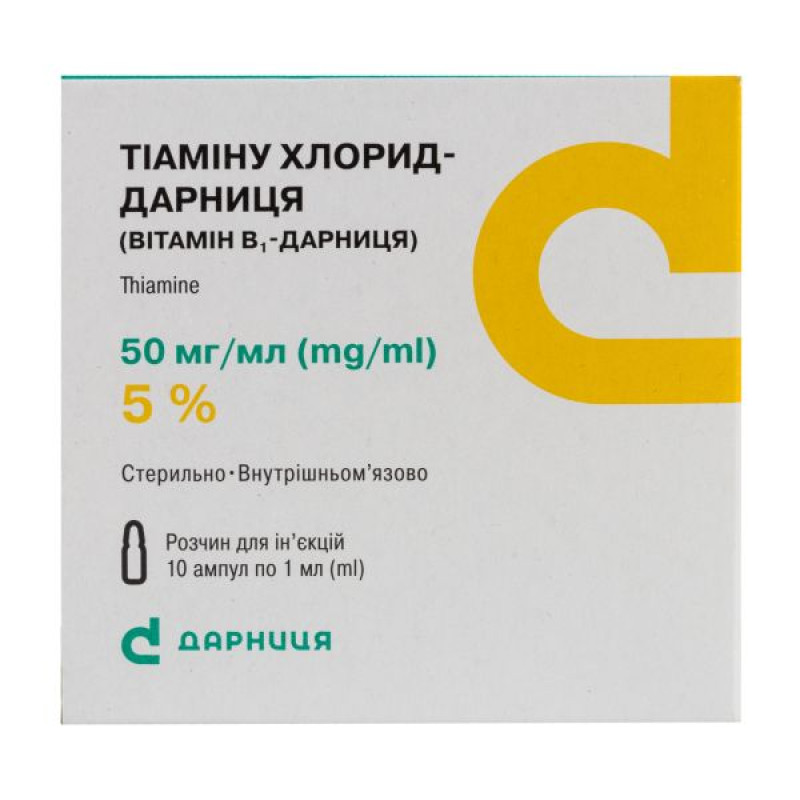
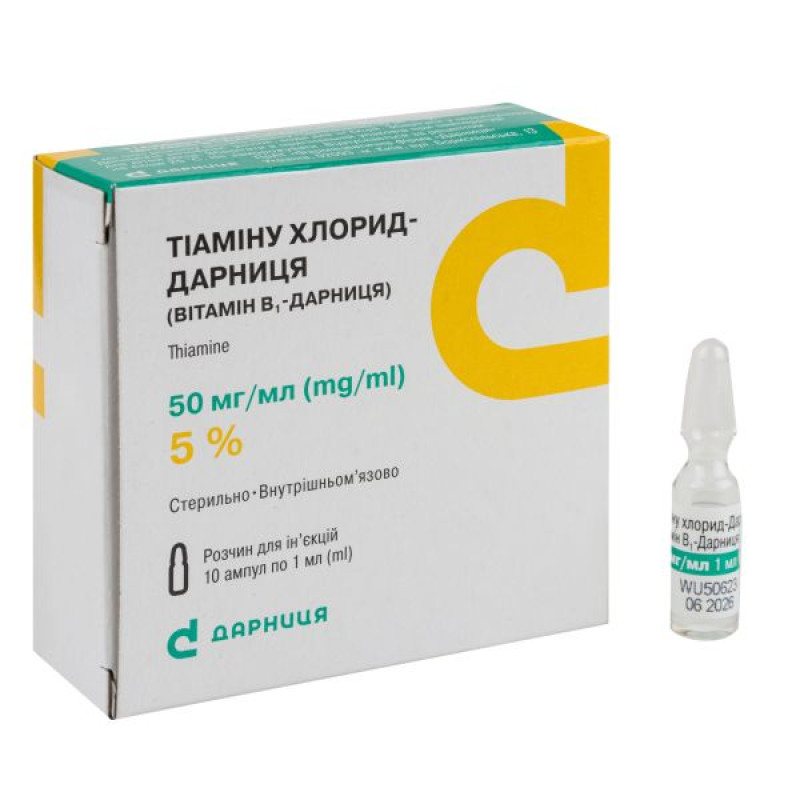
Thiamine chloride-Darnitsa (Vitamin B1-Darnitsa) solution for injection 50 mg/ml ampoule 1 ml No. 10
Instructions for Thiamine chloride-Darnitsa (Vitamin B1-Darnitsa) solution for injection 50 mg/ml ampoule 1 ml No. 10
Composition
active ingredient: thiamine hydrochloride;
1 ml of solution contains thiamine hydrochloride 50 mg;
Excipients: unitiol, water for injection.
