding to other serum proteins is approximately 97%. After repeated administration for more than 3 cycles, no changes in the free fraction (based on trough concentrations) were observed.
Ethinylestradiol binds strongly but nonspecifically to serum albumin (approximately 98.5%) and induces an increase in serum concentrations of GH and GSK. This effect on GH and GSK is due to the action of ethinylestradiol and does not change with changing doses of drospirenone in the range of 2-3 mg.
Folate kinetics are biphasic with a fast and a slow phase. The fast phase probably occurs in folate that has just been absorbed after a single oral dose of 0.451 mg of calcium levomefolate and is characterized by a terminal half-life of approximately 4-5 hours. The slow phase, which reflects the metabolism of the polyglutamate form of folic acid, has an average retention time of 100 days or more.
Metabolism
The two main metabolites of drospirenone detected in human plasma are the acid form of drospirenone, which is formed by opening of the lactone ring, and 4,5-dihydro-drospirenone-3-sulfate, which is the result of reduction and subsequent sulfonation. These metabolites have been shown to be pharmacologically inactive. Drospirenone also undergoes oxidative metabolism by CYP3A4.
Ethinylestradiol has been reported to undergo extensive first-pass metabolism in the intestine and liver. Metabolism of ethinylestradiol and its oxidative metabolites occurs primarily by conjugation with glucuronide or sulfate. CYP3A4 in the liver is responsible for 2-hydroxylation, which is the main oxidation reaction. The 2-hydroxy metabolite undergoes further transformation by methylation and glucuronidation before being excreted in the urine and feces.
L-5-methyltetrahydrofolate (L-5-methyl-THF) is the predominant folic acid compound in the circulatory system, transported under physiological conditions and during the administration of folic acid and calcium levomefolate.
Excretion from the body
The serum concentration of drospirenone is characterized by a terminal half-life in the distribution phase of about 30 hours after both single and multiple administration. Elimination of drospirenone was almost complete after ten days, and the amounts excreted were somewhat higher in feces than in urine. Drospirenone is extensively metabolized, with only minor amounts of unchanged drospirenone excreted in urine and feces. At least 20 different metabolites were detected in urine and feces. About 38-47% of the metabolites in urine were conjugates with glucuronides and sulfates. Almost 17-20% of the metabolites detected in feces were excreted in the form of glucuronides and sulfates.
The terminal half-life in the distribution phase of ethinylestradiol was approximately 24 hours. Ethinylestradiol is not excreted unchanged. Ethinylestradiol is excreted in the urine and feces as glucuronide and sulfate conjugates and undergoes enterohepatic circulation.
L-5-methyl-THF is eliminated from the body in a biphasic manner through urinary excretion of folate in unchanged form and as catabolic products, as well as in feces.
Certain groups of patients
Use in children. The safety and efficacy of Jazz Plus have been established in women of reproductive age. It is expected that the drug will show similar efficacy in postpubertal adolescents up to 18 years of age and women. This drug is not prescribed before the onset of menstruation.
Use in the elderly. Jazz Plus has not been studied in postmenopausal women; it is not recommended for use in this age group.
Racial differences: No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetic properties of drospirenone or ethinyl estradiol were identified in Japanese and Caucasian women (aged 25-35 years) when taking a daily dose of 3 mg drospirenone/0.02 mg ethinyl estradiol for 21 days. Specific studies on the characteristics of other ethnic groups have not been conducted.
Renal impairment. Jazz Plus is contraindicated for use in patients with renal impairment.
The effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of drospirenone (3 mg daily for 14 days) and the effect of drospirenone on serum potassium concentrations were studied in three separate groups of women (n = 28, ages 30-65). All subjects were on a low-potassium diet. Seven subjects continued to take potassium-sparing medications for their underlying disease during the study. On day 14 of drospirenone therapy (steady state), serum drospirenone concentrations in the group with a creatinine clearance
Hepatic impairment. Jazz Plus is contraindicated in patients with liver disease. The mean exposure to drospirenone in women with moderate hepatic impairment is approximately three times higher than in women with normal hepatic function. Jazz Plus has not been studied in women with severe hepatic impairment (see Contraindications and Precautions).
Drug interaction
For more detailed information on interactions with oral contraceptives or possible enzymatic alterations, the prescribing information for all medications administered concomitantly with this drug should be reviewed.
Effects of other drugs on COCs
Substances that reduce the effectiveness of COCs. Drugs or herbal preparations that induce certain enzymes, including CYP3A4, may reduce the effectiveness of COCs or increase breakthrough bleeding.
