Temodal capsules 100 mg No. 5
Instructions for Temodal capsules 100 mg No. 5
Composition
active substance: temozolomide;
1 capsule contains 20 mg or 100 mg of temozolomide;
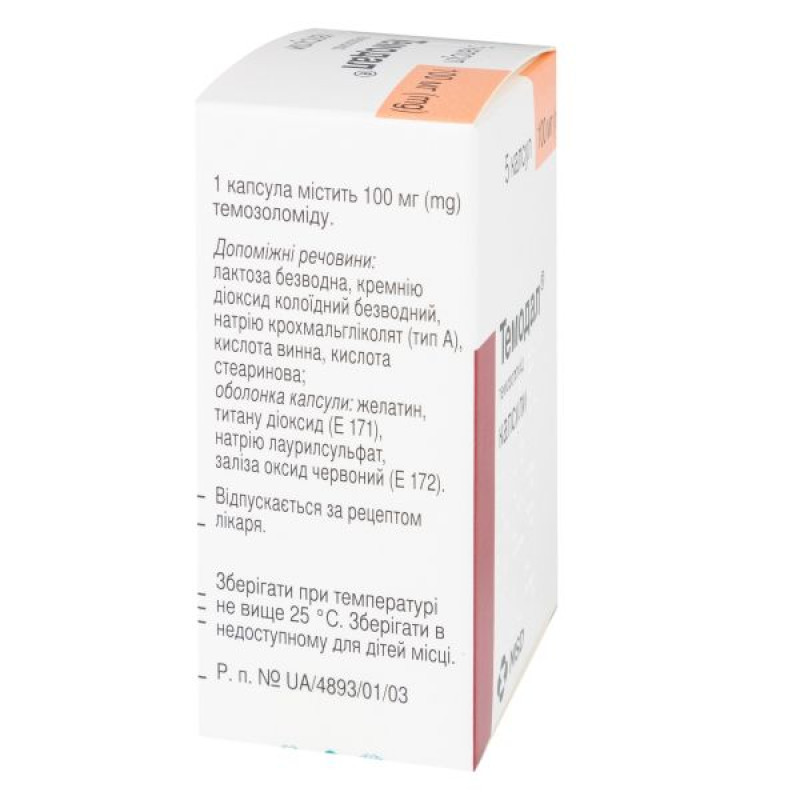
excipients: anhydrous lactose, colloidal anhydrous silicon dioxide, sodium starch glycolate (type A), tartaric acid, stearic acid;
20 mg capsule shell: gelatin, titanium dioxide (E 171), sodium lauryl sulfate, yellow iron oxide (E 172);
100 mg capsule shell: gelatin, titanium dioxide (E 171), sodium lauryl sulfate, red iron oxide (E 172).
Dosage form
Capsules.
Main physicochemical properties: capsules with a cap and a white opaque body. The capsules contain a powder from white to light pink, light beige-brownish. The capsules are printed in black ink: on the cap – TEMODAL; on the body – two stripes, respectively 20 mg or 100 mg and Schering-Plough Logo. The color of the capsule caps corresponds to the dosage: for 20 mg – yellow, for 100 mg – opaque pink.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Antineoplastic agents. Alkylating compounds. ATX code L01A X03.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics.
Temozolomide is a triazene that undergoes rapid chemical conversion to the active 3-methyl-(triazen-1-yl)imidazole-4-carboxamide (MTIC) at physiological pH. The cytotoxicity of MTIC is thought to be primarily due to alkylation of guanine at the O6 position and additional alkylation at the N7 position. The resulting cytotoxic effects appear to involve a mechanism of aberrant methyl reduction.
Pharmacokinetics.
Temozolomide is spontaneously hydrolyzed at physiological pH levels, primarily to the active species 3-methyl-(triazen-1-yl)imidazole-4-carboxamide (MITC). MITC is spontaneously hydrolyzed to 5-amino-imidazole-4-carboxamide (AMIC), a known intermediate in purine and nucleic acid biosynthesis, and to methylhydrazine, which is likely the active alkylating species. The cytotoxicity of MITC is thought to be primarily due to alkylation of DNA, primarily at the O6 and N7 positions of guanine. Relative to the AUC of temozolomide, the exposure to MITC and AMIC is approximately 2.4% and 23%, respectively. The in vivo t1/2 of MITC was similar to that of temozolomide, at 1.8 hours.
