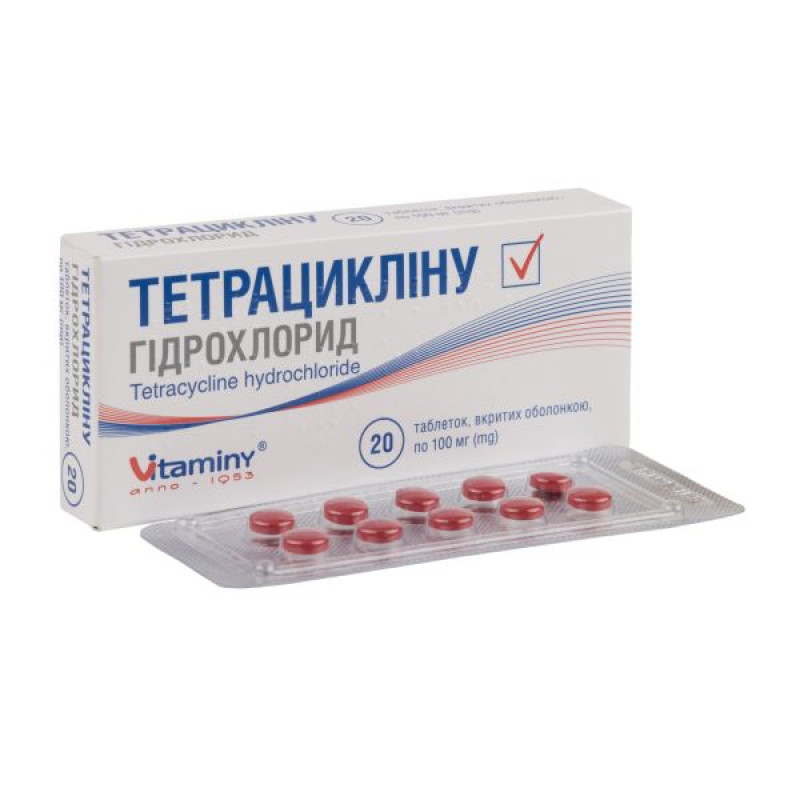
Tetracycline hydrochloride film-coated tablets 100 mg blister No. 20

Instructions Tetracycline hydrochloride film-coated tablets 100 mg blister No. 20
Composition
active ingredient: tetracycline hydrochloride;
1 tablet contains tetracycline hydrochloride 100 mg;
excipients: sugar, gelatin, calcium stearate, talc, potato starch, polysorbate, Opadry II red 85F35289 (mixture of substances: polyvinyl alcohol, polyethylene glycol 3350, titanium dioxide (E 171), talc, carmine (E 120), red
magic AC (E 129), sunset yellow FCF (E 110)).
Dosage form
Film-coated tablets.
Main physicochemical properties: round, film-coated tablets, from crimson to red-brown in color, with a smooth biconvex surface.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Antibacterial agents for systemic use. Tetracyclines.
ATX code J01A A07.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
A broad-spectrum tetracycline antibiotic. Active against gram-positive (staphylococci, including those that produce penicillinase; streptococci, pneumococci, clostridia, listeria, anthrax) and gram-negative bacteria (gonococci, bordetella, Escherichia coli, enterobacteria, Klebsiella, salmonella, shigella), as well as spirochetes, rickettsia, leptospira, pathogens of trachoma, ornithosis. Little or no activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus, seraria, acid-fast bacteria, most strains of Bacteroides fragilis, fungi, influenza viruses, polio, measles. There is evidence of the effectiveness of tetracycline in cholera.
The mechanism of antibacterial action of tetracycline is based on the inhibition of ribosomal protein synthesis of the microbial cell.
In commonly used doses, tetracycline acts bacteriostatically.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, it is rapidly absorbed by 75-77% in the digestive tract (food reduces absorption), binds well to blood plasma proteins. It is rapidly distributed in most body fluids, including bile, secretion around the nasal sinuses, pleural effusion, synovial, ascitic fluids. It accumulates in liver cells, spleen, tumors, teeth; passes through the placenta and penetrates into breast milk. Therapeutic concentrations are reached after 2-3 days. It is excreted by the kidneys by glomerular filtration, with feces (kidneys and bile - 60%), 65% binds to proteins; the half-life in the norm is 6-11 hours, with anuria - 57-108 hours.
Impaired renal excretory function may lead to increased blood concentrations of tetracycline.
