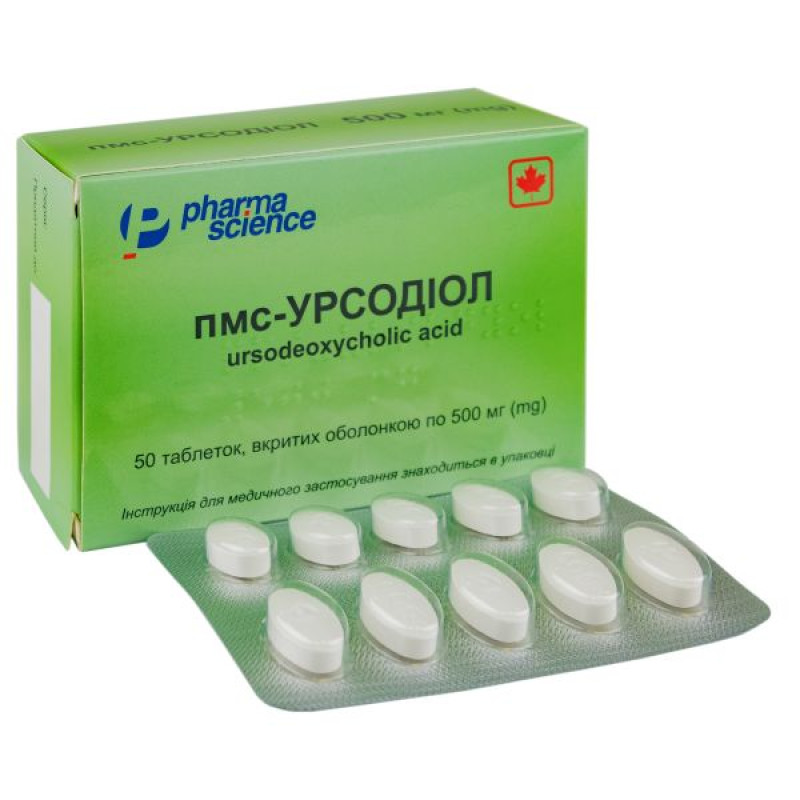
PMS-Ursodiol film-coated tablets 500 mg blister No. 50

Instructions PMS-Ursodiol film-coated tablets 500 mg blister No. 50
Composition
active ingredient: ursodeoxycholic acid;
1 tablet contains 250 mg or 500 mg of ursodeoxycholic acid;
excipients: sodium starch glycolate (type A), povidone, sodium lauryl sulfate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, magnesium stearate, tablet shell (hydroxypropylmethylcellulose, polyethylene glycol).
Dosage form
Film-coated tablets.
Main physicochemical properties:
250 mg tablets: white, elliptical, biconvex, film-coated tablets, debossed with “250” on one side and with or without the “P” logo on the other side;
500 mg tablets:
White, elliptical, biconvex, film-coated tablets with black inscription "UR 500" or imprinted with "500" on one side and imprinted with "P" or plain on the other.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Drugs used to treat liver and biliary tract diseases. Drugs used in biliary pathology.
ATX code A05A A02.
Drugs used in cases of liver disease are lipotropic substances.
ATX code A05B.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Ursodeoxycholic acid is a natural minor component of bile acids. Oral administration of ursodiol leads to a dose-dependent increase in the content of this fraction in the bile acids.
When ursodeoxycholic acid is used in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis, a decrease in cholesterol content is observed, which is due to a decrease in cholestasis and changes in cholesterol metabolism.
Ursodeoxycholic acid is found in small amounts in human bile. After oral administration, ursodeoxycholic acid reduces the cholesterol saturation of bile by inhibiting its absorption in the intestine and reducing cholesterol secretion into the bile. It is possible that due to the dispersion of cholesterol and the formation of liquid crystals, the gradual dissolution of gallstones occurs.
According to current knowledge, it is believed that the effect of ursodeoxycholic acid in liver diseases and cholestasis is due to the relative replacement of lipophilic, detergent-like toxic bile acids with hydrophilic cytoprotective non-toxic ursodeoxycholic acid, improvement of the secretory capacity of hepatocytes, and immunoregulatory processes.
