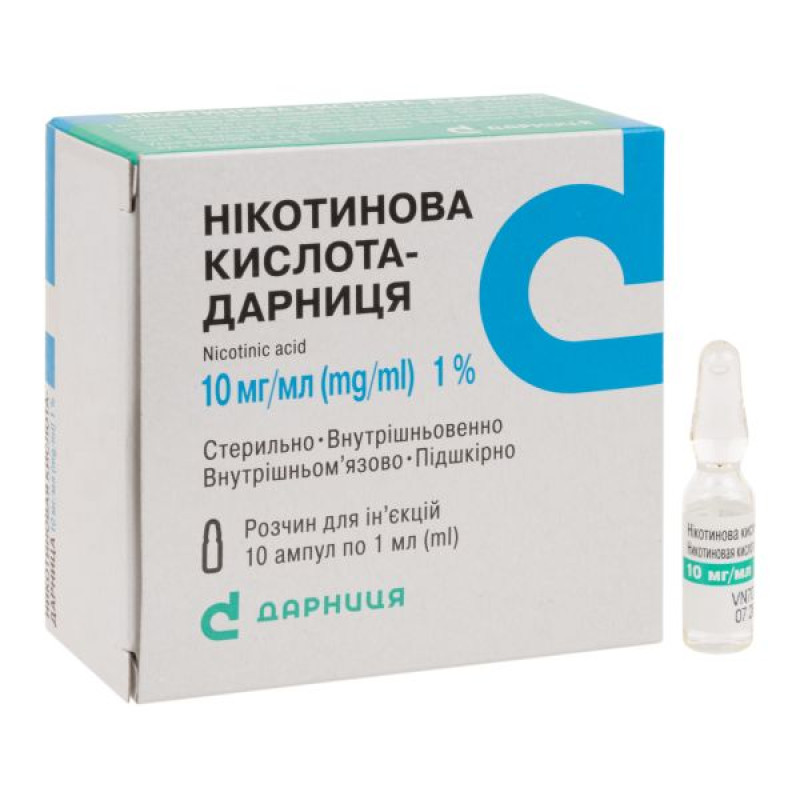
Nicotinic acid-Darnitsa solution for injection 1% ampoule 1 ml No. 10
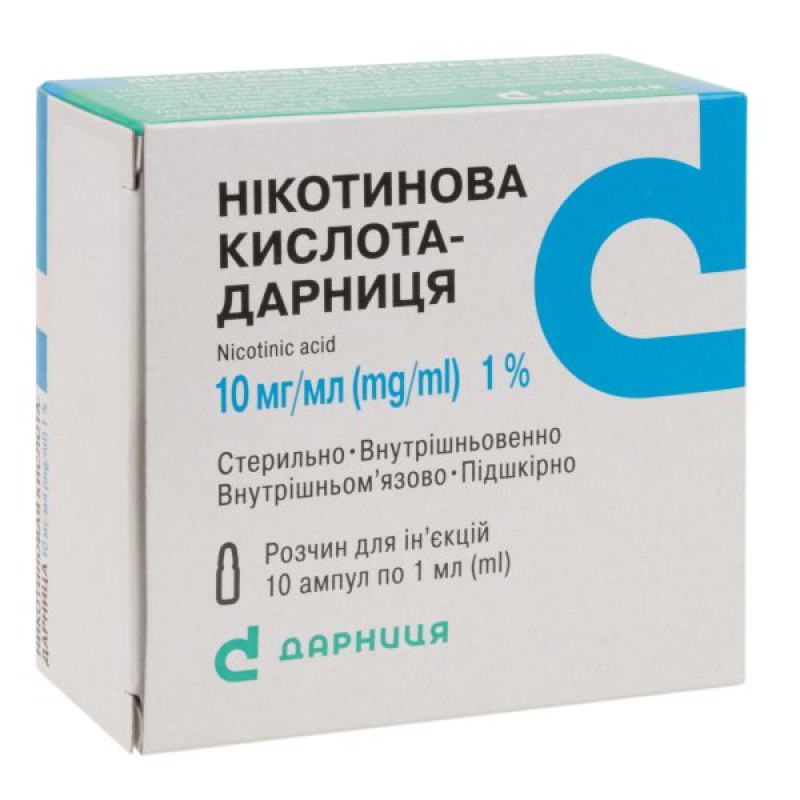
Instructions Nicotinic acid-Darnitsa solution for injection 1% ampoule 1 ml No. 10
Composition
active ingredient: nicotinic acid;
1 ml of solution contains: nicotinic acid - 10 mg;
Excipients: sodium bicarbonate, water for injections.
