Tablets for dizziness and nausea tablets 50 mg blister No. 25
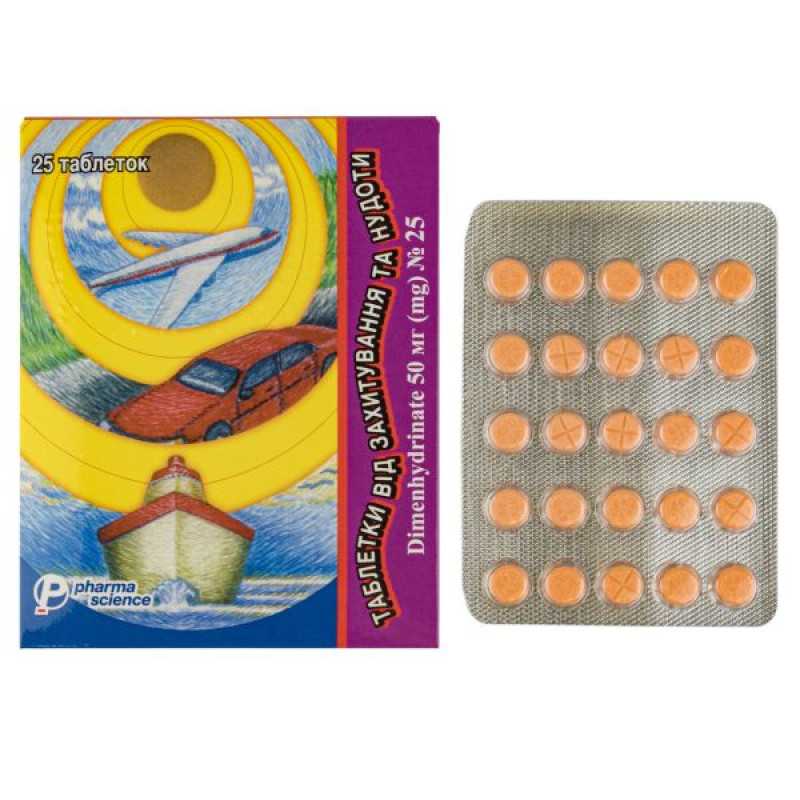
Instructions Tablets for dizziness and nausea tablets 50 mg blister No. 25
Composition
active ingredient: dimenhydrinate;
1 tablet contains 50 mg of dimenhydrinate;
excipients: microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, sunset yellow FCF dye (E 110).
Dosage form
Pills.
Main physicochemical properties: orange tablets, round, flat. On one side of the tablet there is an imprint of "APO 50" or not, on the other side there are two transverse lines.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Drugs used in vestibular disorders. ATX code N07C A.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Dimenhydrinate is the chlorotheophylline salt of the well-known antihistamine diphenhydramine, which blocks H1 receptors and contains approximately 55% diphenhydramine and 45% 8-chlorotheophylline. The pharmacological activity of dimenhydrinate is due to diphenhydramine, which depresses the central nervous system (CNS), has anticholinergic, antiemetic, antihistamine and local anesthetic activity.
Anticholinergic action: inhibition of stimulation of the vestibular apparatus in vertigo (Meniere's syndrome, sea and air sickness). Dimenhydrinate inhibits stimulation of the labyrinth for 3 hours after administration.
Antiemetic action: suppression of the gag reflex. The exact mechanism is not established. Dimenhydrinate suppresses the gag reflex when administered with apomorphine, but is ineffective in vomiting induced by emetogenic chemotherapy. With prolonged use, the antiemetic effect may decrease.
Antihistamine action: significant sedative effect is manifested due to central M-cholinoblocking action. The depressing effect on the CNS lasts for several days of dimenhydrinate use.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, it is well absorbed in the digestive tract. The antiemetic effect occurs after approximately 30 minutes, the duration of action is 3–6 hours. It is widely distributed in the body, including the central nervous system. The degree of binding to blood plasma proteins is 78%.