Use in children
Cystic fibrosis
There is information available from clinical reports regarding the long-term use of ursodeoxycholic acid (up to 10 years) in the treatment of children with hepatobiliary disorders associated with cystic fibrosis. There is evidence that the use of ursodeoxycholic acid can reduce proliferation in the bile ducts, stop the progression of histological changes and even eliminate hepatobiliary changes, provided that therapy is started in the early stages of cystic fibrosis. For best effectiveness, treatment with ursodeoxycholic acid should be started immediately after the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis is clarified.
Pharmacokinetics
When taken orally, ursodeoxycholic acid is rapidly absorbed in the jejunum and upper ileum by passive transport, and in the terminal ileum by active transport. The absorption rate is usually 60–80%. After absorption, the bile acid undergoes almost complete conjugation in the liver with the amino acids glycine and taurine and is then excreted in the bile. The first-pass clearance through the liver is up to 60%.
Depending on the daily dose and the underlying liver disorder or condition, the more hydrophilic ursodeoxycholic acid accumulates in the bile. At the same time, there is a relative decrease in other more lipophilic bile acids.
In the liver, ursodeoxycholic acid is conjugated with glycine or taurine and then secreted into the bile. Ursodeoxycholic acid conjugates are absorbed in the small intestine by passive and active mechanisms. The conjugates can be broken down in the ileum by enzymes. The free ursodeoxycholic acid formed can be reabsorbed and conjugated in the liver. Unabsorbed ursodeoxycholic acid passes to the colon, where it is mainly 7-dehydroxylated to lithocholic acid. Some ursodeoxycholic acid is epimerized to chenodiol via a 7-oxo intermediate. Chenodiol also undergoes 7-dehydroxylation to form lithocholic acid. These metabolites are poorly soluble and are excreted in the feces. A small amount of lithocholic acid undergoes reabsorption and conjugation in the liver with glycine or taurine and sulfation at position 3.
Ursodeoxycholic acid undergoes 7-dehydroxylation more slowly than chenodiol. When comparing equimolar amounts of ursodeoxycholic acid and chenodiol, the equilibrium level of lithocholic acid in the bile acid mixture is lower with ursodeoxycholic acid.
Although cholestatic liver lesions do not develop in humans when ursodeoxycholic acid is used, it should be borne in mind that individual differences in the degree of sulfation of lithocholic acid are possible, although, perhaps, deficient states in the ability to sulfate lithocholic acid are actually extremely rare and have practically not been detected, despite the long experience of clinical use of ursodeoxycholic acid.
In healthy subjects, unconjugated ursodeoxycholic acid is approximately 70% bound to plasma proteins. The extent of binding of conjugated ursodeoxycholic acid to plasma proteins is not known. The volume of distribution of ursodeoxycholic acid has not been determined, but is expected to be small, given that the drug is concentrated primarily in the bile and small intestine. Ursodeoxycholic acid is excreted primarily in the feces. Ursodeoxycholic acid is excreted in the urine, although this remains insignificant (less than 1%) except in cases of severe cholestatic liver disease.
With chronic administration of ursodeoxycholic acid, it becomes the main component of bile acids; at a dose of 13–15 mg/kg/day, its share in the total composition of bile acids accounts for 30–50%.
The biological half-life of ursodeoxycholic acid is 3.5–5.8 days.
Indication
For the dissolution of radiopaque cholesterol gallstones no larger than 15 mm in diameter in patients with a functioning gallbladder, despite the presence of gallstone(s).
For the treatment of gastritis with bile reflux.
For the symptomatic treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) in the absence of decompensated liver cirrhosis.
For the treatment of hepatobiliary disorders in cystic fibrosis in children aged 6 to 18 years.
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to any substance included in the medicinal product.
Acute inflammation of the gallbladder or bile ducts.
Bile duct obstruction (occlusion of the common bile duct or cystic duct).
