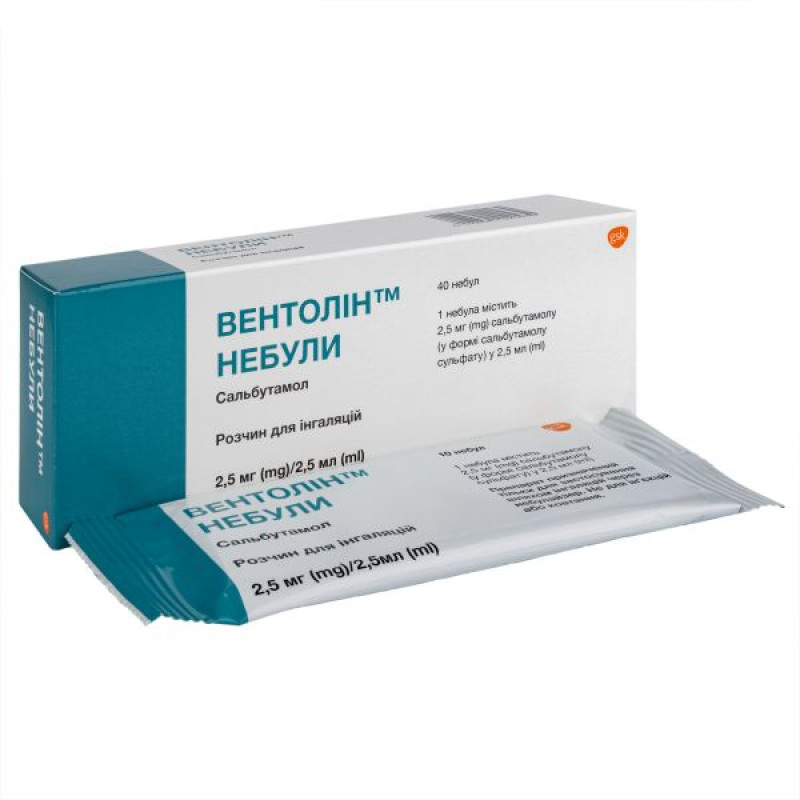
Ventolin nebulized inhalation solution 2.5 mg nebulized 2.5 ml No. 40
Instructions Ventolin nebula inhalation solution 2.5 mg nebula 2.5 ml No. 40
Composition
active ingredient: salbutamol;
1 dose (2.5 ml) of the drug contains 2.5 mg of salbutamol (in the form of salbutamol sulfate);
Excipients: sodium chloride, diluted sulfuric acid, purified water.
Dosage form
Solution for inhalation.
Main physicochemical properties: clear liquid from colorless to pale yellow.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Adrenergic drugs for inhalation use. Selective β2-adrenoceptor agonists. ATC code R03A C02.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Salbutamol is a selective beta2-adrenergic agonist. In therapeutic doses, it acts on beta2-adrenergic receptors of the bronchial muscles.
Pharmacokinetics
After inhalation, 10% to 20% of the administered dose reaches the lower respiratory tract. The remainder remains in the delivery system or in the oropharynx, from where it is swallowed. The portion of the dose that reaches the respiratory tract is absorbed into the lung tissue and enters the bloodstream, but is not metabolized in the lungs.
The bronchodilator effect of the drug occurs within 5 minutes after inhalation, and the duration of action is 4-6 hours.
After entering the systemic circulation, the drug is metabolized in the liver and excreted mainly by the kidneys in an unchanged state and as a phenol sulfate metabolite.
A dose of the drug that has reached the digestive system from the nasopharynx is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, undergoes the first stage of metabolism in the liver to a phenol sulfate compound, and is then excreted by the kidneys.
Indication
Treatment of adults and children aged 4 years and over. The drug is indicated for the rapid relief of acute attacks of bronchial asthma, as well as for the treatment of patients with chronic obstructive bronchitis who do not respond to traditional therapy.
Contraindication
History of hypersensitivity to any component of the drug.
Do not use salbutamol formulations that are not intended for intravenous administration to terminate uncomplicated preterm labor or threatened abortion.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions
Salbutamol should not be administered together with non-selective β-blockers such as propranolol.
Salbutamol is not contraindicated for use in patients treated with MAO inhibitors.
Application features
Ventolin Nebulizer should only be used by inhalation through the mouth and should not be administered by injection or swallowed.
Treatment of bronchial asthma should be carried out according to a step-by-step program, the patient's condition should be assessed clinically and with the help of functional lung tests.
