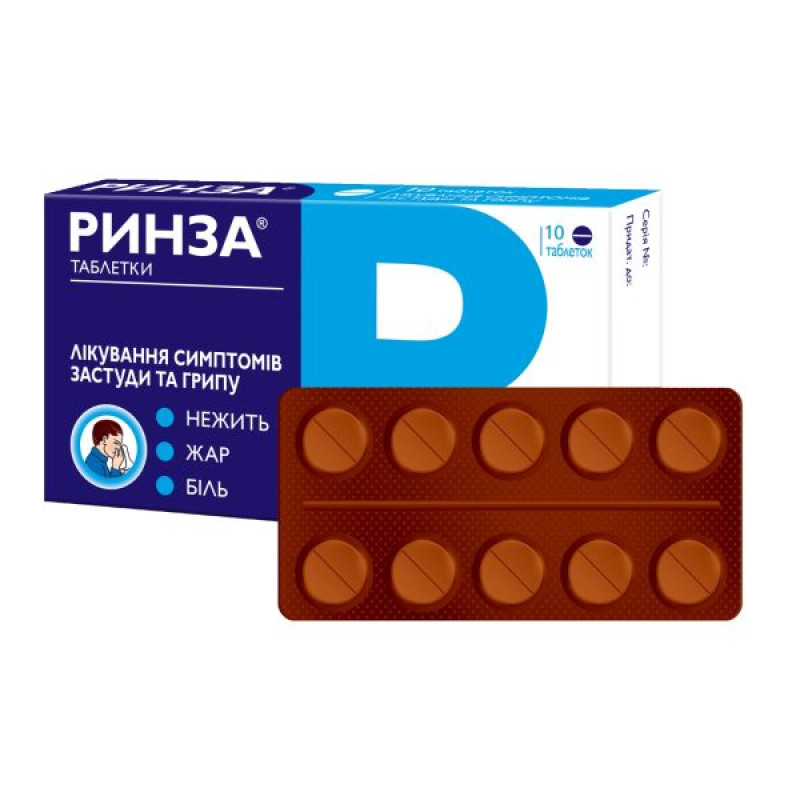
Rinza tablets No. 10

Instructions for Rinza tablets No. 10
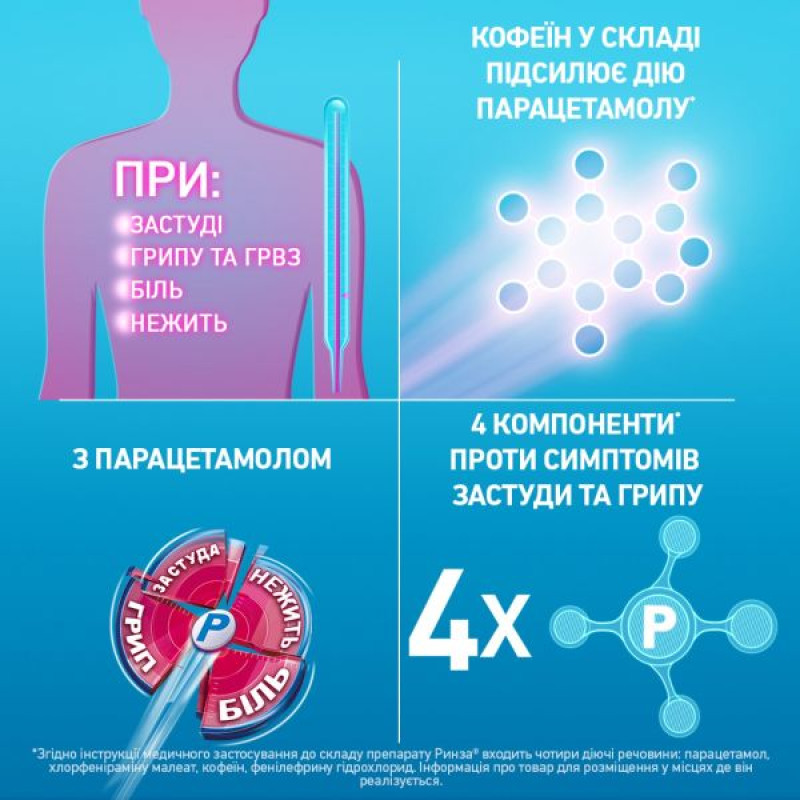
Composition
active ingredients: paracetamol, chlorpheniramine maleate, caffeine, phenylephrine hydrochloride;
1 tablet contains: paracetamol – 500 mg, chlorpheniramine maleate – 2 mg, caffeine – 30 mg, phenylephrine hydrochloride – 10 mg;
excipients: colloidal anhydrous silicon dioxide, corn starch, sodium starch glycolate (type A), magnesium stearate, talc, povidone (K 30), Ponceau 4R dye (E 124).