Substances that increase the plasma concentration of COCs. With the simultaneous use of atorvastatin and certain COCs containing ethinyl estradiol, an increase in the AUC of ethinyl estradiol by almost 20% is observed. Ascorbic acid and acetaminophen may lead to an increase in the plasma concentration of ethinyl estradiol, presumably by inhibiting conjugation. In a clinical drug interaction study conducted in 20 premenopausal women, co-administration of 3 mg drospirenone/0.02 mg ethinyl estradiol once daily with the potent CYP3A4 inhibitor ketoconazole 200 mg twice daily for 10 days resulted in an increase in AUC (0-24) of drospirenone and ethinyl estradiol by 2.68-fold (90% CI: 2.44, 2.95) and 1.4-fold (90% CI: 1.31, 1.49), respectively. The Cmax of drospirenone and ethinyl estradiol increased by 1.97-fold (90% CI: 1.79, 2.17) and 1.39-fold (90% CI: 1.28, 1.52), respectively. Although no clinically relevant effects on safety or laboratory parameters, including serum potassium, were observed, it should be noted that in this study women were only followed for 10 days. The clinical consequences of taking a drospirenone-containing COC and continuous use of a CYP3A4/5 inhibitor are unknown (see section 4.4).
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)/hepatitis C virus (HCV) protease inhibitors and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors: In some cases, significant changes (increase or decrease) in plasma estrogen and progestin concentrations have been observed when COCs were used concomitantly with HIV/HCV protease inhibitors or non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors.
Antibiotics: There have been reports of pregnancy occurring during the use of hormonal contraceptives and antibiotics, but clinical pharmacokinetic studies have not shown a consistent effect of antibiotics on the plasma concentration of synthetic steroids.
Effect of COCs on other drugs
COCs containing ethinylestradiol may inhibit the metabolism of other drugs. COCs have been shown to significantly reduce the plasma concentration of lamotrigine, presumably by inducing lamotrigine glucuronidation. This may result in reduced seizure control and may require adjustment of the lamotrigine dose. For more detailed information on interactions with COCs or possible enzyme changes, the Summary of Product Characteristics of all drugs administered concomitantly with this drug should be consulted.
In vitro, ethinylestradiol is a reversible inhibitor of CYP2C19, CYP1A1 and CYP1A2 isoenzymes and an irreversible inhibitor of CYP3A4/5, CYP2C8 and CYP2J2 isoenzymes. The metabolism of drospirenone and the potential effect of drospirenone on hepatic CYP enzymes have been studied in in vitro and in vivo studies. In in vitro studies, drospirenone had no effect on the metabolism of model substrates CYP1A2 and CYP2D6, but inhibited the metabolism of model substrates CYP1A1, CYP2C9, CYP2C19 and CYP3A4, with CYP2C19 being the most sensitive enzyme. The potential effect of drospirenone on the activity of the CYP2C19 isoenzyme was studied in a clinical pharmacokinetic study using omeprazole as a marker substrate. In a study of 24 postmenopausal women (including 12 women with the homozygous (wild-type) CYP2C19 genotype and 12 women with the heterozygous CYP2C19 genotype), daily oral administration of drospirenone at a dose of 3 mg for 14 days had no effect on the clearance of omeprazole (40 mg, single oral dose) and 5-hydroxyomeprazole formed by the action of CYP2C19. In addition, no significant effect of drospirenone on the systemic clearance of omeprazole sulfone, a metabolite formed by CYP3A4, was found. These results indicate that drospirenone does not inhibit CYP2C19 and CYP3A4 in vivo.
Women receiving thyroid hormone replacement therapy may require higher doses of thyroid hormone because the serum concentration of thyroid hormone-binding globulin increases with COC use.
Interaction with drugs that may increase serum potassium levels. In women taking Jazz Plus simultaneously with other drugs that may increase serum potassium levels, there is a possibility of an increase in serum potassium concentration (see section "Special warnings and precautions for use").
A drug interaction study was conducted comparing drospirenone 3 mg/estradiol 1 mg and placebo in 24 postmenopausal women with moderate hypertension who were receiving enalapril maleate 10 mg twice daily. Potassium levels were monitored in all subjects every other day for
2 weeks. The mean serum potassium concentration in the drospirenone/estradiol group was 0.22 mEq/L higher from baseline than in the placebo group. In addition, serum potassium was measured at various time points over 24 hours at baseline and on day 14 of the study. At day 14, the ratio between Cmax and AUC of serum potassium in the drospirenone/estradiol group and the placebo group was 0.955 (90% CI: 0.914, 0.999) and 1.010 (90% CI: 0.944, 1.08), respectively. No patient in either treatment group developed hyperkalemia (serum potassium > 5.5 mEq/L).
The effect of folates on other drugs.
Folates, such as folic acid and calcium levomefolate, may affect the pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics of certain antifolates (e.g., antiepileptics, methotrexate).
Effects of other drugs on folate.