The active component of dimenhydrinate, diphenhydramine, is metabolized in the liver and excreted primarily as metabolites within 24 hours. A minimal amount of unchanged substance is excreted in the urine.
The half-life is approximately 3.5 hours.
Indication
Prevention and elimination of nausea and vomiting as manifestations of sea and air sickness, during the use of radiotherapy, drugs (except drugs used for chemotherapy in oncological diseases) and after operations.
Symptomatic treatment of Meniere's disease and other vestibular disorders.
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to dimenhydrinate and other antihistamines of similar structure or to any of the excipients included in the product.
Narrow-angle glaucoma, increased intracranial pressure, pheochromocytoma, porphyria, prostatic hyperplasia with urinary retention, epilepsy, eclampsia, acute asthma attack, severe hepatic insufficiency, severe renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance ≤ 25 mmol/min).
Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions
Simultaneous intake of alcohol with dimenhydrinate should be avoided, as it may alter and enhance the effects of dimenhydrinate.
Diphenhydramine may enhance the anticholinergic effects of other drugs (e.g. atropine, antiparkinsonian drugs, tricyclic antidepressants) and the central nervous system (CNS) depressant effects of drugs such as barbiturates, hypnotics, sedatives, tranquilizers, antidepressants, morphine (analgesics, antitussives, drugs for substitution therapy), benzodiazepines, neuroleptics, centrally acting antihypertensive drugs, baclofen, thalidomide.
The drug may enhance the CNS depressant effect of antiepileptic drugs.
Concomitant administration with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) may enhance the anticholinergic effects of diphenhydramine; in isolated cases, paralytic syndrome (sometimes life-threatening), urinary retention, increased intraocular pressure, and possible reduction in blood pressure, central nervous system sedation, and respiratory depression have been reported.
The drug enhances the effect of diazepam, has an effect opposite to the action of amphetamines and their derivatives. Taking dimenhydrinate reduces the effectiveness of corticosteroids and oral anticoagulants.
Concomitant use with bismuth preparations, analgesics and psychotropic drugs, as well as scopolamine may cause visual impairment.
Particular caution should be exercised when prescribing the drug to patients who are taking drugs that prolong the QT interval (class I and II antiarrhythmics: some antibiotics, e.g. erythromycin, antimalarials, antihistamines, neuroleptics), or drugs that cause hypokalemia (e.g. some specific diuretics).
Dimenhydrinate therapy should be discontinued at least three days before allergy testing, as its use may result in a false-negative result.
Application features
The drug should be prescribed with special caution to patients suffering from liver and kidney diseases, hyperthyroidism, bradycardia, arterial hypertension, chronic respiratory diseases, bronchial asthma, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, pyloric stenosis and pyloroduodenal obstruction, gastric ulcer, intestinal obstruction, have congenital long QT syndrome or other clinically significant heart disorders (cardiovascular diseases, circulatory disorders, arrhythmias), and are simultaneously taking other drugs that lead to prolongation of the QT interval or hypokalemia.
Caution should be exercised when prescribing the drug to elderly patients, as they are more likely to develop orthostatic hypotension, obesity, chronic constipation (risk of paralytic syndrome), prostatic hypertrophy, Parkinson's disease, and are more likely to take sedatives. Such patients should take the lowest recommended adult dose, as they are sensitive to the anticholinergic effects of the drug.
The medicine contains lactose.
If you have been told by your doctor that you have an intolerance to some sugars, contact your doctor before taking this medicine.
Patients with rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, the Lapp lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption should not take this medicine.
The medicine contains the dye sunset yellow FCF (E 110), which may cause allergic reactions.
Ability to influence reaction speed when driving vehicles or other mechanisms
Taking the drug may cause drowsiness, impaired coordination of movements, dizziness, and increased reaction time, so while using the drug, you should refrain from driving vehicles or working with mechanisms with an increased risk of injury.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding
The drug is contraindicated during pregnancy. Dimenhydrinate penetrates into breast milk in small amounts, so breastfeeding should be discontinued during treatment.