Dosage form
Solution for injection.
Main physicochemical properties: clear colorless or slightly yellowish liquid with a faint characteristic odor.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Simple preparations of vitamin B1. Thiamine (vitamin B1).
ATX code A11D A01.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics.
Thiamine chloride-Darnitsa is a synthetic preparation of vitamin B1, belongs to the water-soluble vitamins. In the human body, as a result of phosphorylation processes, it is converted into cocarboxylase, which is a coenzyme of many enzyme reactions. Vitamin B1 plays an important role in metabolism and neuro-reflex regulation, affects the conduction of nerve excitation in synapses, has a ganglioblocking and curare-like effect. The drug can weaken the curare-like effect of depolarizing muscle relaxants.
Pharmacokinetics.
The drug is well absorbed. Phosphorylation occurs in the liver. Accumulates in the liver, heart, brain, kidneys, spleen. Excreted by the liver and kidneys, approximately 8-10% - in unchanged form.
Clinical characteristics.
Indication
Treatment of hypo- and avitaminosis B1, neuritis, polyneuritis, radiculitis, neuralgia, peripheral paralysis, encephalopathy, neurasthenia, gastric and duodenal ulcers, intestinal atony, chronic liver damage, myocardial dystrophy, endarteritis, dermatoses of neurogenic origin, pyoderma, eczema, psoriasis.
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug; allergic diseases; idiosyncrasy; premenstrual and menopausal periods in women.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions
When using the drug simultaneously with other medications, it is possible:
with depolarizing muscle relaxants (suxamethonium chloride), choline derivatives - weakening of their therapeutic effect;
with thiosemicarbazone, 5-fluorouracil – inhibition of thiamine activity;
with caffeine, drugs containing sulfur and estrogens - increased body need for thiamine;
with anticonvulsants (phenobarbital, phenytoin, carbamazepine), digoxin, indomethacin, antacids - development of thiamine deficiency;
with cyanocobalamin, pyridoxine – difficulty in converting thiamine into a phosphorylated biologically active form and increased allergenic effect. Simultaneous parenteral administration of thiamine with pyridoxine (vitamin B6) or cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) is not recommended;
with ethanol – slowing down the rate of thiamine absorption;
with adrenomimetics, sympathomimetics - weakening of their therapeutic effect.
Thiamine is unstable when administered intravenously simultaneously with solutions containing sodium hydrosulfite as an antioxidant or preservative.
Thiamine is unstable in alkaline and neutral solutions, administration with carbonates, citrates, barbiturates, Cu2+, iodide, ferric ammonium citrate, and tannic acid is not recommended.
Application features
Before parenteral administration of thiamine chloride solution, a skin test for individual sensitivity to the drug is mandatory. After the injection, monitoring is required for 30 minutes due to the possibility of severe allergic reactions.
Anaphylactic reactions develop more often after intravenous administration in high doses.
Thiamine injections should preferably be given no earlier than 12 hours after pyridoxine injections.
When administered intramuscularly, the drug should be injected deep into the muscle, and when administered intravenously, slowly.
Intramuscular and subcutaneous injections are painful due to the low pH of the solution.
Daily requirement for vitamin B1: for adult men – 1.2-2.1 mg, for the elderly – 1.2-1.4 mg, for women – 1.1-1.5 mg with the addition of 0.4 mg for pregnant women and 0.6 mg for women during breastfeeding, for children, depending on age, – 0.3-0.5 mg.
The drug should not be used as a substitute for a balanced diet, only in combination with diet therapy.
The injectable form of the drug should be used in the treatment of patients with intestinal malabsorption or with gastric resection, when it is impossible to take thiamine in tablet form (nausea, vomiting, pre-| and postoperative period), as well as in severe forms of the disease or at the beginning of treatment to achieve a therapeutic effect more quickly.