A number of drugs (e.g., methotrexate, sulfasalazine, cholestyramine, antiepileptic drugs) reduce folate concentrations.
Indication
Oral contraception
Jazz Plus is indicated for use by women to prevent pregnancy.
Premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD)
Jazz Plus is indicated for the treatment of symptoms of premenstrual dysphoric disorder in women who have chosen oral contraception as their method of contraception. The effectiveness of Jazz Plus in PMDD when used for more than three menstrual cycles has not been studied.
Acne
Jazz Plus is indicated for the treatment of moderate acne in women aged 14 years and older (provided they have regular menses) who are not contraindicated for oral contraceptive therapy. Jazz Plus should be used for the treatment of acne only if the patient wishes to use oral contraception as a contraceptive.
Ensuring folate status
Jazz Plus is prescribed to women who have chosen oral contraception as a method of preventing pregnancy, to increase folate levels in order to reduce the risk of neural tube defects.
Contraindication
Jazz Plus should not be used in women with any of the following conditions.
Impaired kidney function. Adrenal insufficiency. High risk of arterial or venous thrombosis. This category includes, in particular, women who:
smoke and are over 35 years of age (see section "Peculiarities of use");
have deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism (PE), including a history (see section "Special precautions for use");
have cerebrovascular disease (see section "Special instructions for use");
patients with ischemic heart disease (see section "Special instructions for use");
have thrombogenic heart valve defects or thrombogenic heart rhythm disturbances (e.g. subacute
bacterial endocarditis with valve involvement or atrial fibrillation (see section "Special warnings and precautions for use"));
patients with hereditary or acquired hypercoagulopathy (see section "Special instructions for use");
patients with uncontrolled arterial hypertension (see section "Special precautions for use");
patients with diabetes mellitus with vascular complications (see section "Special instructions for use");
suffer from headaches with focal neurological symptoms or migraines with or without aura and are over 35 years of age (see section "Special instructions").
Abnormal uterine bleeding of unknown etiology (see section "Special warnings and precautions for use").
Breast cancer or other cancers sensitive to estrogens or progestins, including a history (see section "Special warnings and precautions for use").
Liver tumors, benign or malignant, or liver disease (see section "Special instructions", "Method of administration and dosage").
Pregnancy (due to the lack of need for COC use during pregnancy) (see section "Special warnings and precautions for use", "Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding").
Use of combination drugs for the treatment of hepatitis C containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir with or without the addition of dasabuvir due to the potential for ALT elevations (see sections “Special warnings and precautions for use” and “Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions”).
Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions
For more detailed information on interactions with hormonal contraceptives or possible enzymatic changes, please refer to the prescribing information for all medications administered concurrently with this medicinal product.
Effects of other drugs on COCs
Substances that reduce the effectiveness of COCs
Drugs and herbal preparations that induce certain enzymes, including cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4), may reduce the effectiveness of COCs or increase breakthrough bleeding. Drugs that may reduce the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives include: phenytoin, barbiturates, carbamazepine, bosentan, felbamate, griseofulvin, oxcarbazepine, rifampin, topiramate and drugs containing St. John's wort. Interactions between oral contraceptives and other drugs may lead to breakthrough bleeding and/or loss of contraceptive efficacy. When treating with enzyme-inducing drugs, an alternative or additional method of contraception should be used during the entire period of treatment with the drug and for 28 days after stopping its use to ensure complete contraception.
Substances that cause an increase in COC plasma concentrations
Concomitant use of atorvastatin and certain COCs containing ethinyl estradiol has been associated with an increase in ethinyl estradiol AUC of approximately 20%. Ascorbic acid and acetaminophen may increase ethinyl estradiol plasma concentrations, presumably by inhibiting conjugation.
Concomitant use of moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, including azole antifungals (ketoconazole, itraconazole, voriconazole, fluconazole), verapamil, macrolides (e.g. clarithromycin, erythromycin), diltiazem and grapefruit juice, may increase plasma concentrations of estrogen or progestin or both. In a clinical drug interaction study conducted in premenopausal women, co-administration of a once-daily formulation of drospirenone 3 mg/ethinyl estradiol 0.02 mg with the potent CYP3A4 inhibitor ketoconazole 200 mg twice daily for 10 days resulted in a modest increase in systemic exposure to drospirenone. Ethinyl estradiol exposure increased slightly (see sections 4.4 and 5.1).
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)/hepatitis C virus (HCV) protease inhibitors and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
In some cases, significant changes (increase or decrease) in plasma concentrations of estrogen and progestin have been observed when COCs were used concomitantly with HIV/HCV protease inhibitors or non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors.
