Zerkalin cutaneous solution 1% bottle 30 ml No. 1
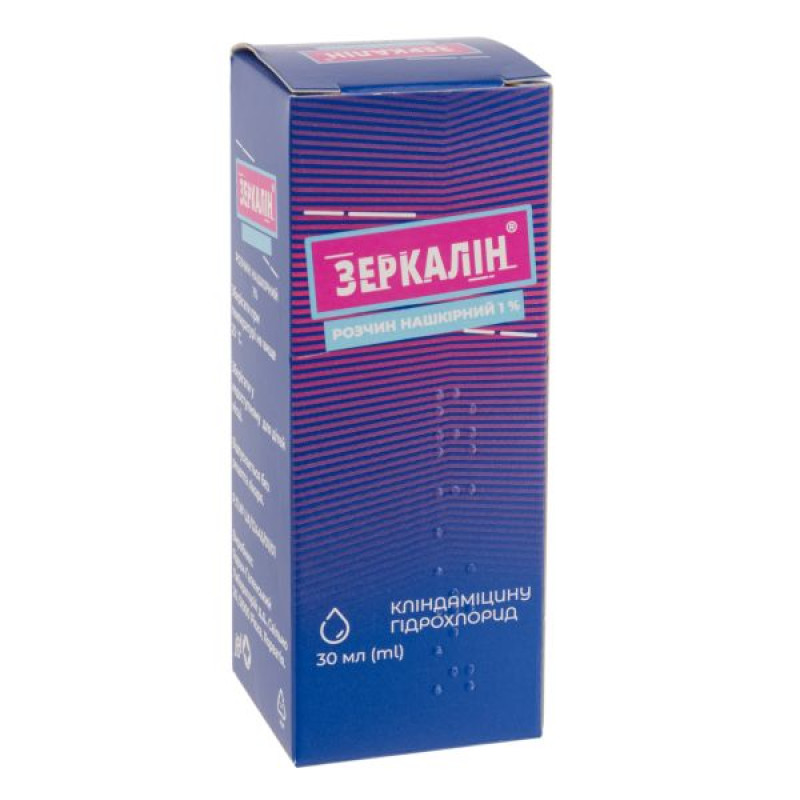

Instructions Zerkalin cutaneous solution 1% bottle 30 ml No. 1
Composition
active ingredient: clindamycin;
1 ml of solution contains clindamycin – 10 mg, in the form of clindamycin hydrochloride;
excipients: ethanol 96%, propylene glycol, purified water.
Dosage form
The solution is topical.
Main physicochemical properties: colorless transparent liquid with the smell of ethanol.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Antimicrobials for the treatment of acne. Clindamycin. ATX code D10A F01.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Clindamycin is a semisynthetic derivative of lincomycin, an antibiotic obtained from a culture of Streptomyces lincolensis. It has bacteriostatic and bactericidal properties, depending on the concentration at the site of action and the sensitivity of microorganisms. Clindamycin inhibits protein synthesis in susceptible bacteria by binding to the 50S subunit of bacterial ribosomes, interrupting the early stages of protein synthesis. It is known that the spectrum of action of clindamycin in vitro and in vivo covers most gram-positive bacteria, most anaerobic pathogens and protozoa. The drug is ineffective against Enterobacteriaceae, fungi and viruses. After topical application to the skin of a 1% solution of clindamycin hydrochloride, the growth of susceptible bacteria, especially anaerobes Propionibacterium acnes, which are found in the sebaceous glands and follicles, is inhibited, and the concentration of free fatty acids (FFA) in sebum is also reduced. This decrease in sebum FFA concentration is a consequence of indirect inhibition of microorganisms that produce lipase, which is necessary for the conversion of triglycerides to FFA, or a direct consequence of a decrease in lipase production by microorganisms. In addition to lipases, Propionibacterium acnes produces proteases, hyaluronidases, and chemotactic factors, which, together with comedonogenic FFA, are responsible for the development of inflammatory lesions (i.e., papules, pustules, nodules, cysts) in acne lesions. Therefore, both antibacterial and anti-inflammatory actions (in which inhibition of leukocyte chemotaxis plays an important role) are important for the development of the effect of topical clindamycin in patients with acne.
