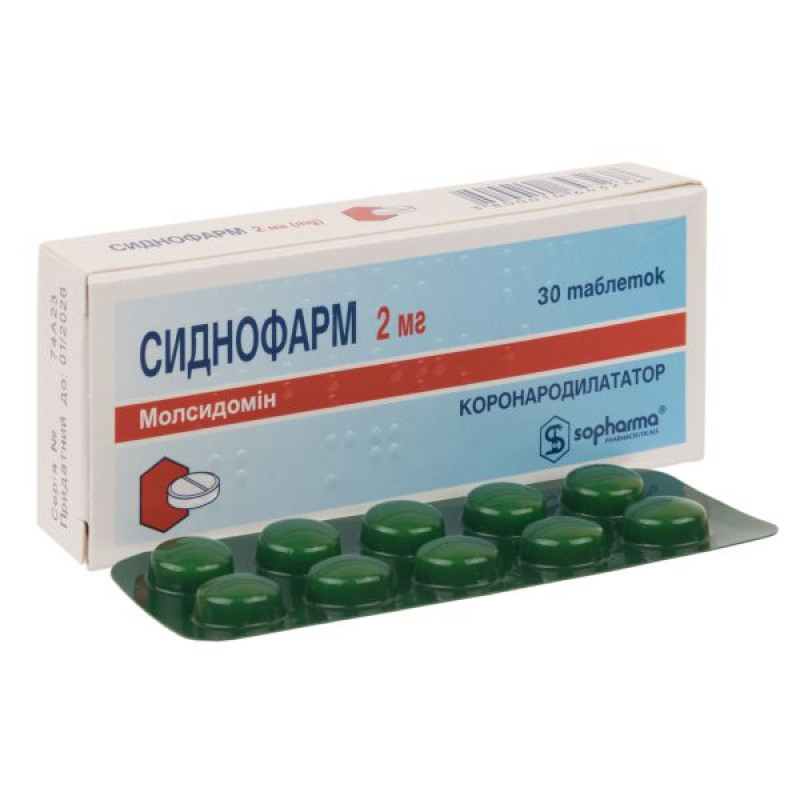
Sydnofarm tablets 2 mg No. 30
Instructions for Sydnopharm tablets 2 mg No. 30
Composition
active ingredient: molsidomine;
1 tablet contains molsidomine 2 mg;
Excipients: lactose monohydrate, mannitol (E 421), wheat starch, microcrystalline cellulose, hypromellose, colloidal anhydrous silica, magnesium stearate, peppermint oil, sunset yellow FCF (E 110).
Dosage form
Pills.
Main physicochemical properties: round, biconvex tablets with a dividing line on one side, 8 mm in diameter, pale pink in color with a minty odor.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Vasodilators used in the treatment of heart disease. Molsidomine. ATC code C01D X12.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Molsidomine exhibits venodilating, antiplatelet, analgesic and long-lasting antianginal effects. Venodilating activity is due to the release of nitric oxide (NO) after a series of metabolic transformations, which stimulates soluble guanylate cyclase, in this regard, molsidomine is considered an NO donor. The accumulation of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) causes relaxation of smooth muscle cells of the vascular wall (mainly veins). Reducing preload, even without affecting myocardial contractility, leads to the restoration of the disturbed ratio between oxygen demand and oxygen supply in patients with coronary insufficiency. It dilates large epicardial coronary arteries affected by atherosclerosis, but capable of dilation, and improves peripheral blood circulation.
Increases tolerance to physical exertion, reduces manifestations of angiospasm. Inhibits the early phase of platelet aggregation, reduces the synthesis and release of serotonin, thromboxane and other proaggregants.
Reduces myocardial preload in patients with chronic heart failure, reduces pulmonary artery pressure, reduces left ventricular filling and myocardial wall tension, stroke volume. The action begins 20 minutes after administration, reaches a maximum in 0.5-1 hour and persists for 6 hours. Unlike nitrate therapy, the development of tolerance with a decrease in effectiveness during long-term therapy with molsidomine is usually not observed.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, it is almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Bioavailability is 60-70%. The maximum concentration (4.4 μg/ml) is reached after 1 hour. When taken orally after a meal, absorption slows down, but does not decrease (the maximum concentration in blood plasma is reached 30-60 min later than when taken on an empty stomach). The minimum effective concentration of molsidomine in blood plasma is 3-5 ng/ml. It practically does not bind to blood plasma proteins. It is metabolized in the liver to form the pharmacologically active compound SIN-1 (3-morpholino-sydnonimine), from which the very unstable substance SIN-1a (N-morpholino-N-aminosintonitrile) is formed, which releases NO to form the pharmacologically inactive compound SIN-1c. Other metabolites are also formed during metabolism. Excreted by the kidneys by 90% (in the form of metabolites), 9% - through the intestines. The half-life is from 1 to 3.5 hours. Does not accumulate (including in patients with renal failure).
In severe liver failure (increase in bromsulfalein test from 20% to 50%), a slowdown in excretion and an increase in the concentration of molsidomine in blood plasma were noted.
Indication
Coronary heart disease: prevention of attacks of stable and unstable angina (especially in elderly patients and with individual intolerance to nitrates). As part of the combined treatment of chronic heart failure.