Absorption: After oral administration to adult patients, temozolomide is rapidly absorbed with peak concentrations occurring 20 minutes after dosing (mean time 0.5 to 1.5 hours). Following oral administration of 14C-labeled temozolomide, the mean faecal excretion of 14C over 7 days post-dose was 0.8%, indicating complete absorption.
Distribution: Temozolomide exhibits low protein binding (10 to 20%), therefore, interactions with substances that are extensively protein bound are not expected.
Human positron emission tomography (PET) studies and preclinical data indicate that temozolomide rapidly crosses the blood-brain barrier and into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). In one patient, the drug was confirmed to be present in the CSF; exposure in the CSF, based on temozolomide AUC, was approximately 30% of the plasma exposure, which is consistent with animal studies.
Elimination: The plasma half-life (t1/2) of temozolomide is approximately 1.8 hours. The primary route of elimination of 14C is the kidney. After oral administration, approximately 5–10% of the dose is excreted unchanged in the urine within 24 hours, with the remainder excreted as temozolomide acid, 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide, or unidentified polar metabolites.
Plasma concentrations increase with dose. Plasma clearance, volume of distribution, and half-life are independent of dose.
Special populations: Analysis of the pharmacokinetics of temozolomide has shown that the clearance of temozolomide is independent of age, renal function or nicotine dependence. In a separate pharmacokinetic study, the plasma pharmacokinetic profiles of the drug in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment were similar to those in patients with normal hepatic function.
In children, the plasma concentration (AUC) is higher than in adults. However, the maximum tolerated dose for children and adults is the same and is 1000 mg/m2 per treatment cycle.
Indication
Treatment:
adult patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme, in combination with radiotherapy and then as monotherapy;
children aged 3 years and older and adult patients with malignant glioma in the form of glioblastoma multiforme or anaplastic astrocytoma in the presence of relapse or progression of the disease after standard therapy.
Contraindication
Temodal® is contraindicated in patients with:
hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any excipient;
hypersensitivity to dacarbazine (DTIK);
severe form of myelosuppression.
Special safety precautions
Capsules should not be opened. If the capsule is damaged, avoid contact of its contents with the skin or mucous membranes. If Temodal® comes into contact with the skin or mucous membranes, wash the area immediately and thoroughly with soap and water.
Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions
Interaction studies have only been conducted in adult patients.
In a separate phase I study, the use of Temodal® with ranitidine did not result in a change in the extent of temozolomide absorption or exposure to its active metabolite, MTIC.
Administration of Temodal® with food resulted in a 33% decrease in Cmax and a 9% decrease in AUC. Since it cannot be excluded that the change in Cmax is clinically significant, Temodal® should not be taken with food.
Based on data from phase II pharmacokinetic studies, concomitant administration of dexamethasone, prochlorperazine, phenytoin, carbamazepine, ondansetron, histamine H2 receptor antagonists, or phenobarbital does not alter the clearance of Temodal®. Concomitant administration of valproic acid caused a slight but statistically significant decrease in temozolomide clearance.
Studies on the effects of temozolomide on the metabolism or elimination of other drugs have not been conducted. However, since temozolomide is not metabolized in the liver and exhibits low protein binding, its effects on the pharmacokinetics of other drugs are unlikely.
The use of Temodal® with other substances that suppress bone marrow may increase the likelihood of developing myelosuppression.
Application features
Opportunistic infections and reactivation of infections: Opportunistic infections (such as Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia) and reactivation of infections such as hepatitis B and cytomegalovirus have been observed during treatment with Temodal (see section 4.8).
Herpetic meningoencephalitis: Postmarketing cases of herpetic meningoencephalitis (including fatalities) have been reported in patients receiving Temodal in combination with radiotherapy, including when used concomitantly with steroids.
Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia. Patients treated with Temodal in combination with radiotherapy in an extended 42-day regimen were at particular risk of developing Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia. Therefore, prophylaxis against Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia should be considered in all patients receiving Temodal and radiotherapy in a 42-day regimen (maximum 49 days), regardless of lymphocyte count. If lymphopenia occurs, prophylaxis should be continued until lymphopenia returns to grade ≤ 1.
The incidence of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia may be higher when Temodal® is used in a longer treatment regimen. All patients receiving Temodal®, and especially those receiving steroids, should be monitored frequently for the development of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia, regardless of the treatment regimen. Fatalities due to respiratory failure have been reported in patients receiving temozolomide, particularly in combination with dexamethasone or other steroids.
Hepatitis B virus: Reactivation of hepatitis has been reported in the presence of hepatitis B virus, some of which have been fatal. Patients with positive serological evidence of hepatitis B (including active disease) should seek advice from a liver specialist before initiating treatment. Patients should be monitored during treatment and treatment decisions should be made accordingly.
Hepatotoxicity. Liver injury, including fatal liver failure, has been reported in patients treated with Temodal®. Baseline liver function tests should be performed before initiating treatment. In the presence of pathology, the physician should assess the benefit/risk of treatment before initiating Temodal®, including the possibility of fatal liver failure. Patients receiving a 42-day treatment cycle should have liver function tests repeated within the cycle. All patients should have liver function tests after each treatment cycle. In patients with significant abnormal liver function changes, the physician should assess the benefit/risk of continuing treatment. Liver toxicity may occur several weeks (or later) after the last course of Temodal®.
Malignancies: Very rare cases of myelodysplastic syndrome and secondary malignancies, including myeloid leukemia, have also been reported.
Antiemetic therapy. Nausea and vomiting are very commonly associated with the use of Temodal®, therefore antiemetic therapy may be administered before or after the use of the drug.
Adult patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme: Prophylaxis of emesis is recommended prior to the first dose in the combination phase and is strongly recommended during the monotherapy phase.
Laboratory parameters: Patients treated with Temodal® may develop myelosuppression, including prolonged pancytopenia, which may lead to aplastic anemia, sometimes with a fatal outcome. Evaluation of some cases was complicated by the use of concomitant medications for the treatment of aplastic anemia, including carbamazepine, phenytoin, and sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim.
Before starting treatment with Temodal®, the following laboratory parameters should be met: absolute neutrophil count ≥ 1.5 × 109/l, platelet count ≥ 100 × 109/l. A complete blood count should be performed on day 22 (21 days after the first dose) or within 48 hours of this day and then weekly until the absolute neutrophil count is greater than 1.5 × 109/l and the platelet count is greater than 100 × 109/l. If the absolute neutrophil count is < 1.0 × 109/l or the platelet count is < 50 × 109/l during any cycle, the dose in the next cycle should be reduced by one level. Possible daily dose levels are: 100 mg/m2, 150 mg/m2 and 200 mg/m2. The lowest recommended dose is 100 mg/m2 per day.
Children: There is no clinical experience with Temodal® in children under 3 years of age. Experience in older children and adolescents is very limited.
Elderly patients: Elderly patients (over 70 years of age) are at higher risk of developing neutropenia and thrombocytopenia compared to younger patients. Therefore, Temodal® should be administered with caution to elderly patients.
Female patients: Women of childbearing potential should use effective contraception to prevent pregnancy during treatment with Temodal® and for at least 6 months after treatment has ended.
Male patients. Temodal® may have genotoxic effects. Men receiving temozolomide treatment are advised not to father a child for at least 3 months after the last dose of the drug. Before starting treatment, advice should be given regarding cryopreservation of sperm, as there is a possibility of irreversible infertility during treatment with Temodal®.
Lactose. Since Temodal® contains lactose, the drug should not be taken by patients with rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, total lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption.
Sodium.
