Nexium film-coated tablets 20 mg blister No. 14

Nexium tablets are used for the indications listed below.
adults:
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): treatment of erosive reflux esophagitis; long-term treatment of patients with cured esophagitis to prevent relapse; symptomatic treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD); in combination with appropriate antibacterial drugs for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori: treatment of duodenal ulcers caused by Helicobacter pylori; prevention of relapse of peptic ulcers in patients with ulcers caused by Helicobacter pylori; patients requiring long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): healing of gastric ulcers caused by NSAIDs; prevention of gastric and duodenal ulcers caused by NSAIDs in patients at risk; long-term treatment after intravenous administration of the drug to prevent relapse of bleeding from peptic ulcers; treatment of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.Children aged 12 and over:
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): treatment of erosive reflux esophagitis; long-term treatment of patients with cured esophagitis to prevent relapse; symptomatic treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD); in combination with antibiotics in the treatment of duodenal ulcers caused by Helicobacter pylori.Composition
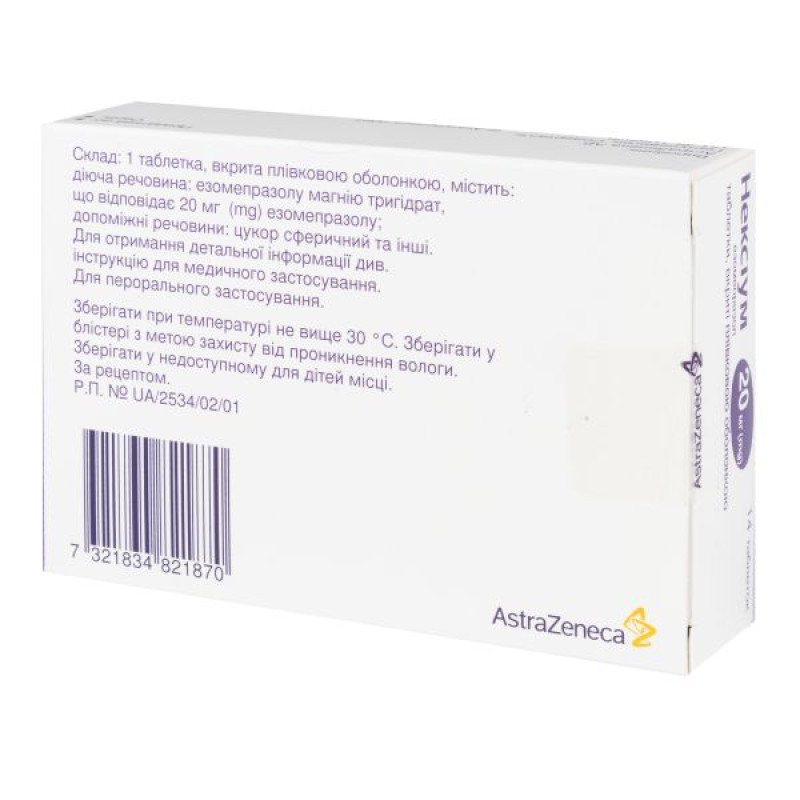
The active substance is esomeprazole (each film-coated tablet contains esomeprazole magnesium trihydrate, equivalent to 20 mg of esomeprazole).
Excipients: glycerol monostearate, hydroxypropylcellulose, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, methacrylate copolymer (type A), microcrystalline cellulose, synthetic paraffin, macrogol, polysorbate 80, crospovidone, sodium stearyl fumarate, spherical sugar, talc, titanium dioxide (E 171), triethyl citrate, reddish-brown iron oxide (E172), yellow iron oxide (E172).
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to the active substance, to benzimidazoles or to any of the excipients; esomeprazole should not be used concomitantly with nelfinavir.Method of application
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (adults)
Treatment of erosive reflux esophagitis: 40 mg once daily for 4 weeks. In patients with untreated esophagitis or persistent symptoms, an additional 4 weeks of treatment is recommended.
Long-term treatment of patients with cured esophagitis to prevent relapse: 20 mg once daily.