Dosage form
Main physicochemical properties: clear colorless liquid.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Peripheral vasodilators. Nicotinic acid and its derivatives. ATC code C04A C01.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Nicotinic acid (vitamin PP) alone or in the form of an amide is a prosthetic group of enzymes – codehydrase I (diphosphopyridine nucleotide – NAD) and codehydrase II (triphosphopyridine nucleotide – NADP), which carry out hydrogen transfer in redox reactions, as well as phosphate transfer.
Taking part in metabolism, tissue respiration, and synthesis processes, nicotinic acid normalizes the content of lipoproteins and triglycerides in the blood.
It has a vasodilating effect on prearterioles and arterioles (including those of the brain), thereby improving microcirculation.
It has a weak anticoagulant effect (increases fibrinolytic activity of the blood), has detoxification properties due to the enhancement of the detoxification function of the liver and kidneys.
Eliminates vitamin PP deficiency and is a specific anti-pellagra remedy.
Pharmacokinetics
Nicotinic acid is rapidly absorbed from the site of administration when administered parenterally. It is evenly distributed throughout all organs and tissues. It is inactivated mainly by methylation and to a lesser extent by conjugation. The products of biotransformation are excreted in the urine. Nicotinic acid can be detected in the urine in its active form if an increased amount of it enters the body.
Indication
Treatment of pellagra (vitamin PP deficiency).
Ischemic cerebral circulation disorders. Vascular spasm of the extremities (endarteritis obliterans, Raynaud's disease). Vascular spasm of the kidneys.
Wounds, ulcers that do not heal for a long time. Complications of diabetes mellitus (diabetic polyneuropathy, microangiopathy).
Hypoacid gastritis, enterocolitis, colitis. Liver diseases (acute and chronic hepatitis).
Neuritis of the facial nerve.
Intoxications of various origins: professional, alcoholic, medicinal (aniline derivatives, barbiturates, anti-tuberculosis drugs, sulfonamides).
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug. Gastric and duodenal ulcer (in the acute stage), gout, hyperuricemia, severe liver failure (including cirrhosis), severe forms of arterial hypertension and atherosclerosis (intravenous administration), decompensated diabetes mellitus, recent myocardial infarction, a history of sudden decrease in peripheral vascular resistance.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions
Oral contraceptives and isoniazid reduce the conversion of tryptophan to nicotinic acid and thus may increase the need for nicotinic acid.
Nicotinic acid reduces the effectiveness and toxicity of probenecid, neomycin, barbiturates, anti-tuberculosis drugs, and sulfonamides.
Antibiotics may increase skin redness caused by nicotinic acid.
Acetylsalicylic acid reduces the effect of skin redness caused by nicotinic acid.
Ciprofibrate is not recommended to be combined with nicotinic acid.
Lovastatin, pravastatin are not recommended for combination with nicotinic acid due to increased risk of adverse reactions. There are reports of cases of rhabdomyolysis when nicotinic acid is used with lovastatin.
Caution should be exercised when combining with antihypertensive agents (possible enhancement of the hypotensive effect), anticoagulants, acetylsalicylic acid (due to the risk of hemorrhage).
The drug potentiates the effects of fibrinolytic agents, antispasmodics and cardiac glycosides, and the toxic effects of alcohol on the liver.
Application features
Since prolonged use can lead to fatty liver disease, to prevent the latter, patients should include foods rich in methionine in their diet or prescribe methionine, lipoic acid. During treatment, it is necessary to monitor liver function. In case of hypersensitivity to the drug (except for use as a vasodilator), it can be replaced with nicotinamide.
The drug should be used with caution in cases of hyperacid gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers (outside the acute stage), hemorrhages, glaucoma, renal failure, moderate arterial hypotension, alcohol abuse, unstable angina (in patients taking nitrates, calcium channel antagonists, β-blockers).