Frequent episodes of hepatic colic.
Radiopaque calcified gallbladder stones.
Violation of gallbladder contractility.
Liver cirrhosis in the decompensation stage.
Unsuccessful outcome of portoenterostomy or lack of adequate biliary outflow in children with bile duct atresia.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions
PMS-Ursodiol should not be used simultaneously with cholestyramine, colestipol or antacids containing aluminum hydroxide and/or smectite (aluminum oxide), as these drugs bind ursodeoxycholic acid in the intestine and thus prevent its absorption and reduce its effectiveness. If the use of drugs containing one of the listed substances is necessary, they should be taken at least 2 hours before or 2 hours after taking PMS-Ursodiol.
PMS-Ursodiol may increase the absorption of cyclosporine from the intestine. In patients taking cyclosporine, the doctor should check the concentration of this substance in the blood and, if necessary, adjust the dose of cyclosporine.
In some cases, the drug may reduce the absorption of ciprofloxacin.
In a clinical study in healthy volunteers, concomitant administration of ursodeoxycholic acid (500 mg/day) and rosuvastatin (20 mg/day) resulted in a slight increase in plasma levels of rosuvastatin. The clinical significance of this interaction for other statins is unknown. Ursodeoxycholic acid reduces the maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) and the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) of the calcium antagonist nitrendipine.
Careful monitoring of the results of concomitant use of nitrendipine and ursodeoxycholic acid is recommended. An increase in the dose of nitrendipine may be necessary.
Considering the above, as well as taking into account the one reported case of interaction with dapsone (reduced therapeutic effect) and the results of in vitro studies, it can be concluded that ursodeoxycholic acid induces the drug-metabolizing enzyme cytochrome P450 3A. However, induction was not observed in a well-designed interaction study with budesonide, a known substrate of cytochrome P450 3A.
Estrogenic hormones and cholesterol-lowering agents such as clofibrate increase hepatic cholesterol secretion and thus may stimulate biliary lithiasis, which counteracts ursodeoxycholic acid, which is used to dissolve gallstones.
Therefore, in the case of concomitant use of drugs that are metabolized by this enzyme, special caution should be exercised and it should be borne in mind that dose adjustment may be necessary.
Application features
PMS-Ursodiol tablets should be taken under the supervision of a doctor.
In the presence of variceal bleeding, hepatic encephalopathy, ascites, and if liver transplantation is necessary, patients should receive appropriate specific treatment.
Monitoring and laboratory data
Monitoring the effectiveness of ursodeoxycholic acid in the treatment of cholestatic liver diseases is based on the analysis of biochemical parameters of cholestasis, as well as the detection of signs of liver cytolysis (increased activity of aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase), which often accompany the progression of cholestasis.
During the first 3 months of therapy, the physician should monitor liver function parameters: aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and γ-glutamyltransferase levels every 4 weeks, and then every 3 months. This allows to determine the presence or absence of an adequate response to treatment in patients with PBC, as well as to timely identify potential liver function abnormalities, especially in patients with PBC in the late stages.
Uses for dissolving cholesterol gallstones
6–10 months after the start of treatment, oral cholecystography should be used to determine the general appearance of the stone and the appearance of gallbladder obstruction in the standing and supine positions (ultrasound). This is necessary to assess therapeutic progress and to promptly detect possible calcification of gallstones.
The drug should not be taken by patients whose gallbladder is not visualized by X-ray methods, patients with calcified stones, impaired gallbladder contractility, or those who have frequent biliary colic.
Patients taking PMS-Ursodiol to dissolve gallstones should use an effective non-hormonal method of contraception, as hormonal contraceptives may increase the formation of gallstones (see sections “Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions” and “Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding”).
Treatment of patients with advanced stage PBC
Cases of decompensated liver cirrhosis, which partially regressed after discontinuation of therapy, have been reported extremely rarely.
In patients with PBC, it is very rare for symptoms to worsen at the beginning of treatment, for example itching may increase. In such cases, the dose of Ursodiol 500 mg film-coated tablets should be reduced to 1 Ursodiol tablet per day; then the dose should be gradually increased as described in the section "Method of administration and dosage".