Pharmacokinetics
It is known that in a specially designed in vitro human skin model after application of clindamycin hydrochloride (labeled with a radioisotope), almost 10% of the dose is absorbed by the stratum corneum of the skin. Clindamycin penetrates well into inflammatory lesions after topical application. The bioavailability of clindamycin after application to the skin is approximately 7.5%.
Indication
Treatment of common acne.
Contraindication
Contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to agents containing clindamycin or lincomycin, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, or antibiotic-associated colitis.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions
Clindamycin has the property of blocking neuromuscular transmission, which can lead to increased action of other drugs with similar properties. Therefore, it should be used with caution in patients receiving such drugs. There is cross-resistance between clindamycin and lincomycin. Antagonism between erythromycin and clindamycin has also been noted.
Application features
Clostridium difficile toxin is known to be the main cause of antibiotic-associated colitis. Colitis is usually characterized by severe persistent diarrhea and severe abdominal cramps and may be accompanied by blood and mucus. Pseudomembranous colitis can be detected by endoscopic examination. Stool culture for Clostridium difficile and stool analysis for C. difficile toxin may aid in the diagnosis of this disease. If significant diarrhea develops, the drug should be discontinued. In cases of severe diarrhea, endoscopic examination of the large intestine should be considered to establish a definitive diagnosis. The use of agents that inhibit peristalsis, such as opiates and diphenoxylate with atropine, may prolong and/or worsen this condition. Vancomycin has been shown to be effective in the treatment of antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis caused by Clostridium difficile. The usual dose for adult patients is 500 mg to 2 g of vancomycin per day orally, divided into 3-4 doses, for 7-10 days. Cholestyramine or colestipol resins are known to bind vancomycin in vitro. If concomitant use of the resin and vancomycin is necessary, it is advisable to use each of these drugs at different times. It is necessary to avoid contact of the drug with the mucous membrane of the eyes and the oral cavity. Hands should be washed thoroughly when applying the solution. In case of accidental contact with sensitive surfaces (eyes, abrasions on the skin, mucous membranes), the affected area should be thoroughly rinsed with cool water. Oral and parenteral use of clindamycin has been associated with the development of severe colitis, which can be fatal. There are no data on the use of the drug in patients with renal and/or hepatic insufficiency. Caution should be exercised when prescribing topical formulations of clindamycin to patients with atopy.
Ability to influence reaction speed when driving vehicles or other mechanisms
The effect of clindamycin on the ability to drive and use machines has not been systematically evaluated.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding
Pregnancy: There are no well-controlled studies of congenital malformations with topical clindamycin in pregnant women. This drug should be used in pregnant women only if clearly needed, based on the benefit/risk assessment.
Breastfeeding. It is not known whether clindamycin is excreted in human milk after topical administration. However, clindamycin has been reported to be present in breast milk after oral and parenteral administration. The drug should be discontinued or breast-feeding should be discontinued for the duration of treatment, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Method of administration and doses
Apply a thin layer of Zerkalin® solution to the affected area of cleansed skin twice a day. The duration of application is determined by the doctor individually.
Children
The safety and efficacy of the drug in children under 12 years of age have not been studied.
Overdose
Clindamycin, when applied topically, can be absorbed in quantities sufficient to produce systemic effects (see section "Special warnings and precautions for use").
Adverse reactions
It is known that with topical formulations of clindamycin, adverse reactions such as diarrhea, bloody diarrhea, and colitis, including pseudomembranous colitis, have been rarely observed (see section "Special warnings and precautions for use").
Abdominal pain and gastrointestinal upset, nausea, vomiting, folliculitis caused by gram-negative organisms, skin irritation, burning, itching, dryness, erythema, oily/greasy skin, contact dermatitis, urticaria, and burning eyes have been reported with topical clindamycin formulations. Hypersensitivity Reactions. Oral and parenteral use of clindamycin has been associated with severe colitis, which may be fatal.
Expiration date
3 years.
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Packaging
30 ml of solution in a glass bottle; 1 glass bottle in a cardboard box.
Vacation category
Without a prescription.
Producer
Jadran-Galensky Laboratories, Dr.
Location of the manufacturer and its business address
Svilno 20, 51000 Rijeka, Croatia.
There are no reviews for this product.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.
No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.