This medicine contains less than 1 mmol sodium (23 mg) per capsule, that is to say essentially ‘sodium-free’.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding
Pregnancy. There are no data on the use of the drug in pregnant women. In preclinical studies in rats and rabbits, which were administered a dose of 150 mg/m2, data on teratogenic effects and/or toxicity to the fetus were obtained. Therefore, Temodal® should not be prescribed to pregnant women. If it is necessary to use the drug during pregnancy, the woman should be informed of the potential risk to the fetus. Women of childbearing potential should be advised to use effective methods of contraception to prevent pregnancy during treatment with Temodal®.
Breastfeeding: It is not known whether Temodal® passes into breast milk; therefore, breastfeeding should be discontinued during treatment with Temodal®.
Women of childbearing potential: Women of childbearing potential should use effective contraception to prevent pregnancy during treatment with Temodal® and for at least 6 months after treatment has ended.
Male fertility. Temodal® may have genotoxic effects. Therefore, men receiving therapy with this drug should use effective contraception, and are also advised not to father a child for at least 3 months after the last dose and to seek advice on cryopreservation of sperm before starting treatment due to the possibility of irreversible infertility due to Temodal® therapy.
The ability to influence the reaction speed when driving or working with other mechanisms
The ability to drive and use machines may be slightly impaired when taking Temodal® due to the possibility of fatigue and drowsiness.
Method of administration and doses
Temodal® should only be prescribed by a physician experienced in the oncological treatment of brain tumors.
Antiemetic therapy can be administered simultaneously.
Temodal® capsules should be taken on an empty stomach.
The capsule should be swallowed whole with a glass of water. The capsules should not be opened or chewed.
If vomiting occurs after taking the drug, you should not take a second dose of the drug on the same day.
Adult patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme.
Temodal® is used in combination with focal radiotherapy (combination phase), followed by 6 cycles of temozolomide monotherapy (monotherapy phase).
Temodal® is administered orally at a dose of 75 mg/m2 daily for 42 days in conjunction with focal radiotherapy (60 Gy in 30 fractions). Dose reduction is not recommended; decisions to interrupt or discontinue Temodal® should be made weekly based on hematological and non-hematological toxicity criteria. Temodal® at this dose may be extended from 42 days of combination therapy to 49 days if all of the following conditions are met:
absolute neutrophil count ≥ 1.5 × 109/l;
platelet count ≥ 100 × 109/l;
General toxicity criteria (GTC): non-hematological toxicity ≤ grade 1 (excluding alopecia, nausea and vomiting).
Complete blood counts should be performed weekly during treatment. Temodal should be interrupted or discontinued during the combined treatment phase based on hematological and non-hematological toxicity criteria as per Table 1.
Table 1
Interruption or complete discontinuation of Temodal® during combination therapy (Temodal® + radiotherapy)
| Toxicity | Discontinuation of Temodal® | Discontinuation of Temodal® |
| Absolute neutrophil count | ³ 0.5 and < 1.5 ´ 109/l | < 0.5 ´ 109/l |
| Platelet count | ³ 10 and < 100 ´ 109/l | < 10 ´ 109/l |
| CRT non-hematological toxicity (excluding alopecia, nausea and vomiting) | KZT, stage 2 | CTS, grade 3 or 4 |
aThe combined treatment phase (Temodal® + focal radiotherapy) may be continued if all of the following conditions are met: absolute neutrophil count ≥ 1.5 × 109/L; platelet count ≥ 100 × 109/L; CRT: non-hematological toxicity ≤ grade 1 (excluding alopecia, nausea and vomiting).
Monotherapy phase.
4 weeks after the completion of the combined phase of Temodal® + radiotherapy, 6 cycles of monotherapy with Temodal® are prescribed. The dose during cycle 1 (monotherapy) is 150 mg/m2 once daily for 5 days followed by a 23-day treatment-free period. The dose of Temodal® for cycle 2 is increased to 200 mg/m2 per day if the CRT non-hematological toxicity during cycle 1 was ≤ grade 2 (except for alopecia, nausea and vomiting), the absolute neutrophil count is ≥ 1.5 ´ 109/l, and the platelet count is ≥ 100 ´ 109/l. If the dose was not increased in cycle 2, the dose is not increased in subsequent cycles. If the dose was increased, the drug is used at a dose of 200 mg/m2 per day for the first 5 days of each subsequent cycle, except in the case of toxicity. Dose reduction or discontinuation of Temodal® during adjuvant therapy should be performed according to Tables 2 and 3.