Dosage form
Pills.
Main physicochemical properties: round, flat, uncoated tablets with beveled edges and a score line on one side, pink in color with dark pink and white inclusions.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Analgesics. Other analgesics and antipyretics. Paracetamol, combinations without psycholeptics. ATX code N02B E51.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
A combined drug with analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects, which are due to the components that make up the drug.
Paracetamol has analgesic and antipyretic effects. It reduces pain associated with rhinitis, sore throat, headache, muscle and joint pain, and also reduces high fever. The analgesic effect is due to the inhibitory effect on prostaglandin synthesis. The antipyretic effect is mediated by the effect on the hypothalamic thermoregulation center.
Chlorpheniramine maleate is a blocker of H1-histamine receptors. Chlorpheniramine has an antiallergic effect: it reduces itching of the eyes, nose and throat, swelling and hyperemia of the mucous membranes of the nasal cavity, nasopharynx and paranasal sinuses, reduces exudative processes. Caffeine has a stimulating effect on the central nervous system, which reduces fatigue and drowsiness, and increases mental and physical performance. Phenylephrine hydrochloride stimulates alpha-adrenergic receptors of vascular smooth muscles. Thus, it causes a vasoconstrictor effect, which causes a decrease in swelling and hyperemia of the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract and nasal sinuses.
Pharmacokinetics
Paracetamol is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Peak plasma concentrations are reached within 0.5–2 hours with somewhat faster absorption when liquid dosage forms are used. In excessive doses, absorption is complete within 4 hours. Distribution of usual analgesic doses results in total serum concentrations of 5 to 20 μg/ml, the corresponding correlation between concentration and analgesic effect is unknown. Serum protein binding ranges from 25 to 50% at toxic concentrations.
Paracetamol is extensively metabolized and excreted in the urine, mainly as inactive gluconate and sulfate conjugates (94%). 2 to 4% is excreted unchanged. About 4% is metabolized by cytochrome P450 oxidase to a toxic metabolite, which is normally detoxified, mainly by conjugation with cysteine and mercapturic acid. The mean half-life is slightly prolonged in newborns (2.2–5 hours) and in patients with cirrhosis. When paracetamol is used for a long time or in high doses in acute conditions, glutathione reserves are depleted and liver necrosis may occur.
Chlorpheniramine maleate is well absorbed after oral administration, the onset of action of the drug is 15–30 minutes, maximum concentrations are reached within 1–2 hours, and the duration of the effect is 4–6 hours. It is mainly metabolized in the liver. Metabolites with antihistamine effect and a small amount of unchanged drug are excreted in the urine. A small amount may penetrate into breast milk.
Caffeine is well absorbed after oral administration (99%). Peak plasma concentrations are 5–25 μg/mL and are reached within 15–45 minutes after a 250 mg dose. Protein binding is 15–17%. Caffeine rapidly crosses the blood-brain barrier and placenta. Therapeutic plasma concentrations are approximately 6–13 μg/mL, with concentrations above 20 μg/mL causing adverse reactions. Concentrations above 100 μg/mL are lethal.
Caffeine is metabolized in the liver. From 0.5 to 3.5% of the drug is excreted unchanged in the urine. Clearance is reduced in alcohol-induced liver disease. In adults, the plasma half-life is 3–7.5 hours (average 3.5 hours). The half-life is prolonged in pregnant women (up to 18 hours) and with the simultaneous use of certain drugs.
Indication
Symptomatic treatment of colds, flu and acute respiratory viral diseases (fever, pain, runny nose).
