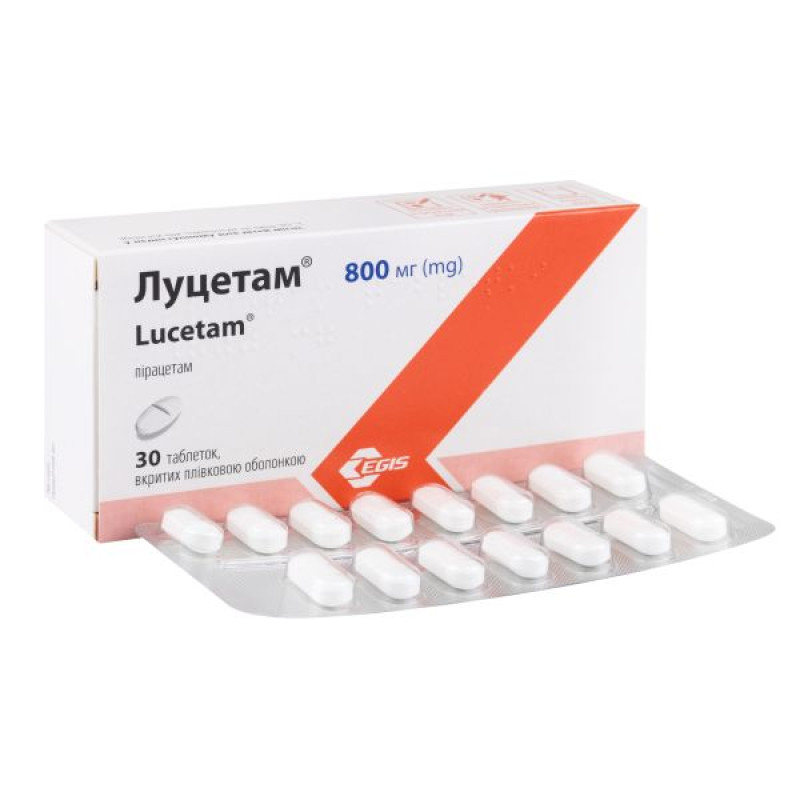
Lucetam film-coated tablets 800 mg blister No. 30

Instructions Lucetam film-coated tablets 800 mg blister No. 30
Composition
active ingredient: piracetam;
1 tablet contains 400 mg or 800 mg or 1200 mg of piracetam;
excipients: magnesium stearate, povidone, dibutyl sebacate;
composition of the tablet shell: Opadry 03F28561 white (macrogol, titanium dioxide (E 171), talc, ethylcellulose aqueous dispersion, hypromellose).
Dosage form
Film-coated tablets.
Main physicochemical properties:
400 mg tablets – white or almost white biconvex oval tablets, film-coated, with a bevel, engraved with “E 241” on one side of the tablet, odorless;
800 mg tablets – white or almost white biconvex oval tablets, film-coated, beveled, with a score on both sides, engraved with “E 242” on one side of the tablet, odorless;
1200 mg tablets – white or almost white, biconvex, oval-shaped tablets, film-coated, with a bevel, engraved with “E 243” on one side of the tablet, odorless.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Psychostimulants and nootropics.
ATX code N06B X03.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics.
The active ingredient of Lucetam® is piracetam, a cyclic derivative of gamma-aminobutyric acid. Piracetam is a nootropic agent that acts on the brain, improving cognitive functions such as learning ability, memory, attention, and mental performance in healthy individuals and patients with cognitive disorders. These effects are not associated with a sedative or stimulant effect. The effects of piracetam are associated with the stimulation of nucleotide metabolism in neurons, an increase in glucose levels and oxygen utilization in the brain, as well as with the enhancement of cholinergic and dopaminergic mechanisms of excitation transmission in nervous tissue. Piracetam has the property of dose-dependent binding to the phospholipid bilayer of cell membranes, and it restores their structure, thus increasing the fluidity and improving membrane function.
There are probably several mechanisms of action of the drug on the central nervous system: changing the speed of propagation of excitation in the brain; enhancing metabolic processes in nerve cells; improving microcirculation by influencing the rheological characteristics of the blood without causing a vasodilator effect. Improves connections between the cerebral hemispheres and synaptic conduction in neocortical structures. Piracetam inhibits platelet aggregation and restores the elasticity of the erythrocyte membrane, reduces erythrocyte adhesion. At a dose of 9.6 g, it reduces the level of fibrinogen and von Willebrand factors by 30-40% and prolongs bleeding time. Piracetam has a protective or restorative cognitive effect in case of impaired brain function (hypoxia, poisoning, electroconvulsive therapy) or after these conditions. Piracetam reduces the severity and duration of vestibular nystagmus.