During treatment, a complete blood count should be performed on day 22 (21 days after the first dose). Dose reduction or discontinuation of Temodal® should be performed according to the recommendations outlined in Table 3.
Table 2
Temodal® dose levels for monotherapy
| Dose level | Dose (mg/m2/day) | Note |
| 1 | 100 | Decrease due to previous toxicity |
| 0 | 150 | Dose during cycle 1 |
| 1 | 200 | Dose during cycles 2–6 in the absence of toxicity |
Table 3
Dose reduction or discontinuation of Temodal® during monotherapy
| Toxicity | Reducing the dose of Temodal® by 1 level | Discontinuation of Temodal® |
| Absolute neutrophil count | < 1.0 ´ 109/l | see link b |
| Platelet count | < 50 ´ 109/l | see link b |
| CRT non-hematological toxicity (excluding alopecia, nausea and vomiting) | KZT, grade 3 | KZT, stage 4 |
The dose levels of Temodal® are listed in Table 2.
bTemodal® should be discontinued if dose level –1 (100 mg/m2) continues to cause unacceptable toxicity or if grade 3 non-hematologic toxicity (excluding alopecia, nausea, and vomiting) recurs after dose reduction.
Recurrent or progressive malignant glioma in adults and children aged 3 years and older
The treatment cycle is 28 days. For chemotherapy-naive patients, Temodal® is administered once daily at a dose of 200 mg/m2 for 5 days followed by a 23-day rest period. For chemotherapy-experienced patients, the initial dose is 150 mg/m2 once daily for 5 days; in cycle 2, the dose may be increased to 200 mg/m2 once daily for 5 days provided that there is no hematological toxicity.
Certain patient groups
Patients with impaired liver or kidney function
The pharmacokinetics of temozolomide are comparable in patients with normal hepatic function and in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment. There are no data on the use of temozolomide in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) or renal impairment. Given the pharmacokinetic properties of temozolomide, it is unlikely that a dose reduction will be necessary in patients with severe hepatic impairment or any degree of renal impairment. However, temozolomide should be used with caution in such patients.
Based on pharmacokinetic studies in patients aged 19 to 78 years, temozolomide clearance is not affected by age. However, elderly patients (over 70 years) are at increased risk of neutropenia and thrombocytopenia.
Children
Temodal® is prescribed to children aged 3 years and older only for the treatment of recurrent or progressive malignant glioma. Experience with the drug in this group of patients is very limited. The safety and efficacy of temozolomide in children aged less than 3 years have not been established. No data are available.
Overdose
Doses of 500, 750, 1000 and 1250 mg/m2 (total dose per 5-day cycle) were clinically evaluated. Dose-related hematological toxicity occurred at all doses but, as expected, was more severe at the higher doses. An overdose of 10,000 mg (total dose per 5-day cycle) was reported in one patient, resulting in pancytopenia, pyrexia, multiorgan failure and death. Bone marrow suppression (with or without infection), in some cases severe and prolonged, with fatal outcome, has been reported in patients receiving the recommended doses (150-200 mg/m2) for more than 5 days (up to 64 days).
In case of overdose, it is recommended to conduct a hematological examination and, if necessary, supportive treatment.
Side effects
Summary of safety profile
Clinical research experience
In patients treated with Temodal® in clinical trials, the most common adverse reactions were nausea, vomiting, constipation, anorexia, headache, fatigue, seizures, and rash. Most hematological adverse reactions were reported with a frequency of “common”; the frequency of grade 3–4 laboratory abnormalities is presented after Table 4.
In patients with recurrent or progressive glioma, nausea (43%) and vomiting (36%) were generally grade 1 or 2 (0–5 episodes of vomiting in 24 hours) and resolved spontaneously or were easily controlled with standard antiemetic therapy. The incidence of severe nausea and vomiting was 4%.