If diarrhea develops, the dose should be reduced; if diarrhea becomes persistent, treatment should be discontinued.
Excipients
This medicinal product contains sodium starch glycolate (type A) and sodium lauryl sulfate. This should be taken into consideration by patients on a controlled sodium diet.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding
Animal studies have not shown any effect of ursodeoxycholic acid on fertility.
There are no data on the effect on human fertility.
There are insufficient data on the use of ursodeoxycholic acid in pregnant women. Animal studies have shown reproductive toxicity in early pregnancy. PMS-Ursodiol film-coated tablets should not be used in pregnancy unless clearly necessary. Women of childbearing potential should only take the drug when using reliable contraception.
It is recommended to use non-hormonal contraceptives or oral contraceptives with a low estrogen content. Patients receiving PMS-Ursodiol, film-coated tablets, for the dissolution of gallstones should use effective non-hormonal contraceptives, since hormonal oral contraceptives may increase the risk of gallstone formation. Pregnancy should be excluded before starting treatment.
According to several recorded cases of use of the drug in breastfeeding women, the content of ursodeoxycholic acid in milk was extremely low, so no adverse effects should be expected in infants.
Ability to influence reaction speed when driving vehicles or other mechanisms
No effect on the ability to drive or use machines was observed.
Method of administration and doses
PMS-Ursodiol should be administered orally.
There are no age restrictions for the use of the drug. Patients who weigh less than 47 kg or who have difficulty swallowing tablets should use ursodeoxycholic acid in another dosage form (capsules or suspension).
To dissolve cholesterol gallstones
Administer approximately 10 mg ursodeoxycholic acid/kg body weight, equivalent to:
for patients weighing up to 60 kg 500 mg
61 – 80 kg 750 mg
81 – 100 kg 1000 mg
over 100 kg 1250 mg
The tablets should be swallowed whole with water, once a day in the evening before bedtime.
The tablets must be taken regularly.
The time required for gallstones to dissolve is usually 6–24 months. If a reduction in the size of gallstones is not observed after 12 months of treatment, therapy should not be continued.
For the treatment of gastritis with bile reflux
Take 250 mg once a day with some liquid in the evening before bedtime.
Usually, for the treatment of gastritis with bile reflux, the drug should be taken for 10–14 days. The duration of use depends on the patient's condition. The doctor should decide on the duration of treatment in each case individually.
For the symptomatic treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC)
The daily dose depends on body weight and varies from 750 mg to 1750 mg (14±2 mg ursodeoxycholic acid/kg body weight).
During the first 3 months of treatment, the daily dose should be divided into 3 doses during the day. If liver function improves, the daily dose can be taken once a day in the evening.
| Body weight (kg) | Daily dose (mg/kg body weight) | Distribution of drug intake | |||
| first 3 months | in the future | ||||
| morning | day | evening | evening (1 time per day) | ||
| 47 – 62 | 12 – 16 | 250 mg | 250 mg | 250 mg | 750 mg |
| 63 – 78 | 13 – 16 | 250 mg | 250 mg | 500 mg | 1000 mg |
| 79 – 93 | 13 – 16 | 250 mg | 500 mg | 500 mg | 1250 mg |
| 94 – 109 | 14 – 16 | 500 mg | 500 mg | 500 mg | 1500 mg |
| over 110 | 500 mg | 500 mg | 750 mg | 1750 mg | |
The tablets should be swallowed whole with liquid. It is necessary to adhere to the regularity of administration.
The use of PMS-Ursodiol in primary biliary cirrhosis may be unlimited in time.
In patients with primary biliary cirrhosis, in rare cases, clinical symptoms may worsen at the beginning of treatment, for example, itching may increase. If this occurs, therapy should be continued at 250 mg per day, then gradually increased (increase the daily dose by 250 mg every week) until the prescribed dosage regimen is reached.
