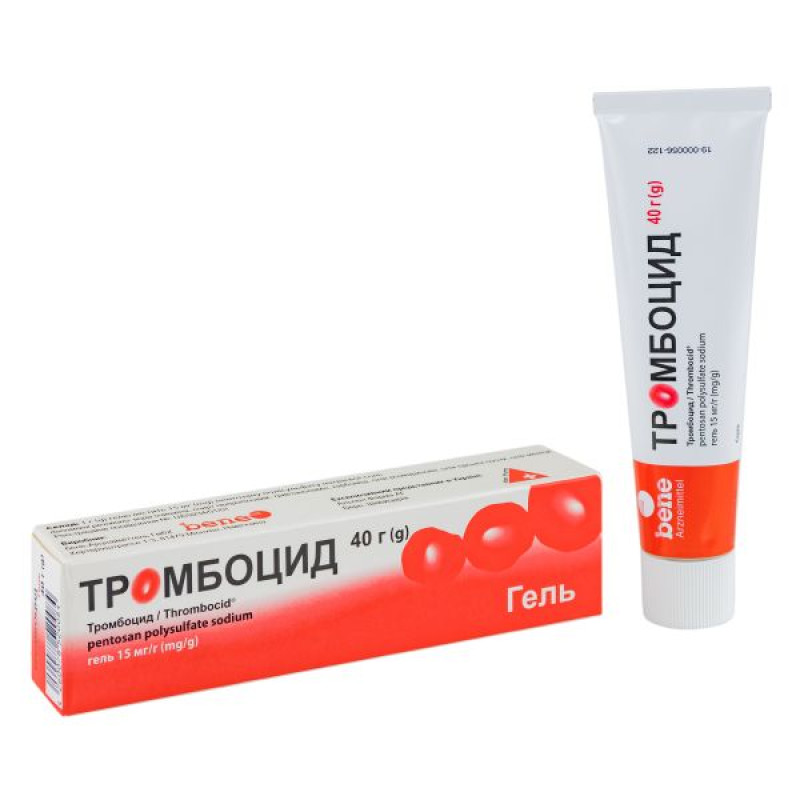
Trombocid gel 15 mg/g tube 40 g
Instructions for use: Trombocid gel 15 mg/g, tube 40 g
Composition
active ingredient: pentosan polysulfate sodium;
1 g of gel contains 15 mg of pentosan polysulfate sodium salt;
excipients: purified water, isopropyl alcohol, triethanolamine, carbomer, rosemary oil, mountain pine oil, lemon balm oil.
Dosage form
Gel.
Main physicochemical properties: transparent gel from colorless to light yellow with a fragrant odor.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Angioprotectors. Agents used for varicose veins. Heparin or heparinoids for topical use. Pentosan polysulfate sodium salt.
ATX code C05B A04.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics.
The systemic effect of pentosan polysulfate sodium salt on hemostasis occurs in three stages.
First, the drug inhibits platelet aggregation induced by collagen or adenosine diphosphate.
Secondly, pentosan polysulfate sodium salt affects blood coagulation, mainly due to AT III-independent inhibition of blood coagulation factor Xa, interacts with factor VIIIa and inhibits factor V activation. Unlike heparin, the drug has little effect on thrombin activity.
Third, pentosan polysulfate sodium affects fibrinolysis: it releases t-PA from the endothelium, activates factor XII, and modifies fibrin production. These effects stimulate thrombin release.
In addition, pentosan polysulfate sodium salt has a systemic effect on fat metabolism, releasing lipoprotein lipase from endothelial and liver cells and reducing the level of total cholesterol, total fats and triglycerides in the blood.
The mechanism of action of the heparinoid, pentosan polysulfate sodium salt, is comparable to the mechanism of action of heparin and other heparin-like substances.
Pentosan polysulfate sodium salt, as a result of local action, enhances capillary blood circulation in the affected tissues due to its fibrinolytic and anticoagulant activity. Pentosan polysulfate sodium salt has an anti-inflammatory effect, inhibits hyaluronidase, reduces increased vascular permeability in the affected tissues and reduces edema. Essential oils have an additional antispasmodic effect and relieve pain in the affected area.
Pharmacokinetics.
Absorption
When pentosan polysulfate sodium is administered subcutaneously, it is rapidly and almost completely absorbed. However, at a dose of 75 mg, the drug undergoes a fairly intense first-pass effect.
When pentosan polysulfate sodium is administered orally, it is rapidly absorbed, but only to a small extent and is subject to an intense first-pass effect. An absorption rate of 3.3–3.5% of the administered dose, increasing to approximately 11% within a week after multiple administration, was achieved at a dose of 2–10 mg/kg of 3H-pentosan polysulfate sodium.
Distribution
Studies in animals given intravenously 3N-pentosan polysulfate sodium salt have shown that the drug interacts with epithelial cells of the genitourinary tract and is enriched in the epithelium of the vascular system. The highest concentrations of radioactivity were found in the liver and spleen, while in the kidneys, lungs, skin and bone marrow they were much lower. Histological studies have confirmed that pentosan polysulfate sodium salt, like heparin, is mainly taken up by cells of the reticulohistiocytic system. Gamma scintigraphy performed on volunteers after administration of 125I pentosan polysulfate sodium salt confirmed that the drug accumulates in the liver and spleen. It has a low affinity for erythrocytes and cannot cross the placental barrier.