It is recommended to start parenteral administration with small doses (no more than 0.5 ml for adults), and only if well tolerated, administer higher doses.
Use with caution in cases of increased excitability of the nervous system, hyperacidic forms of duodenal ulcer.
In Wernicke's encephalopathy, it is necessary to take thiamine before administering glucose.
If an allergy to vitamin B1 is detected, the patient should avoid rice, buckwheat, meat, and bread (varieties baked from wholemeal flour).
Thiamine may weaken the effect of depolarizing muscle relaxants, adrenolytic and sympathomimetic agents.
The drug (when taken in high doses) may distort the results of the determination of theophylline in blood serum by spectrophotometric method and urobilinogen using Ehrlich's reagent.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding
The drug can be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding according to indications in recommended doses.
Ability to influence reaction speed when driving vehicles or other mechanisms
During treatment, caution should be exercised when driving vehicles and working with complex mechanisms due to the possibility of developing side effects from the nervous system.
Method of administration and doses
Adults.
The drug is administered intramuscularly (deep into the muscle) at a dose of 25-50 mg (0.5-1 ml) once a day, daily. The administration should begin with small doses - no more than 25 mg (0.5 ml of a 5% solution) and only if well tolerated, higher doses should be administered - 50 mg (1 ml of a 5% solution). The course of treatment is 10-30 injections.
Wernicke-Korsakoff encephalopathy: the drug is administered intramuscularly (deep into the muscle) at a dose of 50-100 mg (1-2 ml of a 5% solution) 2 times a day until clinical improvement. The possibility of an allergic reaction to the administration of vitamin B1 should be taken into account.
Children over 8 years of age: the drug is prescribed in a dose of 12.5 mg (0.25 ml of 5% solution) once a day, daily. The course of treatment is 10-30 injections.
Children
For children, a 2.5% solution of thiamine chloride is usually used. A 5% solution may be administered to children over 8 years of age.
Overdose
Symptoms: possible increase in symptoms of side effects of the drug. The development of hypercoagulation, disorders of purine metabolism is not excluded.
Treatment: drug withdrawal, symptomatic therapy.
Adverse reactions
When using the drug, the following side effects are possible:
Heart: tachycardia, palpitations;
Vascular: collapse;
from the nervous system: headache, dizziness, anxiety, paresthesia;
On the part of the organs of vision: optic nerve damage;
Respiratory system, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: difficulty breathing, shortness of breath;
Gastrointestinal tract: difficulty swallowing, nausea, intestinal hemorrhages;
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: hyperemia, itching;
from the immune system: hypersensitivity reactions, including dermatitis, rash, urticaria, angioedema, bronchospastic syndrome with convulsions, anaphylactic shock;
On the part of the hepatobiliary system: impaired liver enzyme activity;
general disorders and changes at the injection site: increased sweating, chills, tremor, general weakness, edema, fever; injection site reactions, rash, itching;
the phenomenon of synaptoplegia - the ability of thiamine to form complexes with various mediators can be accompanied by a decrease in blood pressure, the occurrence of cardiac arrhythmias, impaired contraction of skeletal (including respiratory) muscles, and depression of the central nervous system; thiamine chloride contributes to the development of staphylococcal resistance to antibiotics.
Expiration date
3 years.
Storage conditions
Store in the original packaging at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. Do not freeze.
Keep out of reach of children.
Incompatibility.
Thiamine chloride should not be mixed in the same syringe:
- with benzylpenicillin or streptomycin, as this will lead to the destruction of antibiotics;
- with nicotinic acid or solutions containing sulfites, as this will lead to the destruction of thiamine;
- with carbonates, citrates, barbiturates, Cu2+, iodides, tannic acid, since thiamine is unstable in alkaline and neutral solutions.
Packaging
1 ml in an ampoule; 5 ampoules in a contour blister pack; 2 contour blister packs in a pack.
Vacation category
According to the recipe.
Producer
PrJSC "Pharmaceutical Company "Darnitsa".
Location of the manufacturer and its business address
Ukraine, 02093, Kyiv, Boryspilska St., 13.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.