Indication
Infectious-inflammatory diseases caused by microorganisms sensitive to the drug, such as: bronchitis, pneumonia, purulent pleurisy, subacute septic endocarditis, bacterial and amoebic dysentery, whooping cough, tonsillitis, scarlet fever, gonorrhea, brucellosis, tularemia, typhus and relapsing typhus, psittacosis, ornithosis, biliary and urinary tract infections, purulent meningitis, purulent infections of the skin and soft tissues, cholera.
Prevention of postoperative infections.
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to the drug and to related antibiotics, local anesthetics (lidocaine, procaine); fungal diseases, systemic lupus erythematosus. The drug should not be prescribed to mothers during breastfeeding and children under 12 years of age; to patients with liver and kidney diseases with severe functional insufficiency. Cases of benign intracranial hypertension have been reported with the simultaneous use of tetracyclines with vitamin A or retinoids, therefore their simultaneous use should be contraindicated.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions
Taking tetracyclines orally simultaneously with antacids containing calcium, aluminum and magnesium, with sodium bicarbonate and cholestyramine may be accompanied by a decrease in the bioavailability of the antibiotic due to the formation of non-absorbable complexes and an increase in the pH of the gastric contents. Therefore, it is necessary to observe intervals of 1-3 hours between taking tetracyclines and antacids.
It is not recommended to combine tetracyclines with iron preparations, as this may disrupt their mutual absorption.
Concomitant use of tetracycline with digoxin or lithium preparations may increase the concentration of the latter in the blood serum.
The combination of drugs based on ergot alkaloids with tetracycline increases the risk of developing ergotism.
Tetracycline should be used with caution with methotrexate, as it may increase the toxicity of the latter. If concomitant administration of the drugs is necessary, regular monitoring of toxicity is required.
The drug should not be used in combination with typhoid vaccine to prevent a decrease in the therapeutic effect of the latter.
Combination with penicillins, cephalosporins, which have a bactericidal effect and are antagonists of bacteriostatic antibiotics (including tetracycline), should be avoided.
Retinoids such as acitretin, isotretinoin, and tretinoin (for acne) can cause benign intracranial hypertension when used concomitantly with tetracyclines, so their concomitant use should be contraindicated.
The simultaneous use of tetracyclines and combined oral contraceptives (COCs) containing an estrogen component leads to the need for "back-up contraception" due to the observed decrease in COC reliability.
The combination of tetracycline with oleandomycin and erythromycin is considered synergistic.
Requires caution when used together with diuretics.
Use caution when prescribing tetracycline with diabetes medications (insulin, glibenclamide, or gliclazide).
Tetracyclines may enhance the effect of indirect anticoagulants due to inhibition of their metabolism in the liver, which requires careful monitoring of prothrombin time.
Increases the nephrotoxicity of methoxyflurane; when used together with retinol, the risk of developing intracranial hypertension increases.
Chymotrypsin increases the concentration and duration of tetracycline circulation.
When taken simultaneously with bismuth subsalicylate, the absorption of tetracyclines is reduced and their bioavailability is reduced.
Tetracycline should be administered with caution together with analgesics (methoxyflurane); atovaquone and hepatotoxic drugs.
Application features
In case of impaired renal function, cumulation of the drug and an increased risk of side effects are possible.
Tetracycline hydrochloride should be prescribed with caution in cases of leukopenia.
With prolonged use of the drug, blood tests, kidney and liver function tests should be performed periodically.
During use of the drug, insolation and UV radiation should be avoided.
Prolonged use of tetracycline hydrochloride may lead to the development of superinfection caused by resistant microorganisms; in this case, adequate antimicrobial therapy should be prescribed.
If symptoms of candidiasis appear, prescribe antifungal drugs and vitamins.
Tetracycline drugs can cause irreversible tooth discoloration (yellow-gray-brown) when used during tooth development (second half of pregnancy and early childhood up to 12 years of age).
Do not use in patients with porphyria.
The drug should be used with caution in patients with myasthenia gravis due to the possibility of mild neuromuscular blockade.
The anti-anabolic effect of tetracyclines may be the cause of increased residual urea nitrogen levels.
The use of tetracycline can lead to exacerbation of systemic lupus erythematosus.
During tetracycline therapy, diarrhea caused by Clostridium difficile may develop.
Tetracycline hydrochloride should not be taken simultaneously with milk or other dairy products, as this impairs its absorption.