Antibacterial agents
There are reports of cases of pregnancy during the use of hormonal contraceptives and antibiotics, however, clinical studies studying pharmacokinetic properties have not revealed a persistent effect of antibiotics on the concentration of synthetic steroids in blood plasma.
Effect of COCs on other drugs
COCs containing ethinylestradiol may inhibit the metabolism of other drugs. COCs have been shown to significantly reduce the plasma concentration of lamotrigine, presumably by inducing lamotrigine glucuronidation. This may result in reduced seizure control and may require adjustment of the lamotrigine dose. For more detailed information on interactions with COCs or possible enzyme changes, the Summary of Product Characteristics of all drugs administered concomitantly with this drug should be consulted.
COCs that increase plasma concentrations of cytochrome CYP450 enzymes
In clinical studies, there was no or minor increase in plasma concentrations of CYP3A4 substrates (e.g. midazolam) with the use of ethinylestradiol-containing hormonal contraceptives, while plasma concentrations of CYP2C19 substrates (e.g. omeprazole and voriconazole) and CYP1A2 substrates (e.g. theophylline and tizanidine) may be increased to a minor to moderate extent.
Clinical studies do not indicate that drospirenone has an inhibitory potential for human CYP enzymes when used at clinically relevant concentrations (see section "Pharmacological properties").
Women receiving thyroid hormone replacement therapy may require higher doses of thyroid hormone because the serum concentration of thyroid hormone-binding globulin increases with COC use.
Interaction with drugs that may increase serum potassium levels
In women taking Jazz Plus simultaneously with other drugs that can increase serum potassium levels, there is a possibility of an increase in serum potassium concentration (see sections "Special instructions for use", "Pharmacological properties").
Effects of folate on other drugs
Folate may alter the pharmacokinetic or pharmacodynamic properties of some antifolate drugs, including antiepileptic drugs (e.g. phenytoin), methotrexate or pyrimethamine, which may lead to a reduced pharmacological effect of antifolate drugs.
Certain drugs have been reported to cause folate depletion by inhibiting the enzyme dehydrofolate reductase (e.g., methotrexate and sulfasalazine), by reducing folate absorption (e.g., cholestyramine), or by unknown mechanisms (e.g., antiepileptic drugs such as carbamazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbital, primidone, and valproic acid).
Impact on laboratory test results
The use of contraceptive steroids may affect the results of certain laboratory tests, in particular coagulation factors, lipid levels, glucose tolerance and binding proteins. Drospirenone increases plasma renin and aldosterone activity, which is induced by its moderate antimineralocorticoid activity. Folate may mask vitamin B12 deficiency (see section "Special instructions" and subsection "Effect of COCs on other drugs" in the section "Interaction with other drugs and other types of interactions").
Application features
The essential features of PMDD, according to the fourth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM-IV), are markedly depressed mood, agitation or tension, affective lability, and persistent anger or irritability. Other features include decreased interest in usual activities, difficulty concentrating, lack of energy, changes in appetite or sleep, and a sense of loss of control. Physical symptoms associated with PMDD include breast tenderness, headache, joint and muscle pain, bloating, and weight gain. In the presence of this disorder, these symptoms occur regularly during the luteal phase and disappear within a few days after the onset of menstruation. The disorder significantly interferes with work, school, or usual social activities and relationships. Diagnosis is made by a physician using DSM-IV criteria based on a prospective assessment of symptoms observed over at least two menstrual cycles. Other cyclical mood disorders must be ruled out when making a diagnosis.
The effectiveness of Jazz Plus for the treatment of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) has not been evaluated.
Smoking and serious cardiovascular complications
Smoking increases the risk of serious cardiovascular complications with COC use. This risk increases with age, particularly in women over 35 years of age, and with the number of cigarettes smoked. For this reason, COCs should not be used in women over 35 years of age who smoke (see section 4.3).
Thromboembolic disorders and other vascular diseases
The use of Jazz Plus should be discontinued in the event of arterial or venous thromboembolic complications (VTE).
Based on the available information on COCs containing drospirenone and 0.03 mg ethinylestradiol (Yarina®), COCs containing drospirenone are associated with a higher risk of VTE than COCs containing levonorgestrel or other progestins. Epidemiological studies comparing the risks of VTE have shown that there is no increased risk or a three-fold increase. Before starting Jazz Plus in a woman who has not previously used a COC or in a woman who is switching from another contraceptive that does not contain drospirenone, the risks and benefits of using a COC containing drospirenone should be weighed against the potential for VTE. In addition to other factors that contraindicate the use of COCs, known risk factors for VTE include smoking, obesity and a family history of VTE (see section 4.3).
Several studies have compared the risk of VTE in women taking Yarina® (containing 0.03 mg ethinylestradiol and 3 mg drospirenone) and in women using other COCs, to see whether
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.