Lidocaine solution for injection 10 mg/ml blister 3.5 ml No. 10
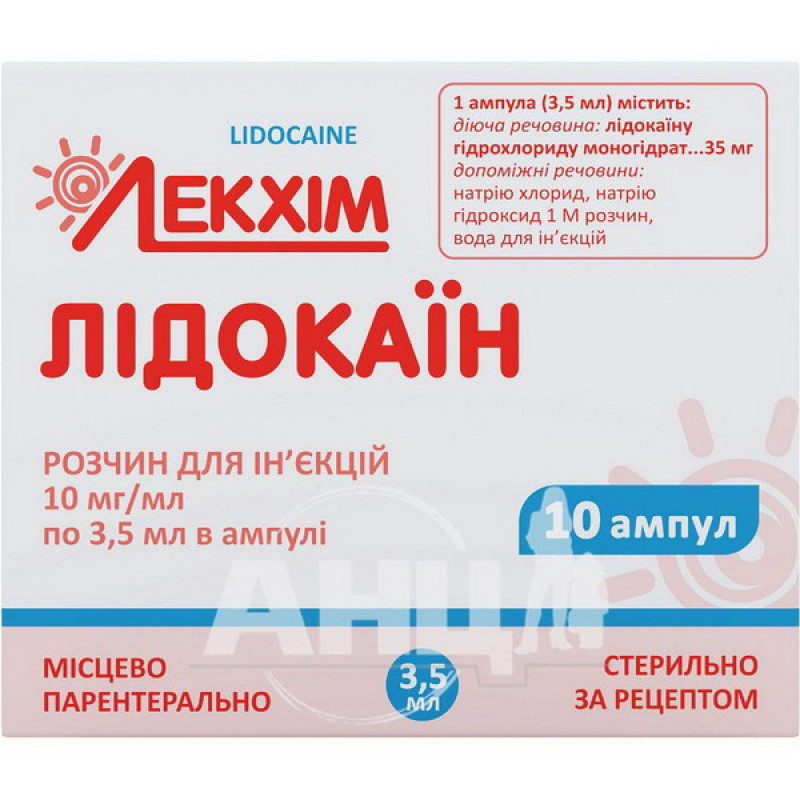
Lidocaine injection solution is indicated for local anesthesia (terminal, infiltration, conduction) in surgery, ophthalmology, dentistry, otorhinolaryngology; used as a solvent for antibacterial agents of the cephalosporin group.
Composition
Active ingredient: lidocaine;
1 ml of solution contains lidocaine hydrochloride monohydrate 10 mg;
Excipients: sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide 1 M solution, water for injections.
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, other amide local anesthetics, history of epileptiform seizures to lidocaine, severe bradycardia, severe arterial hypotension, cardiogenic shock, severe forms of chronic heart failure (II-III degree), sick sinus syndrome, Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, Adams-Stokes syndrome, atrioventricular (AV) blockade of II and III degree, hypovolemia, severe liver / kidney dysfunction, porphyria, myasthenia gravis, retrobulbar administration to patients with glaucoma; contraindicated in patients in the first three months after myocardial infarction with reduced cardiac output of the left ventricle (less than 35% of normal); blood clotting disorders, anticoagulant therapy; infections at the injection site; contraindicated in non-contact patients; significant decrease in left ventricular function.
Method of application
The introduction of lidocaine requires a preliminary test to determine individual sensitivity to this drug.
For terminal anesthesia in adults, lubricate the mucous membranes with a drug at a dose of 2 mg/kg of lidocaine, the duration of anesthesia is 15-30 minutes.
The maximum dose for adults is 20 ml.
Application features
Pregnant women
It is not recommended to prescribe during pregnancy.
Children
Doses for children should be reduced according to age, body weight, and physical condition.
Drivers
The drug affects the function of the central nervous system, therefore, after using lidocaine, it is not recommended to drive vehicles or work with other mechanisms.
Overdose
Possible increase in adverse reactions.
Symptoms: psychomotor agitation, dizziness, general weakness, decreased blood pressure, tremor, visual impairment, tonic-clonic convulsions, coma, collapse, AV block, asphyxia, apnea, depression, drowsiness, anxiety, tinnitus. With a significant overdose, impaired consciousness, respiratory depression, shock, myocardial infarction are possible. The first symptoms of overdose in healthy volunteers occur when the concentration of lidocaine in the blood exceeds 0.006 mg/kg; convulsions - at 0.01 mg/kg.
Treatment: discontinuation of the drug, oxygen therapy, anticonvulsants, vasoconstrictors (noradrenaline, mezaton), anticholinergics. The patient should be in a horizontal position; it is necessary to ensure access to fresh air, oxygen supply and / or artificial respiration. Symptoms from the central nervous system are corrected by the use of short-acting benzodiazepines / barbiturates. If an overdose occurs during anesthesia, a short-acting muscle relaxant should be used. To correct bradycardia and conduction disorders, use atropine (0.5-1 mg intravenously), with arterial hypotension - sympathomimetics in combination with β-blocker agonists. In case of cardiac arrest, immediate resuscitation measures are indicated. In the acute phase of lidocaine overdose, dialysis is ineffective. There is no specific antidote.
Interaction
Chlorpromazine, pethidine, bupivacaine, quinidine, disopyramide, amitriptyline, imipramine, nortriptyline - when used in combination with lidocaine, the concentration of the latter in the blood plasma decreases. Anticonvulsants, barbiturates (phenytoin) - when used in combination with lidocaine, acceleration of lidocaine metabolism in the liver, decrease in blood concentration, and increase in cardiodepressive effect are possible. Isadrin, glucagon - when used in combination with lidocaine, the clearance of lidocaine increases. Norepinephrine, mexiletine - when used in combination with lidocaine, the clearance of the latter decreases (toxicity increases); hepatic blood flow decreases. Acetazolamide, thiazide and loop diuretics - when used in combination with lidocaine, as a result of creating hypokalemia, they reduce the effect of the latter.Storage conditions
Store in the original packaging at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Keep out of reach of children.
Shelf life - 3 years.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.