Protamine sulfate solution for injection 1000 IU/ml in 5 ml vials No. 5
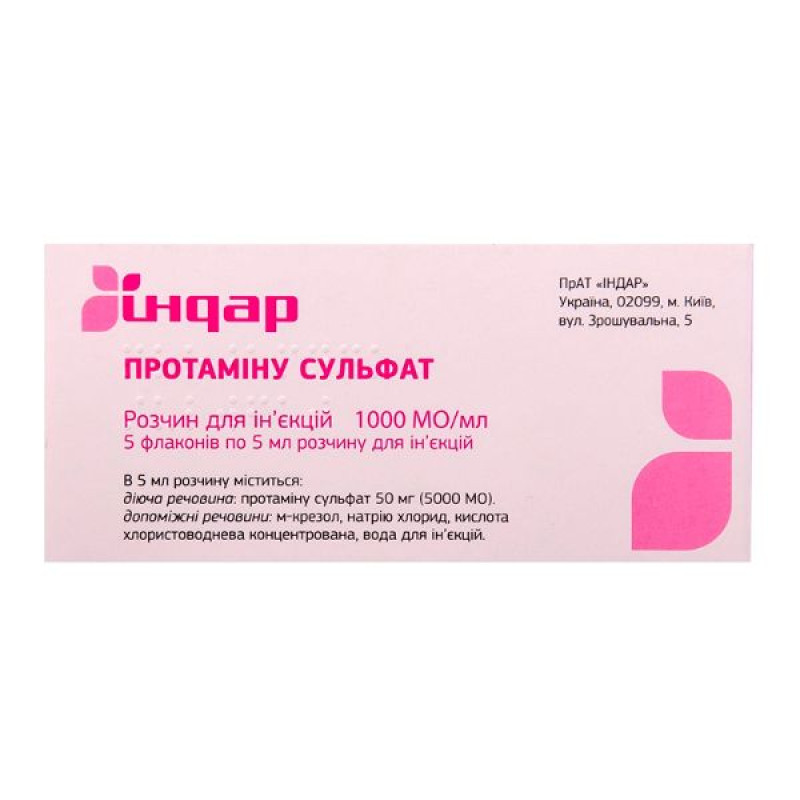
Protamine Sulfate solution for injection 1000 IU/ml in 5 ml vials No. 5
Composition
active ingredient: Protamine Sulfate;
1 ml of injection solution contains 10 mg (1000 IU) of Protamine Sulfate;
Excipients: m-cresol, sodium chloride, concentrated hydrochloric acid, water for injections.
Dosage form
Solution for injection.
Main physicochemical properties: clear colorless liquid.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Antidotes. Protamine. ATX code V03A B14.
Pharmacodynamics
The active ingredient of the drug Protamine Sulfate - has a hemostatic effect. Neutralizes the effect of heparin, reduces its anticoagulant properties. Forms stable complexes with heparin, while heparin loses its ability to inhibit blood clotting. Complex formation is due to a large number of cationic groups (due to arginine), which bind to the anionic centers of heparin. Protamine Sulfate is effective in some types of hemorrhages associated with heparin-like blood clotting disorders.
Pharmacokinetics
When administered intravenously, the effect occurs instantly ("on the needle") and lasts about 2 hours. Protamine Sulfate is excreted from the body mainly by the kidneys and to a lesser extent - through the liver with bile. Together with heparin, it forms an inactive complex, the half-life of which is 24 minutes. Protamine Sulfate is inactivated in blood plasma by enzymes, while the protamine-heparin complex probably breaks down into its components with the release of heparin.
Indication
Use to neutralize the excessive unwanted anticoagulant effect of heparin: in case of overdose, before and after operations on the background of heparin therapy, after operations on the heart and blood vessels using extracorporeal blood circulation, during hemodialysis using heparin.
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug. Idiopathic and congenital hyperheparinemia (in such cases Protamine Sulfate is ineffective and may even increase bleeding); severe arterial hypotension, thrombocytopenia, adrenal insufficiency, hypovolemia.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions
Protamine Sulfate is incompatible with antibiotics of the cephalosporin and penicillin groups, as well as radiopaque substances, since a precipitation reaction may develop.
Application features
During therapy, blood coagulation parameters should be monitored. Before administration, ensure that the patient's blood volume is adequate (hypovolemia increases the risk of collapse). Too rapid administration of the drug may cause a feeling of heat, skin hyperemia, decreased blood pressure, bradycardia, shortness of breath, and allergic reactions.
The use of protamine is associated with the risk of anaphylactic reactions, which can lead to bronchospasm, collapse and cardiac arrest. Therefore, all precautions should be taken.
Protamine Sulfate does not neutralize the effect of indirect anticoagulants of the coumarin type.
When using Protamine Sulfate, unlike other protamine salts, there is no "heparin rebound" effect (when heparin activation decreases before the release of the heparin-protamine complex after the use of extracorporeal circulation).
Cross-sensitivity may occur in diabetic patients receiving protamine-zinc-insulin. Such patients may develop anaphylactic reactions to Protamine Sulfate.
Due to the increased risk of hypersensitivity reactions, protamine should be used with caution in patients who have undergone coronary angioplasty or cardiopulmonary bypass; in infertile men. Due to the risk of anaphylactoid reactions, resuscitation equipment must be available.
Ability to influence reaction speed when driving vehicles or other mechanisms
Unknown.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding
Controlled studies on the effects of the drug on pregnant women have not been conducted to date. Therefore, the drug can be prescribed to pregnant women only if the expected positive effect for the mother outweighs the possible risk to the fetus.
It is not known whether protamine passes into breast milk. Breastfeeding should be discontinued during use of the drug.
Method of administration and doses
Protamine Sulfate should be administered as a very slow intravenous or subcutaneous injection.
The required amount of Protamine Sulfate depends on the level of heparin circulating in the blood; due to the short half-life of heparin, the dose of protamine required to neutralize it decreases in proportion to the time elapsed since the heparin was administered. With bolus injections of heparin, the dose of Protamine Sulfate depends on the time elapsed since the heparin was injected.
Table 1.
Protamine Sulfate Doses Used Depending on the Time Elapsed Since the Heparin Injection
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.