Animal experiments have shown that piracetam protects the central nervous system from hypoxia, brain injury, toxic and electroconvulsive effects, and also reduces the harmful effects of these factors.
Pharmacokinetics.
After oral administration, piracetam is rapidly and almost completely absorbed. The maximum concentration (Cmax) in the blood plasma is reached approximately 30 minutes after administration: Cmax in the cerebrospinal fluid is reached after 5 hours and is 40-60 μg/ml. The bioavailability of the drug is almost 100%.
The volume of distribution of piracetam is almost 0.6 l/kg. Simultaneous food intake does not affect the extent of absorption of the drug, but the Cmax value decreases and the tmax increases.
The half-life of the drug from blood plasma is 4-5 hours, from cerebrospinal fluid - 8.5 hours. This period may be prolonged in renal failure. It does not bind to blood plasma proteins, is not metabolized in the body. 80-100% of piracetam is excreted by the kidneys unchanged by glomerular filtration. Renal clearance of piracetam in healthy volunteers is 86 ml/min. The pharmacokinetics of piracetam does not change in patients with liver failure. Piracetam penetrates the blood-brain and placental barriers (the concentration in the fetus reaches 70-90% of its concentration in the mother's body) and penetrates into breast milk. Piracetam is dialyzed (the efficiency of removal is 50-60%). In animal studies, it was found that piracetam selectively accumulates in the tissues of the cerebral cortex, mainly in the frontal, parietal and occipital areas, cerebellum, basal ganglia, caudate nucleus, hippocampus, lateral geniculate body and choroid plexus of the brain.
Indication
Adults:
symptomatic treatment of pathological conditions accompanied by memory impairment and cognitive disorders, with the exception of diagnosed dementia;
Treatment of cortical myoclonus: as a monotherapy or as part of complex therapy.
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to piracetam and other pyrrolidone derivatives, as well as to other components of the drug.
Acute cerebrovascular accident (hemorrhagic stroke).
End-stage renal failure.
Huntington's cholera.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions
When used together with thyroid hormones (T3+T4), increased irritability, disorientation, and sleep disturbances are possible.
Acenocoumarol
Clinical studies have shown that in patients with severe recurrent thrombosis, the use of piracetam in high doses (9.6 g/day) did not affect the dosage of acenocoumarol to achieve a prothrombin time (INR) of 2.5-3.5, but with its simultaneous use, a significant decrease in the level of platelet aggregation, fibrinogen levels, von Willebrand factors (VIII: C; VIII: vW: Ag; VIII: vW: Rco), blood and plasma viscosity was observed.
Pharmacokinetic interactions
The likelihood of changes in the pharmacodynamics of piracetam under the influence of other drugs is low, since 90% of the drug is excreted unchanged in the urine.
In vitro, piracetam does not inhibit cytochrome P450 isoforms CYP1A2, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 2E1 and 4A9/11 at concentrations of 142, 426, 1422 μg/ml.
At a concentration of 1422 μg/ml, a slight inhibition of CYP2A6 (21%) and ZA4/5 (11%). However, the Ki level of these two CYP isomers is sufficient when exceeding 1422 μg/ml. Therefore, metabolic interaction with drugs that are biotransformed by these enzymes is unlikely.
Antiepileptic drugs
The use of piracetam at a dose of 20 mg/day daily for 4 weeks or more did not change the concentration-level curve and Cmax of antiepileptic drugs in serum (carbamazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbital, sodium valproate) in patients with epilepsy.
Alcohol
Co-administration with alcohol did not affect the serum concentration of piracetam, and serum alcohol concentration did not change when 1.6 g of piracetam was administered.
Application features
Effect on platelet aggregation
Due to the fact that piracetam reduces platelet aggregation (see section "Pharmacological properties"), it is necessary to prescribe the drug with caution to patients with impaired hemostasis, conditions that may be accompanied by bleeding (gastrointestinal ulcer), during major surgical operations (including dental interventions), patients with symptoms of severe bleeding or patients with a history of hemorrhagic stroke; patients using anticoagulants, platelet antiaggregants, including low doses of acetylsalicylic acid. The drug is excreted by the kidneys, therefore special attention should be paid to patients with renal failure.
Elderly patients
During long-term therapy in elderly patients, regular monitoring of renal function is recommended, and if necessary, the dose should be adjusted depending on the results of the creatinine clearance test (see section "Method of administration and dosage").
Interruption of application
When treating patients with cortical myoclonus, abrupt discontinuation of treatment should be avoided due to the risk of generalization of myoclonus or the occurrence of seizures.
Warnings related to the content of excipients.