Symptomatic treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). The dose for patients without esophagitis is 20 mg once daily. If after 4 weeks of treatment the symptoms are not controlled, the patient should be re-evaluated. After symptoms have resolved, 20 mg once daily may be sufficient for continued control. If necessary, the drug can be switched to an “on-demand” regimen, i.e. 20 mg once daily. The use of the drug “on-demand” for continued control of symptoms is not recommended in patients at risk of developing gastric and duodenal ulcers who are taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
In combination with appropriate antibacterial drugs for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori (adults)
Also for the treatment of duodenal ulcers caused by Helicobacter pylori and the prevention of recurrence of peptic ulcers in patients with ulcers caused by Helicobacter pylori: 20 mg of Nexium with one gram of amoxicillin and 500 mg of clarithromycin twice daily for 7 days.
Patients requiring long-term use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (adults)
Treatment of stomach ulcers caused by the use of NSAIDs: the usual dose is 20 mg once a day. The duration of treatment is 4-8 weeks.
Prevention of gastric and duodenal ulcers caused by the use of NSAIDs in patients at risk: 20 mg once daily.
Long-term treatment after intravenous administration of the drug for the prevention of recurrent bleeding from peptic ulcers (adults)
The recommended dose is 40 mg once daily for 4 weeks after intravenous administration of the drug for the prevention of recurrent bleeding from peptic ulcers.
Treatment of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (adults)
The recommended initial dose of Nexium is 40 mg twice daily. The dose is then adjusted individually; treatment is continued for as long as clinically indicated. Based on available clinical data, control of the condition can be achieved in most patients with doses of 80 to 160 mg of esomeprazole per day. If doses exceed 80 mg per day, the dose should be divided and administered twice daily.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (children over 12 years old)
Treatment of erosive reflux esophagitis: 40 mg once daily for 4 weeks. In patients with untreated esophagitis or persistent symptoms, an additional 4 weeks of treatment is recommended.
Symptomatic treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). The dose for patients without esophagitis is 20 mg once daily. If after 4 weeks of treatment, control of symptoms has not been achieved, the patient should be re-evaluated. After symptom control, further control may be achieved by using the drug at a dose of 20 mg once daily.
Treatment of duodenal ulcers caused by Helicobacter pylori (children over 12 years of age)
When choosing an appropriate combination therapy, official national, regional and local guidelines on bacterial resistance, duration of treatment (usually 7 days, but sometimes up to 14 days) and appropriate use of antibacterial drugs should be taken into account. Treatment should be carried out under specialist supervision.
Dosage recommendations:
body weight 30-40 kg - in combination with two antibiotics: "Nexium" 20 mg, amoxicillin 750 mg and clarithromycin 7.5 mg/kg body weight - all drugs are used simultaneously twice a day for a week; body weight> 40 kg: in combination with two antibiotics: "Nexium" 20 mg, amoxicillin 1 g and clarithromycin 500 mg - all drugs are used simultaneously twice a day for a week.Application features
Pregnant women
The drug should be prescribed with caution to pregnant women.
Esomeprazole should not be used during breastfeeding.
Animal studies of the racemic mixture of omeprazole indicate no effect of omeprazole on fertility when administered orally.
Drivers
Esomeprazole has minimal influence on the ability to drive and use machines. Adverse reactions such as dizziness (rare) and blurred vision (rare) have been reported. If these disorders occur, patients should not drive or use machines.
Overdose
Currently, data on intentional overdose are very limited. Symptoms described when taking the drug in a dose of 280 mg included gastrointestinal symptoms and weakness. A single dose of esomeprazole in a dose of 80 mg did not cause any negative consequences. There is no specific antidote known. Esomeprazole is highly bound to plasma proteins, so the removal by dialysis is insignificant. As with any overdose, symptomatic and general supportive therapy should be provided.
Side effects
Among the side effects that are most frequently encountered during clinical trials (as well as during post-marketing use of the drug), headache, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea are noted.
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 30 °C, out of the reach of children. Store in a blister in order to protect from moisture.
Shelf life - 3 years.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.