An increase in the frequency of use of short-acting inhaled β2-agonists indicates worsening asthma control. In this case, the patient's therapy should be reviewed.
Sudden and progressive worsening of asthma is a life-threatening condition that requires initiation or increase in the use of corticosteroids. Daily monitoring of peak expiratory flow is recommended for patients at risk.
Patients treated with Ventolin Nebula at home should be warned about the following: if the usual effective dose of the drug does not bring relief or the duration of this relief decreases, you should consult a doctor and not increase the dose of the drug or the frequency of its use on your own.
Ventolin should not be used with caution in patients receiving large doses of other sympathomimetics.
Sympathomimetics, including salbutamol, have been shown to have effects on the cardiovascular system. Post-marketing experience and published literature have reported rare cases of myocardial ischemia associated with the use of salbutamol. Patients with severe cardiovascular disease (e.g., ischemic heart disease, arrhythmia, or severe heart failure) treated with salbutamol should seek medical attention if they develop chest pain or other symptoms suggestive of worsening cardiac disease. Attention should be paid to evaluating symptoms such as dyspnea and chest pain, which may be due to both cardiac and respiratory disease.
Salbutamol should be prescribed with caution to patients with thyrotoxicosis.
Severe hypokalemia may result from treatment with β2-agonists; this is mainly observed with parenteral or nebulized forms. Particular attention is paid to patients with acute severe bronchial asthma, as hypokalemia may be potentiated by concomitant use of xanthine derivatives, steroids, diuretics, and hypoxia. In this situation, it is recommended to check the level of potassium in the blood serum.
As with other inhaled medications, paradoxical bronchospasm with increased wheezing may occur. In this case, alternative forms of the drug or other rapid-acting inhaled bronchodilators should be prescribed immediately. Ventolin Nebulizer should be discontinued immediately and, if necessary, other rapid-acting bronchodilators should be prescribed on a permanent basis.
Like other β-adrenergic agonists, Ventolin Nebuliser Solution may cause reversible metabolic changes, such as increased blood sugar levels.
Compensation for such changes in diabetic patients is not always possible, therefore there are isolated reports of the development of ketoacidosis in such patients. Concomitant use of corticosteroids may exacerbate this condition.
Very rarely, cases of lactic acidosis have been reported in patients with acute asthma treated with high doses of intravenous and nebulized salbutamol (see section 4.8). Increased blood lactate levels may lead to dyspnea and compensatory hyperventilation, which may be mistaken for a lack of efficacy in asthma treatment and, in turn, lead to inappropriate intensification of short-acting inhaled bronchodilators.
β2-agonists. Therefore, it is recommended to monitor the serum lactate level in such patients and, accordingly, the presence of metabolic acidosis in them.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding
Salbutamol should be used during pregnancy only if the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. In post-marketing experience, there have been isolated reports of various congenital anomalies, including cleft palate and limb defects, in children whose mothers used salbutamol during pregnancy. Some of these women also used other medications during pregnancy. A clear causal relationship between the occurrence of such anomalies and salbutamol has not been established.
Since salbutamol may pass into breast milk, its use during breast-feeding is not recommended unless the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the infant. It is unknown whether the presence of salbutamol in breast milk has any harmful effects on the infant.
Ability to influence reaction speed when driving vehicles or other mechanisms
There is no data on the effects; in case of adverse reactions from the nervous system (tremor), driving or working with other mechanisms should be restricted.
Method of administration and doses
Ventolin Nebules is intended only for inhalation use by inhalation through the mouth using a nebulizer, it should be used under the supervision of a physician.
The solution should not be injected or swallowed.
Increased β2-agonist requirements may indicate worsening asthma. In these circumstances, the patient's treatment regimen should be reviewed and the need for concomitant glucocorticosteroid therapy considered.
Adults (including elderly patients)
The usual starting dose of inhaled salbutamol is 2.5 mg. This can be increased to 5 mg. The inhalation can be repeated up to 4 times a day.
For the treatment of adult patients with severe airway obstruction, doses may be increased to 40 mg per day, however, such treatment should be carried out in a hospital setting under close medical supervision.
Children aged 12 and over
Doses are the same as for adults.
Children aged 4 to 11 years
The usual starting dose of inhaled salbutamol is 2.5 mg. This can be increased to 5 mg. The inhalation can be repeated up to 4 times a day.
For children under 4 years of age, other dosage forms of the drug should be used.