Use in children
Children with cystic fibrosis aged 6 to 18 years
The dose is 20 mg/kg/day and is divided into 2–3 doses, with a subsequent increase in dose to 30 mg/kg/day if necessary.
| Body weight (kg) | Daily dose (mg/kg) | PMS-Ursodiol, film-coated tablets, 250 mg or 500 mg | ||
| morning | day | evening | ||
| 20 – 29 | 17 – 25 | 250 mg | -- | 250 mg |
| 30 – 39 | 19 – 25 | 250 mg | 250 mg | 250 mg |
| 40 – 49 | 20 – 25 | 250 mg | 250 mg | 500 mg |
| 50 – 59 | 21 – 25 | 250 mg | 500 mg | 500 mg |
| 60 – 69 | 22 – 25 | 500 mg | 500 mg | 500 mg |
| 70 – 79 | 22 – 25 | 500 mg | 500 mg | 750 mg |
| 80 – 89 | 22 – 25 | 500 mg | 750 mg | 750 mg |
| 90 – 99 | 23 – 25 | 750 mg | 750 mg | 750 mg |
| 100 – 109 | 23 – 25 | 750 mg | 750 mg | 1000 mg |
| >110 | 750 mg | 1000 mg | 1000 mg | |
Children
For the dissolution of cholesterol gallstones and symptomatic treatment of PBC:
There are no fundamental age restrictions for the use of ursodeoxycholic acid in children, but children weighing less than 47 kg and/or children who have difficulty swallowing are recommended to use ursodeoxycholic acid in the form of a suspension.
For the treatment of hepatobiliary disorders in cystic fibrosis:
be used in children aged 6 to 18 years.
Overdose
In case of overdose, diarrhea is possible. Other symptoms of overdose are unlikely, since the absorption of ursodeoxycholic acid decreases with increasing dose and therefore most of the dose taken is excreted in the feces.
If diarrhea occurs, the dose should be reduced, and if diarrhea is persistent, therapy should be discontinued.
Treatment is symptomatic and involves restoring fluid and electrolyte balance.
Additional information regarding special patient groups
Long-term therapy with high doses of ursodeoxycholic acid (28–30 mg/kg/day) in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis (off-label use) was associated with a higher incidence of serious adverse events.
Side effects
The frequency of undesirable effects is estimated as follows:
very common: more than 1 in 10 treated;
common: from more than 1 in 100 treated to 1 in 10 treated;
uncommon: from more than 1 in 1000 treated to 1 in 100 treated;
rare: from more than 1 in 10,000 treated to 1 in 1,000 treated;
very rare / frequency unknown: less than 1 in 10,000 treated / cannot be estimated from the available data.
Gastrointestinal: dyspepsia; nausea and abdominal pain, cases of anorexia, esophagitis, peptic ulcer were noted.
During clinical trials, pasty stools or diarrhea were commonly reported during treatment with ursodeoxycholic acid.
Very rarely, severe abdominal pain in the right hypochondrium has been noted during the treatment of PBC.
On the part of the liver and gallbladder: very rarely, calcification of gallstones may occur during treatment with ursodeoxycholic acid.
Skin: cases of itching. Very rarely, allergic reactions are possible, including rash, urticaria.
Metabolic disorders: cases of increased creatinine and increased blood glucose.
General disorders: asthenia, chest pain and peripheral edema.
Cardiovascular system: increased blood pressure.
From the hematopoietic system: cases of leukopenia.
Hypersensitivity reactions: very rarely, allergic reactions are possible, including rash, urticaria.
Expiration date
5 years.
Storage conditions
Store out of the reach of children at a temperature not exceeding 30 ºС.
Packaging
100 tablets in vials.
10 tablets in a blister, 5 blisters in a cardboard box.
Vacation category
According to the recipe.
Producer
Pharmascience Inc.
Location of the manufacturer and address of its place of business
6111 Royalmount Avenue, 100, Montreal, Quebec H4P 2T4, Canada/6111 Royalmount Avenue, 100, Montreal, Quebec H4P 2T4, Canada.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.