This medicine contains 2 mmol (46 mg) of sodium per 24 g of piracetam. This should be taken into consideration by patients on a controlled sodium diet.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding
Do not use the drug during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Ability to influence reaction speed when driving vehicles or other mechanisms
Caution should be exercised when driving or operating other machinery.
Method of administration and doses
Administer the drug orally, with a small amount of water.
Adults.
Treatment of conditions accompanied by memory impairment and cognitive disorders.
The initial daily dose is 4.8 g during the first week of treatment. Usually the dose should be divided into 2-3 doses.
The maintenance dose is 2.4 g per day, divided into 2-3 doses.
Subsequently, a gradual dose reduction of 1.2 g per day is possible.
Treatment of cortical myoclonus.
The initial daily dose is 24 g for 3 days. If the desired therapeutic effect is not achieved during this time, continue using the drug at the same dosage (24 g/day) for up to 7 days. If the desired therapeutic effect is not achieved on the 7th day of treatment, treatment should be discontinued. If the therapeutic effect has been achieved, then starting from the day when a stable improvement is achieved, start reducing the dose of the drug by 1.2 g every 2 days until the manifestations of cortical myoclonus reappear. This will make it possible to establish an average effective dose.
The daily dose should be divided into 2-3 doses. Treatment with other antimyoclonic agents is maintained in previously prescribed doses. Treatment should be continued until the symptoms of the disease disappear. To prevent deterioration of the patient's condition, the drug should not be abruptly discontinued. The dose should be gradually reduced by 1.2 g every 2-3 days. Repeated courses of treatment with the drug should be prescribed every 6 months, adjusting the dose depending on the patient's condition, until the symptoms of the disease disappear or decrease.
Use in elderly patients.
Dosage for patients with renal impairment.
Since the drug is excreted from the body by the kidneys, caution should be exercised when treating patients with renal insufficiency.
The increase in half-life is directly related to the deterioration of renal function and creatinine clearance. This also applies to elderly patients, in whom creatinine clearance is age-dependent. The interval between doses should be adjusted based on renal function.
The dose should be calculated based on the patient's creatinine clearance using the formula:
Treatment for such patients should be prescribed depending on the severity of renal failure, adhering to the following recommendations:
| Degree of renal failure | Creatinine clearance (ml/min) | Dosage |
| normal kidney function | > 80 | Usual dose divided into 2 or 4 doses |
| light | 50-79 | 2/3 of the usual dose in 2-3 doses |
| moderate | 30-49 | 1/3 of the usual dose in 2 doses |
| severe | < 30 | 1/6 of the usual dose once |
| terminal stage | - | Contraindicated |
Dosage in patients with hepatic impairment
Dose adjustment is not required only for patients with impaired liver function.
In case of diagnosed or suspected liver and kidney function disorders, dose adjustment should be performed as indicated in the section "Dosage in patients with renal impairment".
Children
Do not apply.
Overdose
Symptoms: increased side effects of the drug. Symptoms of overdose were observed with oral administration of the drug at a dose of 75 g.
Treatment is symptomatic: gastric lavage, induce vomiting. There is no specific antidote, hemodialysis can be used (removal of 50-60% of piracetam).
Side effects
Adverse reactions noted during clinical trials of piracetam.
From the nervous system: hyperkinesia.
Metabolism and nutrition disorders: weight gain.
Mental disorders: nervousness, depression.
General disorders and administration site conditions: asthenia.
Adverse reactions reported during post-marketing surveillance are listed below by system organ class.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: hemorrhagic disorders.
Immune system disorders: hypersensitivity, anaphylactoid reactions.
Mental disorders: nervousness, depression; increased excitability, anxiety, confusion, hallucinations.
From the nervous system: hyperkinesia; drowsiness; ataxia, balance disorders, increased frequency of epileptic seizures, headache, insomnia, tremor.
From the side of the organs of hearing and labyrinth: dizziness.
On the part of the digestive system: abdominal pain, upper abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: angioedema, dermatitis, rash, urticaria, itching.
From the reproductive system and breastfeeding: increased sexual activity.
Research: weight gain.
Expiration date
5 years.
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 30 °C in a place inaccessible to children.
Packaging
400 mg tablets: 60 tablets in a glass bottle or 15 tablets in a blister (4 blisters) in a cardboard box.
800 mg tablets: 30 tablets in a glass bottle or 15 tablets in a blister (2 blisters) in a cardboard box.
Tablets 1200 mg: 20 tablets in a glass bottle or 10 tablets in a blister (2 blisters) in a cardboard box.
Vacation category
According to the recipe.
Producer
CJSC Pharmaceutical Plant EGIS, Hungary.
Location of the manufacturer and address of the place of implementation of its activities.
9900, Kermend, 65 Matyas Kirai Street, Hungary.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.