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients, glaucoma (especially angle-closure), acute angina attack, acute myocardial infarction, acute circulatory failure, including shock (including cardiogenic), vascular collapse, severe arterial hypotension (systolic blood pressure less than 100 mm Hg), simultaneous use of phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) inhibitors (sildenafil, vardenafil, tadalafil) due to the high risk of developing arterial hypotension; toxic pulmonary edema, decreased central venous pressure; simultaneous administration of nitric oxide donors in any form and soluble guanylate cyclase stimulants (e.g. riociguat) is contraindicated due to the risk of hypotension.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions
When used simultaneously with peripheral vasodilators, slow calcium channel blockers (SCBs), antihypertensive agents and ethanol, the antihypertensive effect of the drug is enhanced. Sydnofarm can be used simultaneously with other antianginal drugs (for example, added to two- or three-component therapy - nitrates, BCC and β-adrenoceptor blockers). Alcohol consumption should be avoided during treatment with Sydnofarm.
When used simultaneously with acetylsalicylic acid, its antiplatelet activity is enhanced.
Ergot alkaloids: There is a potential for pharmacodynamic interactions between nitric oxide donors and ergot alkaloids, which could lead to antagonistic drug effects. The concomitant use of nitric oxide donors and ergot alkaloids should be avoided.
The concomitant use of molsidomine and soluble guanylate cyclase stimulators (e.g. riociguat), which are nitric oxide receptor agonists, is contraindicated because the combination may lead to an increased risk of hypotension.
Application features
Do not use for the treatment of acute angina attacks!
Molsidomine does not usually cause a significant decrease in blood pressure, but caution should be exercised when used in patients with hypotension or at increased risk of hypotension, in elderly patients with reduced circulating blood volume, and in patients treated with other vasodilators. Careful monitoring should be ensured and the dose adjusted according to the patient's condition.
During therapy with Sydnopharm, it should be taken into account that resting blood pressure (BP), in particular systolic BP, may decrease. In this case, the hypertensive initial blood pressure reacts much more strongly than the normotensive or hypotensive blood pressure.
Use with caution in hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy, constrictive (stenosing) pericarditis, pericardial tamponade, decreased pressure in the ventricles of the heart, aortic stenosis or mitral stenosis, acute myocardial infarction, impaired left ventricular function (left ventricular failure).
Given that 90-95% of molsidomine metabolites are excreted by the kidneys, it is possible to reduce the dose or increase the intervals between doses of the drug, taking into account the individual patient's response to the drug. Patients with hepatic or renal insufficiency should use lower doses with a gradual increase until the desired therapeutic effect is obtained. In severe liver dysfunction (increase in bromsulfalein test by 20-50%), the concentration of molsidomine in the blood plasma increases and the half-life increases, which requires dose adjustment.
Special attention should be paid to patients after hemorrhagic stroke, with impaired cerebral circulation and increased intracranial pressure; patients with recent myocardial infarction, patients with glaucoma and a tendency to hypotensive reactions or in the presence of arterial hypotension. Sydnofarm should be used only under strict medical supervision with continuous monitoring of blood circulation.
With long-term use of nitrates, it is recommended to include molsidomine in the treatment regimen to prevent the development of nitrate tolerance.
Elderly patients with liver or kidney dysfunction should be prescribed the drug in lower doses.
The drug contains 0.06 g of lactose monohydrate. Patients with rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, the Lapp lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption should not take this medicine.
Wheat starch may contain gluten, but in small amounts, and is therefore considered safe for people with celiac disease.
Dye E 110 may cause allergic reactions.
Ability to influence reaction speed when driving vehicles or other mechanisms
Given the adverse reactions of the drug (dizziness) and the possible negative impact on concentration, the drug should be prescribed with caution to persons who drive a car or work with other mechanisms after a thorough assessment of the possible risk.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding
The use of the drug during pregnancy is contraindicated.
The drug should not be used during breastfeeding. If treatment is necessary, breastfeeding should be discontinued.
Method of administration and doses
The medicine should be taken orally during or after meals, with sufficient liquid.
For the prevention of angina attacks, prescribe 1-2 mg (½-1 tablet) 4-6 times a day on the first and second days of therapy, after which the dose can be increased to 2-4 mg 2-3 times a day if necessary.
The dosage regimen is individual and depends on the type and stage of the disease, the severity of clinical symptoms. Usually the daily dose is 2-4 mg (1-2 tablets), divided into 2 equal doses. Sometimes the dose can be increased to 6-8 mg (3-4 tablets), which should be divided into 3-4 doses.
The maximum daily dose is 12 mg.
The duration of treatment depends on the course of the disease and is determined by the doctor.
Children
The use of the drug in children is contraindicated.
Overdose
Symptoms: bradycardia, weakness, drowsiness, severe headache, dizziness and hypotension, tachycardia, accompanied by nausea and vomiting; in severe cases - collapse.
Treatment: measures are taken to quickly remove the drug from the body (gastric lavage, forced diuresis), symptomatic therapy.
There are no data on the effectiveness of dialysis in overdose.
Adverse reactions
From the nervous system: headache (usually minor, disappears during further treatment), dizziness, increased fatigue, slowed psychomotor and motor reactions (in most cases at the beginning of treatment), weakness.
Gastrointestinal: nausea, loss of appetite, diarrhea, vomiting.
Cardiovascular system: thrombocytopenia, circulatory failure, pronounced decrease in blood pressure, orthostatic hypotension, rarely - to the development of collapse or shock, tachycardia, facial flushing. In these cases, a dose reduction or discontinuation of the drug may be required.
Immune system disorders: hypersensitivity reactions, including allergic reactions, itching, rash, bronchospasm, asthma, anaphylactic shock.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: urticaria.
Expiration date
3 years.
Storage conditions
Keep out of reach of children.
Store in the original packaging at a temperature not exceeding 25 ºС.
Packaging
10 tablets in a blister of PVC film and aluminum foil. 3 blisters in a cardboard pack.
Vacation category
According to the recipe.
Producer
JSC "Sopharma".
Location of the manufacturer and its business address
16 Ilienskoe Shose St., Sofia, 1220, Bulgaria.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.