A list of adverse reactions is provided in Table 4.
Adverse reactions reported during clinical trials and post-marketing use of Temodal® are listed in Table 4. These adverse reactions are classified by system organ class and frequency. Frequencies are defined as: very common (≥ 1/10); common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10); uncommon (≥ 1/1,000 to < 1/100); rare (≥ 1/10,000 to < 1/1,000); very rare (< 1/10,000); not known (cannot be estimated from the available data). Within each frequency grouping, adverse reactions are presented in order of decreasing seriousness.
Table 4
Adverse reactions in patients treated with Temodal®
| Infections and infestations | |
| Often | infection, herpes simplex, pharyngitis1, oral candidiasis |
| Infrequently | Opportunistic infections (including Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia), sepsis§, herpetic meningoencephalitis§, cytomegalovirus infection, cytomegalovirus reactivation, hepatitis B virus§, herpes simplex, reactivation of infections, wound infection, gastroenteritis2 |
| Neoplasms malignant, benign and unspecified | |
| Infrequently | myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), secondary malignancy, including myeloid leukemia |
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders | |
| Often | Febrile neutropenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, lymphopenia, leukopenia, anemia |
| Infrequently | prolonged pancytopenia, aplastic anemia§, pancytopenia, petechiae |
| Immune system disorders | |
| Often | allergic reactions |
| Infrequently | anaphylaxis |
| Endocrine system disorders | |
| Often | Cushingoid3 |
| Infrequently | diabetes insipidus |
| Metabolism and metabolic disorders | |
| Very often | anorexia |
| Often | hyperglycemia |
| Infrequently | hypokalemia, increased alkaline phosphatase |
| Mental disorders | |
| Often | agitation, amnesia, depression, restlessness, confusion, insomnia |
| Infrequently | behavioral disorders, emotional lability, hallucinations, apathy |
| Nervous system disorders | |
| Very often | seizures, hemiparesis, aphasia/dysphasia, headache |
| Often | ataxia, balance disorder, cognitive disorder, impaired concentration, decreased level of consciousness, dizziness, hypoaesthesia, memory impairment, neurological disorders, neuropathy4, paraesthesia, somnolence, speech disorder, taste perversion, tremor |
| Infrequently | status epilepticus, hemiplegia, extrapyramidal disorders, parosmia, gait disturbance, hyperesthesia, sensory disturbances, coordination disorder |
| Visual impairment | |
| Often | hemianopia, blurred vision, visual impairment5, visual field defect, diplopia, eye pain |
| Infrequently | decreased visual acuity, dry eyes |
| Hearing disorders | |
| Often | deafness6, vertigo, tinnitus, earache7 |
| Infrequently | hearing loss, hyperacusis, otitis media |
| Infrequently | palpitation |
| Vascular disorders | |
| Often | hemorrhage, pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, hypertension |
| Infrequently | cerebral hemorrhage, flushing, hot flashes |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | |
| Often | pneumonia, shortness of breath, sinusitis, bronchitis, cough, upper respiratory tract infection |
| Infrequently | respiratory failure§, interstitial pneumonitis/pneumonitis, pulmonary fibrosis, nasal congestion |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | |
| Very often | diarrhea, constipation, nausea, vomiting |
| Often | Stomatitis, abdominal pain8, dyspepsia, dysphagia |
| Infrequently | bloating, fecal incontinence, gastrointestinal disorders, hemorrhoids, dry mouth |
| Hepatobiliary system disorders | |
| Infrequently | hepatic failure§, liver injury, hepatitis, cholestasis, hyperbilirubinemia |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | |
| Very often | rash, alopecia |
| Often | erythema, dry skin, itching |
| Infrequently | toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, angioedema, erythema multiforme, erythroderma, skin exfoliation, photosensitivity reactions, urticaria, exanthema, dermatitis, increased sweating, pigmentation disorders |
| Unknown | drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | |
| Often | myopathy, muscle weakness, arthralgia, back pain, musculoskeletal pain, myalgia |
| Renal and urinary disorders | |
| Often | frequent urination, urinary incontinence |
| Infrequently | dysuria |
| Reproductive system and mammary gland disorders | |
| Infrequently | vaginal bleeding, menorrhagia, amenorrhea, vaginitis, breast pain, impotence |
| General disorders and reactions related to the method of administration of the drug | |
| Very often | fatigue |
| Often | fever, influenza-like symptoms, asthenia, malaise, pain, edema, peripheral edema9 |
| Infrequently | feeling unwell, tremors, facial swelling, tongue discoloration, thirst, dental disorders |
| Laboratory indicators | |
| Often | increased liver enzymes10, weight decreased, weight increased |
| Infrequently | increased gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT) levels |
| Injury, poisoning and procedural complications | |
| Often | radiation injury11 |
1Including pharyngitis, nasopharyngeal pharyngitis, streptococcal pharyngitis.