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to any of the components of the drug; severe atherosclerosis of the coronary vessels; severe cardiovascular diseases, including conduction disorders, severe ischemic heart disease; decompensated heart failure; arterial hypertension; tendency to vasospasm; thrombosis; thrombophlebitis; severe renal and hepatic dysfunction; glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency; congenital hyperbilirubinemia, Gilbert's syndrome; Dubin-Johnson syndrome, Rotor syndrome; acute pancreatitis, acute hepatitis; diabetes mellitus; thyroid disease; pyloroduodenal obstruction; bronchial asthma; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; emphysema; chronic bronchitis; Stevens-Johnson syndrome; pheochromocytoma; hyperthyroidism; phenylketonuria; blood diseases; severe leukopenia; anemia; bladder neck obstruction; Prostatic hypertrophy with difficulty urinating, prostatic hyperplasia; increased intraocular pressure; angle-closure glaucoma; increased excitability, sleep disturbances; epilepsy; alcoholism; old age; hypersensitivity to other xanthine derivatives (theophylline, theobromine); do not use together with antidepressants; do not use together with drugs that suppress or increase appetite and amphetamine-like psychostimulants; do not use together with vasodilators; do not use together with beta-blockers and other sympathomimetics; do not use together with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAO) and within 2 weeks after stopping the use of MAO inhibitors.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions
The simultaneous use of the drug with other medicines containing paracetamol or other active substances that are part of the drug Rinza® should be avoided.
Rinza® potentiates the effect of MAO inhibitors, beta-blockers, sedatives and ethanol. In addition, MAO inhibitors and furazolidone when used together with Rinza® can cause an excited state, hypertensive crisis and hyperpyrexia (due to chlorpheniramine maleate). When taken simultaneously with antidepressants, antiparkinsonian drugs, neuroleptics and phenothiazine derivatives, an atropine-like effect may occur (manifested by dry mouth, urinary retention, constipation).
Phenylephrine with other sympathomimetics increases the risk of adverse cardiovascular reactions, may reduce the effectiveness of ß-blockers and other antihypertensive drugs (reserpine, methyldopa) with an increased risk of arterial hypertension and adverse cardiovascular reactions. The suppressive effect of chlorpheniramine maleate can be significantly increased by simultaneous use of the drug with hypnotics, barbiturates, sedatives, neuroleptics, tranquilizers, anesthetics, narcotic analgesics, alcohol. Phenylephrine can also cause adverse reactions when combined with indomethacin and bromocriptine (severe arterial hypertension). Rauwolfia alkaloids reduce the therapeutic effect of phenylephrine. Chlorpheniramine enhances the anticholinergic effect of atropine, antispasmodics, tricyclic antidepressants, MAO inhibitors, antiparkinsonian drugs. The use of chlorpheniramine with MAO inhibitors and furazolidone can lead to hypertensive crisis, agitation and hyperpyrexia. Caffeine enhances the effect (improves bioavailability) of analgesics-antipyretics, potentiates the effects of xanthine derivatives, alpha- and beta-adrenomimetics, psychostimulants. Cimetidine, hormonal contraceptives, isoniazid enhance the effect of caffeine. Caffeine reduces the effect of opioid analgesics, anxiolytics, hypnotics and sedatives, is an antagonist of anesthetics and other drugs that depress the central nervous system, a competitive antagonist of adenosine drugs, ATP. With simultaneous use of caffeine with ergotamine, the absorption of ergotamine from the gastrointestinal tract improves, with thyroid-stimulating drugs - the thyroid effect increases. Caffeine reduces the concentration of lithium in the blood.
Application features
Do not exceed the indicated dose. Avoid concomitant use with other medicines containing paracetamol or other active substances that are part of the drug Rinza®. This medicine is not recommended for use simultaneously with sedatives and hypnotics.
The drug should be prescribed by a doctor only after assessing the risk/benefit ratio in the following cases: moderate heart disease; heart rhythm disorders; urination disorders; liver diseases. Use with caution in productive cough, in patients with congenitally prolonged QT interval or in case of prolonged use of drugs that can prolong the QT interval.
Serious skin reactions, such as acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis, have been reported very rarely in patients taking paracetamol. Patients should be informed of the symptoms of serious skin reactions. The drug should be discontinued if skin rash or other signs of hypersensitivity appear.