The drug should be taken standing up and washed down with a full glass of water to prevent damage to the esophagus and irritation of the digestive tract mucosa, strictly adhere to the prescribed regimen throughout the course of treatment, do not miss doses and take them at regular intervals. If you miss a dose, take it as soon as possible; do not take it if it is almost time for the next dose; do not double the dose.
Therapy should be carried out under the supervision of a physician. If signs of hypersensitivity to the drug and adverse reactions appear, discontinue use of the drug and, if necessary, prescribe another antibiotic (not from the tetracycline group).
It can mask the manifestations of syphilis, so serological testing should be performed monthly for 4 months.
To prevent possible complications, it is very advisable to simultaneously use hepatoprotectors, choleretics, eubiotics, vitamins, and antifungal drugs.
The dye sunset yellow FCF (E 110), which is part of the tablet coating, may cause allergic reactions.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding
The drug is contraindicated for use during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Ability to influence reaction speed when driving vehicles or other mechanisms
There is no data on the negative impact of the drug on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery.
Method of administration and doses
Tetracycline should be taken one hour before or two hours after a meal, as food and some dairy products interfere with absorption. The tablets should be taken with water.
The dosage and course of treatment are determined by the doctor depending on the nature and course of the disease. The course of treatment must be continued for three days after the disappearance of clinical manifestations of the disease.
All infections caused by β-hemolytic streptococcus should be treated for at least 10 days.
Adults (including elderly patients) and children over 12 years of age. The usual single dose is 200 mg (2 tablets) every 6 hours. In severe infections, the dose may be increased to 500 mg every six hours.
The maximum daily dose is 2 g.
Renal insufficiency. In general, tetracyclines are contraindicated in renal insufficiency unless the use of this class of drugs is considered absolutely necessary. The daily dose should be reduced by reducing the recommended individual doses and/or by extending the intervals between doses.
Children
Do not use the drug in children under 12 years of age.
Overdose
Symptoms: increased severity of the described side effects.
Treatment: symptomatic therapy.
Adverse reactions
The drug is generally well tolerated. In some cases, the following reactions may occur:
- From the cardiovascular system: pericarditis.
- On the part of the digestive system: anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain or discomfort, constipation, dry mouth, sore throat, hoarseness, heartburn, stomatitis, glossitis with papillary hypertrophy and blackening of the tongue, esophagitis, gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, proctitis, dysphagia, hepatotoxic effects (stomach pain, nausea, vomiting), increased activity of "liver" transaminases, hyperbilirubinemia, pancreatitis (abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting), intestinal dysbacteriosis, staphylococcal enterocolitis, less often - pseudomembranous colitis. Liver damage with clinical manifestations (malaise, fever and/or pain in the right hypochondrium, stomach pain, nausea, vomiting) is possible.
- From the nervous system: dizziness, photophobia, unsteady gait, headache, with prolonged use - increased intracranial pressure (anorexia, headache, vomiting, optic nerve swelling, vision changes), temporary loss of vision, hearing impairment.
- From the side of the hematopoietic organs: hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, anemia, Moszkovich disease, eosinophilia, agranulocytosis.
- From the urinary system: azotemia, hypercreatininemia, acute renal failure, nephritis, vaginitis.
- Allergic and immunopathological reactions: maculopapular rashes, exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, skin hyperemia, urticaria, angioedema, anaphylactoid reactions, anaphylaxis, photosensitization.
- Respiratory system: bronchospasm.
- Others: hypovitaminosis, hypersensitivity, candidiasis, pigmentation of the skin, mucous membranes, hypertrophy of the lingual papillae (change in tongue color), excessive growth of fungi, itching of the anus and genitals, defects in tooth enamel, change in tooth enamel color in children (staining of teeth in yellow or gray-brown color), impaired bone formation, slowing of linear bone growth (in children); changes in laboratory parameters (levels of alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, blood urea nitrogen may increase).
If signs of increased sensitivity and side effects appear, the course of treatment should be stopped and a doctor should be consulted.
Expiration date
3 years.
Storage conditions
Store in the original packaging at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Keep out of reach of children.
Packaging
10 tablets in blisters; No. 10x1 or No. 10x2 blisters in a cardboard pack.
Vacation category
According to the recipe.
Producer
PJSC "Vitamins".
Location of the manufacturer and its business address
Ukraine, 20300, Cherkasy region, Uman city, Leninskaya Iskra st., 31.
Applicant
PJSC "Vitamins".
Location of the applicant and/or applicant's representative
Ukraine, 20300, Cherkasy region, Uman city, Leninskaya Iskra st., 31.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.