2Including gastroenteritis, viral gastroenteritis.
3Including Cushingoid, Cushing's syndrome.
4Including neuropathy, peripheral neuropathy, polyneuropathy, peripheral sensory neuropathy, peripheral motor neuropathy.
5Including vision impairment, eye disorders.
6Including deafness, bilateral deafness, sensorineural deafness, unilateral deafness.
7Including ear pain, ear discomfort.
8Including abdominal pain, abdominal pain lower, abdominal pain upper, abdominal discomfort.
9Including peripheral edema, peripheral swelling.
10 Including liver function test elevations: alanine aminotransferase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, hepatic enzymes increased.
11Including radiation injury, radiation skin injury.
§Including fatal cases.
Glioblastoma multiforme discovered for the first time
Laboratory indicators
Myelosuppression (neutropenia and thrombocytopenia) was observed, which is a dose-dependent toxicity of most cytotoxic agents, including temozolomide. During the combination phase and temozolomide monotherapy, grade III or IV neutropenia was observed in 8% of patients and grade III or IV thrombocytopenia in 14% of patients.
Recurrent or progressive malignant glioma
Laboratory indicators.
Grade III or IV thrombocytopenia and neutropenia occurred in 19% and 17% of patients treated for malignant glioma, respectively. This resulted in hospitalization and/or discontinuation of temozolomide in 8% and 4% of patients, respectively. Myelosuppression was predictable (usually in the first few cycles with a nadir between days 21 and 28) and resolved rapidly, usually within 1–2 weeks. There was no evidence of cumulative myelosuppression. The presence of thrombocytopenia may increase the risk of bleeding, and the presence of neutropenia or leukopenia may increase the risk of infection.
According to the population pharmacokinetic analysis, the highest rate was observed in the first cycle of therapy - grade IV neutropenia (absolute neutrophil count < 0.5 × 109/L) in 12% of women and 5% of men; grade IV thrombocytopenia (< 20 × 109/L) in 9% of women and 3% of men. In data on 400 patients with recurrent glioma, grade IV neutropenia occurred in 8% of women and 4% of men during the first cycle of therapy, and grade IV thrombocytopenia occurred in 8% of women and 4% of men, and grade IV thrombocytopenia occurred in 8% of women and 3% of men. In a study of 288 patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme, grade IV neutropenia occurred in 3% of men and 0% of men during the first cycle of therapy, and grade IV thrombocytopenia occurred in 1% of women and 0% of men.
Children.
Oral temozolomide has been studied in children (aged 3–18 years) with recurrent brainstem glioma or recurrent highly differentiated astrocytoma when administered daily for 5 days every 28 days. Although data are limited, it is expected that the tolerability in children will be similar to that in adults. The safety of temozolomide in children under 3 years of age has not been established.
Expiration date
3 years.
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Keep out of reach of children.
Packaging
1 capsule in a sachet; 5 (1 × 5) or 20 (1 × 20) sachets in a cardboard box.
Vacation category
According to the recipe.
Producer
Organon Heist bv, Belgium.
Merck Sharp & Doom B.V., Netherlands.
Location of the manufacturer and its business address.
Industrial Park 30, 2220 Heist-op-den-Berg, Belgium.
Vaarderweg 39, 2031 BN Haarlem, Netherlands.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.