Taking the drug in amounts that exceed the recommended doses may lead to liver damage.
Patients with liver disease should consult a doctor before taking the drug.
If, on the recommendation of a doctor, the drug is used for a long period, it is necessary to monitor the functional state of the liver and the peripheral blood picture.
Before using the drug, you should consult a doctor if you are using warfarin or similar drugs that have an anticoagulant effect. The drug may affect the results of laboratory tests for blood glucose and uric acid.
When using the drug, excessive consumption of coffee, strong tea, other tonic drinks, alcohol, as well as the use of medications containing caffeine should be avoided, as this may cause sleep problems, tremors, tension, irritability, discomfort behind the sternum due to palpitations, dizziness, and arrhythmia.
Taking the drug Rinza® may cause drowsiness.
During treatment, you should refrain from drinking alcohol.
Taking Rinza® may cause a positive analytical result in doping control.
Patients should take the drug with caution when performing work that requires concentration and quick mental and mental reactions.
If the high fever persists for 3 days or more or occurs again, and the pain does not stop for more than 5 days, you should consult a doctor.
Ability to influence reaction speed when driving vehicles or other mechanisms
While using the drug, you should not drive vehicles or operate potentially dangerous mechanisms.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding
It is not recommended to use the drug Rinza® during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Method of administration and doses
Adults and children over 15 years of age are prescribed Rinza® 1 tablet 3–4 times a day 1–2 hours after meals. Wash down with sufficient liquid. A single dose should not exceed 1 tablet. The maximum daily dose is 4 tablets. Do not exceed the recommended dose. The duration of taking the drug is no more than 5 days.
Children
It is not recommended for children under 15 years of age.
Overdose
Symptoms of paracetamol overdose. It is known that toxic effects in adults are possible after taking 10–15 g of paracetamol. The following symptoms may be observed: decreased appetite, pale skin, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, feeling of discomfort in the epigastric region (0–24 hours); increased activity of hepatic transaminases, lactate dehydrogenase, bilirubin level, as well as a decrease in prothrombin level (24–48 hours); hepatotoxic effect, which is characterized by general symptoms (pain, weakness, adynamia, increased sweating) and specific (hepatomegaly, jaundice, increased activity of liver enzymes) symptoms. The hepatotoxic effect can lead to the development of hepatonecrosis and be complicated by the development of hepatic encephalopathy (impaired thinking, depression of higher nervous activity, excitement and stupor), DIC syndrome, hypoglycemia, metabolic acidosis, arrhythmia, seizures, respiratory depression, coma, cerebral edema, hypocoagulation, collapse. Rarely, liver dysfunction develops rapidly and can be complicated by renal failure. When taking large doses, liver pain, disorientation, excitement, dizziness, sleep and heart rhythm disturbances, bacterial infection, fungal infection, sepsis, coagulopathy, hypophosphatemia, lactic acidosis, cardiomyopathy, hypotension, respiratory failure, gastrointestinal bleeding, pancreatitis, acute renal failure, acute liver failure, multiple organ failure syndrome may occur. Glucose metabolism disorders may occur. With prolonged use of high doses, aplastic anemia, pancytopenia, agranulocytosis, neutropenia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia are possible.
In patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, hemolytic anemia may occur when taking large doses of paracetamol.
Symptoms of overdose associated with potentiation of the parasympatholytic action of the antihistamine component and the sympathomimetic action of phenylephrine. Drowsiness, followed by possible agitation (especially in children); visual impairment; nausea, vomiting, headache; circulatory disorders, comatose state; convulsions; behavioral changes; arterial hypertension; bradycardia; atropine-like psychosis.
Symptoms of phenylephrine hydrochloride overdose: dizziness, impaired consciousness, arrhythmias; tachycardia, tremor, hyperreflexia, irritability, restlessness, vomiting, agitation, anxiety, convulsions, headache, hypertension, stroke and paresthesia.