The clinical efficacy of nebulized salbutamol in infants under 18 months of age has not been established.
Since transient hypoxemia is possible, the need for supplemental oxygen therapy should be considered.
Ventolin Nebuliser should normally be used undiluted. However, if inhalations are required for a prolonged period (more than 10 minutes), the contents of the nebuliser may be diluted with sterile saline.
Aerosol inhalation can be performed using a special face mask, a T-shaped manifold or through an endotracheal tube. The room where inhalation is performed should be periodically ventilated. In case of risk of hypoxia due to hypoventilation of the inhaled air, the air should be enriched with oxygen.
Only a doctor can increase the dosage and frequency of use of the drug, given the possibility of side effects if the dose is exceeded.
Instructions for use of Ventolin Nebules
1. Open the aluminum bag with nebules only when necessary.
3. Take the ribbon of nebula in one hand, with the other hand, squeeze the outermost nebula.
4. Turn the outermost nebula down and away from you to disconnect it from the others.
5. Put the remaining nebulas back into the aluminum bag, close it and place it in the package.
6. Holding the nebula by the top, roll the other edge to open the nebula.
7. Tilt the open end of the nebula into the nebulizer container and squeeze it slowly. Make sure that all the contents of the nebula are in the nebulizer container.
8. Prepare the nebulizer for use according to the instructions for use.
Use a new nebulizer for each use, which should be opened immediately before use. If any liquid remains after inhalation, do not save it for reuse, simply discard it.
Children
Ventolin should not be prescribed to children under 4 years of age.
Overdose
The most common signs and symptoms of salbutamol overdose are transient changes pharmacologically induced by β-agonists, such as tachycardia, tremor, hyperactivity and metabolic disturbances including hypokalaemia and lactic acidosis (see sections 4.4 and 4.8).
Hypokalaemia may occur as a result of an overdose of salbutamol, therefore serum potassium levels should be monitored. Lactic acidosis has been reported with high therapeutic doses or overdose of short-acting β2-agonists, therefore serum lactate levels should be monitored. Metabolic acidosis should be monitored accordingly, particularly if tachypnea persists or increases despite improvement in bronchospasm symptoms (e.g. reduction in wheezing).
Adverse reactions
The adverse reactions listed below are classified by system organ class and frequency. The frequency of occurrence is classified as very common (≥1/10), common (≥1/100 and <1/10), uncommon (≥1/1,000 and <1/100), rare (≥1/10,000 and <1/1,000), very rare (<1/10,000), including isolated reports. In general, very common and common adverse reactions are determined from clinical trial data, while rare, very rare and unknown adverse reactions are determined from spontaneous reports.
On the part of the immune system
Very rare: hypersensitivity reactions including angioedema, urticaria, bronchospasm, hypotension and collapse.
From the side of metabolism, metabolism
Rare: Hypokalaemia. Potentially severe hypokalaemia may result from treatment with β2-agonists.
Frequency unknown: lactic acidosis (see section "Special warnings and precautions for use").
Neurological disorders
Common: tremor, headache.
Very rare: hyperactivity.
Cardiac disorders
Common: tachycardia.
Uncommon: palpitations.
Very rare: cardiac arrhythmias, including atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia and extrasystole.
Frequency not known: myocardial ischemia (see section "Special warnings and precautions for use").
Since these reports are spontaneous, their frequency cannot be determined from post-marketing surveillance.
From the vascular side
Rare: peripheral vasodilation.
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
Very rare: paradoxical bronchospasm.
Gastrointestinal tract
Uncommon: irritation of the mucous membranes of the mouth and pharynx.
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Uncommon: muscle cramps.
Expiration date
3 years. After opening the aluminum foil bag – 3 months.
Storage conditions
Keep out of reach of children. Store below 30°C. Store the opened aluminum foil sachet in a place protected from light at a temperature below 30°C.
Packaging
10 plastic ampoules (nebules) in an aluminum foil bag; 4 bags placed in a cardboard box.
Vacation category
According to the recipe.
Producer
Aspen Bad Oldesloe GmbH (Germany)
"Aspen Bad Oldesloe GmbH" (Germany).
Location of the manufacturer and its business address
Aspen Bad Oldesloh GmbH, Industristrasse 32-36, 23843-Bad Oldesloh, Germany
Aspen Bad Oldesloe GmbH, Industriestrasse 32-36, 23843-Bad Oldesloe, Germany.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.