The use of the drug may lead to an increase in the need for insulin in patients with diabetes mellitus. It is not advisable to use it for the correction of dyslipidemia in patients with diabetes mellitus.
Regular monitoring of glucose levels is necessary due to a possible decrease in glucose tolerance, as well as serum uric acid levels due to a possible increase due to prolonged therapy.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding
The drug is contraindicated during pregnancy. If necessary, use of the drug should be discontinued breastfeeding.
Ability to influence reaction speed when driving vehicles or other mechanisms
Studies on the effect of the drug on reaction speed have not been conducted, however, if dizziness and drowsiness are observed during treatment with the drug, you should refrain from working with complex mechanisms.
Method of administration and doses
Administer to adults and children over 15 years of age intravenously (slowly), intramuscularly and subcutaneously (intramuscular and subcutaneous injections are painful).
For intravenous jet administration, a single dose of the drug should be diluted in 10 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride solution; administer over at least 5 minutes (no more than 2 mg of nicotinic acid per minute).
For intravenous drip administration, dilute a single dose of the drug in
100-200 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride solution, administration rate – 30-40 drops per minute.
Pellagra. Administer intravenously or intramuscularly 10 mg (1 ml) 1-2 times a day. The course of treatment is 10-15 days.
Ischemic cerebrovascular disorders. Administer 10 mg (1 ml) intravenously (slowly).
Other indications. Administer subcutaneously or intramuscularly 10 mg (1 ml) once a day for 10-15 days. It is possible to add to the infusion solution: 10 mg (1 ml) of nicotinic acid per 100-200 ml of infusion solution.
Higher doses for intravenous administration: single dose – 100 mg (10 ml), daily dose – 300 mg (30 ml).
Children
The drug is prescribed to children over 15 years of age.
Overdose
Symptoms: increased side effects from the cardiovascular system - arterial hypotension, headache, possible loss of consciousness, dizziness, feeling of flushing.
Treatment: drug withdrawal, detoxification therapy, symptomatic treatment. There is no specific antidote.
Adverse reactions
From the cardiovascular system: a feeling of flushing, which may be accompanied by shortness of breath, tachycardia, palpitations, increased sweating, chills, edema, tingling and burning sensations; arrhythmias; with rapid intravenous administration - a significant decrease in blood pressure, orthostatic hypotension, collapse.
From the side of the central and peripheral nervous system: dizziness, paresthesia, headache.
On the part of the immune system, skin and subcutaneous tissue: hyperemia of the skin of the face and upper half of the trunk with a tingling and burning sensation, dry skin and mucous membrane of the eyes, rarely - retinal edema, very rarely in patients with ischemic heart disease - acanthosis. These symptoms are transient and disappear after discontinuation of the drug. Hypersensitivity reactions, including respiratory tract, urticaria, itching, rash.
Local reactions: soreness, swelling at the site of subcutaneous and intramuscular injections.
With prolonged use in large doses - hyperuricemia, decreased glucose tolerance, impaired liver function, fatty liver, jaundice, increased levels of aspartate aminotransferase, lactate dehydrogenase, alkaline phosphatase, uric acid, hypophosphatemia, decreased platelet count, prolonged prothrombin time, hyperpigmentation, hyperkeratosis, convulsions, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, exacerbation of gastric ulcer, amblyopia, insomnia, myalgia, decreased blood pressure, rhinitis, blurred vision, eyelid edema, myopathy, exfoliative dermatitis.
Expiration date
5 years.
Storage conditions
Store in original packaging at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. Do not freeze.
Keep out of reach of children.
Incompatibility.
Do not mix with solutions of thiamine chloride (thiamine is destroyed), pyridoxine hydrochloride, cyanocobalamin, euphylline, salicylates, tetracycline, sympathomimetics, hydrocortisone.
Packaging
1 ml in an ampoule; 5 ampoules in a contour blister pack; 2 contour blister packs in a pack; 10 ampoules in a box.
Vacation category
According to the recipe.
Producer
PrJSC "Pharmaceutical Company "Darnitsa".
Location of the manufacturer and its business address
Ukraine, 02093, Kyiv, Boryspilska St., 13.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.