Symptoms of chlorpheniramine maleate overdose. Atropine-like symptoms may occur: mydriasis, photophobia, dryness and redness of the skin and mucous membranes, dry mouth, fever, intestinal atony, decreased level of consciousness, fever, urinary retention, tachycardia, hypertension, hypotension, nausea, vomiting, agitation, confusion, hallucinations, mental disorders, seizures or arrhythmia. Central nervous system depression is accompanied by respiratory disorders and cardiovascular system disorders (decreased pulse rate, decreased blood pressure up to vascular failure). Rhabdomyolysis and renal failure may rarely develop in patients with prolonged agitation, convulsions or in patients in a coma.
Symptoms of caffeine overdose. Headache, tremor, chills, hot flashes, delirium, rigidity, altered consciousness, hypertension with subsequent hypotension, supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias, increased excitability and irritability, cardiac extrasystoles, loss of appetite, weakness, fever, hallucinations, hypokalemia, hyponatremia, increased blood sugar, metabolic acidosis, acute skeletal muscle necrosis. Large doses of caffeine can cause epigastric pain, vomiting, diuresis, rapid breathing, tachycardia or cardiac arrhythmia, effects on the central nervous system (dizziness, insomnia, affective state, anxiety, tremor, convulsions).
Treatment: activated charcoal, gastric lavage, symptomatic therapy, administration of methionine 8–9 hours after overdose and N-acetylcysteine 12 hours after (as antidotes to paracetamol), monitoring of the respiratory and circulatory systems (adrenaline should not be used). In case of convulsions, diazepam is prescribed.
Adverse reactions
In most cases, the drug is well tolerated. Side effects caused by the components of the drug were observed occasionally, usually as a result of prolonged use of the drug in high doses.
Gastrointestinal: heartburn, epigastric discomfort, dyspepsia, hypersalivation, decreased appetite, nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea or flatulence. With long-term use of large doses of the drug - epigastric pain.
On the part of the hepatobiliary system: impaired liver function, increased activity of liver enzymes, increased levels of hepatic transaminases, usually without the development of jaundice, hepatonecrosis (when using high doses), hepatotoxic effect.
Nutritional and metabolic disorders: hypoglycemia, up to hypoglycemic coma, zinc and copper metabolism disorders.
Vascular disorders: increased blood pressure (especially in patients with hypertension).
From the nervous system: headache, feeling of fear, general weakness, dizziness; psychomotor agitation and disorientation, insomnia, anxiety, restlessness, irritability or nervousness, tremor, confusion, depressive states, tingling and heaviness in the limbs, dyskinesia, tinnitus, epileptic seizures, convulsions, coma, paresthesias.
Mental disorders: hallucinations, behavioral changes (anxiety, fear, irritability, sleep disturbances, depression), psychotic reactions, insomnia, disorientation, agitation.
Renal and urinary disorders: nephrotoxicity (including renal colic, interstitial nephritis, papillary necrosis), urinary disorders, dysuria, urinary retention and stranguria (difficulty urinating).
From the blood and lymphatic system: bruising or bleeding; anemia, hemolytic anemia, methemoglobinemia (cyanosis, shortness of breath, heart pain), thrombocytopenia; aplastic anemia, pancytopenia, sulfhemoglobinemia (bruising or bleeding), neutropenia, agranulocytosis, leukopenia.
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: pharyngitis, bronchospasm in patients sensitive to acetylsalicylic acid and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
On the part of the organs of vision: visual impairment and dry eyes, mydriasis, accommodation disorders, increased intraocular pressure.
On the part of the immune system: skin rash, generalized rash, itching, urticaria, hyperemia; bronchial obstruction, erythema multiforme exudative, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis; hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, anaphylactic shock, angioedema. Sometimes allergic-type reactions, including asthma attacks, are observed in patients with intolerance to acetylsalicylic acid.
General disorders and administration site conditions: sleep disturbances, dry nose, mouth or throat; drowsiness, general weakness, increased sweating.
Expiration date
3 years.
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C, in the original packaging, out of the reach of children.
Packaging
10 tablets in a blister; 1 blister in a cardboard box.
Vacation category
Without a prescription.
Producer
Unique Pharmaceutical Laboratories (a division of J.B. Chemicals and Pharmaceuticals Ltd.).
Location of the manufacturer and its business address
Plot No. 101/2 and 102/1, Daman Industrial Estate, Airport Road, Village Kadaya, Daman - 396 210, India.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.