Method of administration and doses
Take orally, regardless of meals. The tablet can be washed down with a small amount of water.
Prevention and elimination of nausea and vomiting as manifestations of sea and air sickness, during the use of radiotherapy, medications and after surgery
To prevent sea and air sickness, the recommended dose should be taken at least half an hour before boarding a vehicle (plane or ship).
Adults and children over 12 years of age:
The recommended dose is 50 mg (1 tablet) 30–60 minutes before the start of the trip, the dose can be repeated if necessary by 50–100 mg every 4–6 hours.
The maximum daily dose should not exceed 400 mg.
For children aged 6–12 years:
The recommended dose is 25–50 mg (1/2–1 tablet), which can be repeated every 6–8 hours if necessary. The maximum daily dose should not exceed 150 mg.
For children aged 2–6 years:
The recommended dose is 25 mg (1/2 tablet), which can be repeated every 6–8 hours if necessary. The maximum daily dose should not exceed 75 mg.
The maximum daily dose in pediatric practice should not exceed 5 mg/kg.
Elderly patients should use an initial dose of 25 mg (1/2 tablet).
With Meniere's disease and other vestibular disorders
Adults: 50–100 mg (1–2 tablets) every 4–6 hours as needed, not to exceed a maximum daily dose of 400 mg.
Use with caution in patients with renal and/or hepatic insufficiency.
In case of liver failure, the dose should be reduced by 2 times.
In renal failure, the dose is normal.
Children
The efficacy and safety of the drug in children under 2 years of age have not been established. The drug can be used in children over 2 years of age.
Overdose
Symptoms: The first symptoms of overdose appear 0.5–2 hours after taking a toxic dose (25 mg/kg body weight), mainly in the form of headache, dizziness, fatigue and drowsiness.
After some time, additional symptoms appear: itching, constriction of skin vessels, dilation of the pupils with slowing of the pupillary reflex, cycloplegia, nystagmus, decreased muscle strength, tendon reflex, and urinary retention. The heart rate increases significantly, and blood pressure increases or decreases.
Symptoms of central nervous system (CNS) depression (slurred speech, disorientation in time and space, ataxia, coma) or CNS excitation (convulsions, psychosis with hallucinations) are also observed, which gradually increase.
Treatment: gastric lavage, administration of enterosorbents, symptomatic therapy.
Adverse reactions
On the part of the organs of vision: glaucoma, visual impairment, increased intraocular pressure, possible blurred vision, diplopia.
On the part of the auditory system: tinnitus.
From the cardiovascular system: palpitations, tachycardia, arrhythmia, angina attacks, arterial hypotension, including orthostatic.
Gastrointestinal: stomach pain, diarrhea, constipation, dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, increased or decreased appetite, weight gain.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: allergic reactions, photosensitivity, exfoliative dermatitis, rash, urticaria.
From the lymphatic system and hematopoietic system: hemolytic anemia.
On the part of the immune system: angioedema, rarely anaphylactic shock.
On the part of the urinary system: urination disorders (urinary retention due to anticholinergic effect), difficulty urinating.
Hepatobiliary system: liver dysfunction, cholestatic jaundice.
On the part of the respiratory system: nasal congestion, increased viscosity of bronchial secretions.
Others: arthralgia, decreased sweating, dry mucous membranes.
Long-term use of dimenhydrinate may lead to dependence on the drug.
Expiration date
5 years.
Storage conditions
Store out of the reach of children at a temperature not exceeding 30 °C.
Packaging
25 tablets in a blister, 1 blister in a cardboard box.
Vacation category
Without a prescription.
Producer
Pharmascience Inc.
Location of the manufacturer and its business address
6111 100 Royalmount Avenue, Montreal, Quebec H4P 2T4, Canada.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.