Metabolism
Pentosan polysulfate sodium salt is metabolized mainly in the liver and spleen, and also partially in the kidneys. The drug is first desulfated to pentosan and simultaneously depolymerized (in the kidneys) with the formation of low molecular weight fractions of pentosan polysulfate sodium salt, which are also desulfated. Both desulfation and depolymerization are processes that can be saturated by increasing the dose.
Breeding
Due to the high affinity for tissues that accumulate pentosan polysulfate sodium, the drug is initially very rapidly eliminated from plasma. With intravenous administration in doses of 1–100 mg, the half-life increases from 7 to 55 minutes with increasing saturation of the structures that store this compound. The terminal half-life of pentosan polysulfate sodium is 24 hours and is dose-independent in the clinically relevant dose range.
Excretion
Pentosan polysulfate sodium and its metabolites are excreted primarily by the kidneys. Biliary excretion is of minor importance: after a 30-minute intravenous infusion of 75 mg of 3H-pentosan polysulfate sodium, cumulative renal excretion was found to be 27 ± 3% of the administered dose, while cumulative fecal excretion was only 4 ± 5%.
The pharmacokinetics of pentosan polysulfate sodium salt are equivalent to those of heparin and other related drugs of similar chemical structure and quantitatively. That is, the accumulation of pentosan polysulfate sodium salt in vascular epithelial cells and in the reticulohistiocytic system is a feature characteristic of this class of substances, and not only a feature of pentosan polysulfate sodium salt. The feature of pentosan polysulfate sodium salt plays the same key role when applied to heparin and low molecular weight heparins.
Bioavailability
Due to extensive first-pass metabolism, the bioavailability of pentosan polysulfate sodium is much lower than its absorption level and is about 35% after subcutaneous administration of 75 mg pentosan polysulfate sodium. After multiple oral administration of pentosan polysulfate sodium tablets at a dose of 700 mg per day, the bioavailability is initially only about 0.4% due to its low absorption level and extensive first-pass metabolism and increases to about 3% within two weeks. After topical application, the bioavailability of pentosan polysulfate sodium is similar to the bioavailability after oral administration.
Indication
Local symptomatic treatment of superficial thrombophlebitis.
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to pentosan polysulfate sodium salt or to any other component of the drug.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions
Concomitant use of the drug with heparin or other anticoagulants may lead to increased anticoagulant effects.
Application features
The medicine should not be applied to open wounds.
Use with caution in the elderly, especially when concomitantly using other medications, particularly those that affect blood clotting processes.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding
There is currently no information or experience with the use of the drug during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Pentosan polysulfate sodium salt does not penetrate the placental barrier.
Animal studies have not shown any evidence of embryotoxic or fetotoxic effects. However, the drug should not be used during pregnancy.
It is not known whether pentosan polysulfate sodium passes into breast milk, therefore the drug should not be used during breastfeeding.
Ability to influence reaction speed when driving vehicles or other mechanisms
The drug does not affect the reaction speed when driving vehicles or other mechanisms.
Method of administration and doses
The gel is applied in a thin layer to the affected areas and adjacent areas, rubbing in lightly, 3 times a day.
The duration of the treatment course is set individually, depending on the patient's condition, the course of the disease, and the achieved effect.
Children.
The medicine is not recommended for use in children under 16 years of age.
Overdose
Symptoms of intoxication caused by overdose:
To date, no case of overdose has been observed.
Therapeutic measures in case of overdose:
The antidote for pentosan polysulfate sodium salt is protamine sulfate.
Side effects
The assessment of adverse reactions is based on the following frequency indicators:
very common (≥ 1/10);
common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10);
uncommon (≥ 1/1000 to < 1/100);
rare (≥ 1/10,000 to < 1/1000);
very rare (< 1/10,000);
not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data).
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Very rare: blisters at the application site, skin reactions such as a feeling of warmth, itching, redness, swelling at the application site.
Other possible side effects
Sometimes hypersensitivity reactions and dry skin may occur at the site of application of the medicine.
Similar to high- and low-molecular-weight heparins, pentosan polysulfate sodium, when administered intravenously, subcutaneously, or intramuscularly, may cause heparin-associated thrombocytopenia, regardless of the dose used. Although this adverse reaction is not related to the topical use of the drug, it should be reported to a physician if it occurs.
Expiration date
5 years.
The shelf life after first opening the tube is 6 months.
Do not use after the expiry date stated on the packaging.
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C out of the reach of children.
Packaging
40 g or 100 g of gel in a tube; 1 tube in a cardboard box.
Vacation category
Without a prescription.
Producer
bene-Arzneimittel GmbH.
Location of the manufacturer and address of its place of business.
Herterichstrasse 1-3, 81479 Munich, Germany.
Address
Herterichstrasse 1-3, 81479 Munich, Germany.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.